DOGM128 with Arduino Hardware
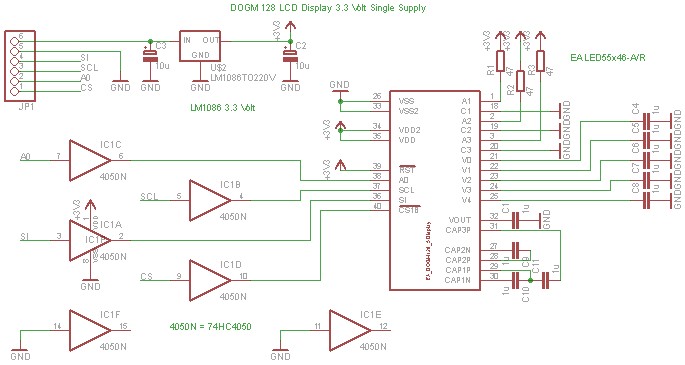
The DOGM graphics module should be connected to the Arduino board as illustrated. Pin 12 (MISO) of the Arduino board must remain unused. Furthermore, the DOGM graphics module requires an address line (A0), which can be connected to any output port. The schematic provided demonstrates the usage of the DOGM graphics module with a 3.3-volt supply. Level translation from 5 volts to 3.3 volts is accomplished using the HC4050 integrated circuit.
The DOGM graphics module is a versatile display component that facilitates the visualization of data and graphics in embedded systems. It operates at a supply voltage of 3.3 volts, which is essential for compatibility with various microcontroller platforms, including the Arduino. The connection configuration is crucial for ensuring proper communication between the module and the Arduino.
In the provided schematic, the DOGM graphics module is interfaced with the Arduino board. It is important to note that Pin 12 (MISO) on the Arduino should not be utilized for this connection, as it is designated for the Master In Slave Out function in SPI communication, which may interfere with the operation of the graphics module. Instead, the module requires an address line (A0) that can be connected to any available output pin on the Arduino. This flexibility allows for customization of the pin configuration based on the specific requirements of the project.
To facilitate the operation of the DOGM graphics module, the schematic also includes an HC4050 integrated circuit. This component serves as a level shifter, enabling the safe translation of voltage levels from 5 volts, which is commonly used in Arduino systems, down to 3.3 volts, suitable for the DOGM module. The HC4050 is a hex buffer/driver that can convert high logic levels (5V) to low logic levels (3.3V) without signal degradation, ensuring reliable communication between the Arduino and the graphics module.
In summary, the proper configuration and connection of the DOGM graphics module with the Arduino, alongside the implementation of the HC4050 for level shifting, are essential for achieving optimal performance and functionality in embedded applications. The schematic serves as a useful guide for engineers and hobbyists alike, enabling them to effectively integrate the DOGM graphics module into their projects.The Dogm-graphics-module should be connected to the Arduino board as shown below. Pin 12 (MISO) of the Arduino board must not be used. Additionally the Dogm-graphics-module requires an addess line (A0) which can be connected to any output port. The following schematic shows the use of the dogm-graphics-module with a 3. 3 volt supply. The level tran slation (5 volt to 3. 3 volt) is done by the HC4050 integrated circuit. 🔗 External reference
The DOGM graphics module is a versatile display component that facilitates the visualization of data and graphics in embedded systems. It operates at a supply voltage of 3.3 volts, which is essential for compatibility with various microcontroller platforms, including the Arduino. The connection configuration is crucial for ensuring proper communication between the module and the Arduino.
In the provided schematic, the DOGM graphics module is interfaced with the Arduino board. It is important to note that Pin 12 (MISO) on the Arduino should not be utilized for this connection, as it is designated for the Master In Slave Out function in SPI communication, which may interfere with the operation of the graphics module. Instead, the module requires an address line (A0) that can be connected to any available output pin on the Arduino. This flexibility allows for customization of the pin configuration based on the specific requirements of the project.
To facilitate the operation of the DOGM graphics module, the schematic also includes an HC4050 integrated circuit. This component serves as a level shifter, enabling the safe translation of voltage levels from 5 volts, which is commonly used in Arduino systems, down to 3.3 volts, suitable for the DOGM module. The HC4050 is a hex buffer/driver that can convert high logic levels (5V) to low logic levels (3.3V) without signal degradation, ensuring reliable communication between the Arduino and the graphics module.
In summary, the proper configuration and connection of the DOGM graphics module with the Arduino, alongside the implementation of the HC4050 for level shifting, are essential for achieving optimal performance and functionality in embedded applications. The schematic serves as a useful guide for engineers and hobbyists alike, enabling them to effectively integrate the DOGM graphics module into their projects.The Dogm-graphics-module should be connected to the Arduino board as shown below. Pin 12 (MISO) of the Arduino board must not be used. Additionally the Dogm-graphics-module requires an addess line (A0) which can be connected to any output port. The following schematic shows the use of the dogm-graphics-module with a 3. 3 volt supply. The level tran slation (5 volt to 3. 3 volt) is done by the HC4050 integrated circuit. 🔗 External reference