Driver circuits
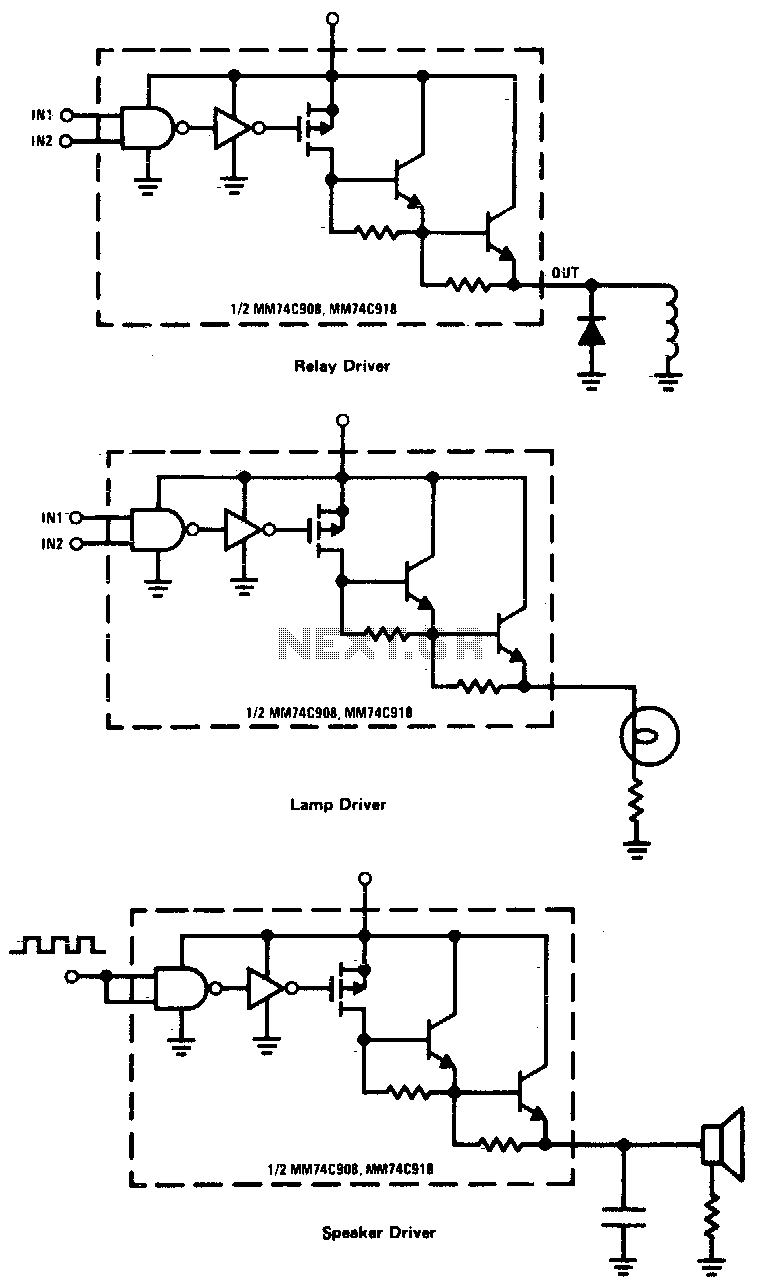
CMOS drivers for relays, lamps, speakers, and similar applications provide extremely low standby power consumption. When operating at Vcc = 15 V, the power dissipation per package is typically 750 nW when the outputs are not drawing current. Consequently, these drivers can remain connected to a line, such as a telephone line, drawing virtually zero current until they are activated.
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) drivers are integral components in various electronic applications, particularly in driving loads such as relays, lamps, and speakers. Their design focuses on minimizing power consumption during standby conditions, making them suitable for battery-operated and energy-efficient devices. The specified power dissipation of 750 nW at a supply voltage of 15 V indicates that these drivers are highly efficient, especially when the outputs are not in an active state.
The operational principle of CMOS technology relies on the complementary action of p-channel and n-channel MOSFETs, which allows for minimal power loss. In the standby mode, the drivers effectively isolate the load from the power source, resulting in negligible current draw. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where devices must remain connected for extended periods without depleting their power source, such as in remote monitoring systems or telecommunications.
When activated, the CMOS drivers can quickly switch the connected load, providing the necessary current to drive relays or other devices. The rapid switching capability ensures that the response time is minimal, which is essential for applications requiring timely activation or deactivation of loads. Furthermore, the integration of these drivers into a circuit can simplify the design, as they often require fewer external components compared to traditional driving methods.
In summary, CMOS drivers serve as efficient and reliable components for controlling various loads in electronic circuits, offering the benefits of low standby power consumption and fast switching capabilities. Their application extends across multiple domains, making them a valuable choice for modern electronic designs.CMOS drivers for relays, lamps, speakers, etc, offers extremely low standby power. At Vcc = 15 V, power dissipation per package is typically 750 nW when the outputs are not drawing current Thus, the drivers can be sitting out on line (a telephone line, for example) drawing essentially zero current until activated.
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) drivers are integral components in various electronic applications, particularly in driving loads such as relays, lamps, and speakers. Their design focuses on minimizing power consumption during standby conditions, making them suitable for battery-operated and energy-efficient devices. The specified power dissipation of 750 nW at a supply voltage of 15 V indicates that these drivers are highly efficient, especially when the outputs are not in an active state.
The operational principle of CMOS technology relies on the complementary action of p-channel and n-channel MOSFETs, which allows for minimal power loss. In the standby mode, the drivers effectively isolate the load from the power source, resulting in negligible current draw. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where devices must remain connected for extended periods without depleting their power source, such as in remote monitoring systems or telecommunications.
When activated, the CMOS drivers can quickly switch the connected load, providing the necessary current to drive relays or other devices. The rapid switching capability ensures that the response time is minimal, which is essential for applications requiring timely activation or deactivation of loads. Furthermore, the integration of these drivers into a circuit can simplify the design, as they often require fewer external components compared to traditional driving methods.
In summary, CMOS drivers serve as efficient and reliable components for controlling various loads in electronic circuits, offering the benefits of low standby power consumption and fast switching capabilities. Their application extends across multiple domains, making them a valuable choice for modern electronic designs.CMOS drivers for relays, lamps, speakers, etc, offers extremely low standby power. At Vcc = 15 V, power dissipation per package is typically 750 nW when the outputs are not drawing current Thus, the drivers can be sitting out on line (a telephone line, for example) drawing essentially zero current until activated.