Dual Input-Combining Stereo Line Amplifier
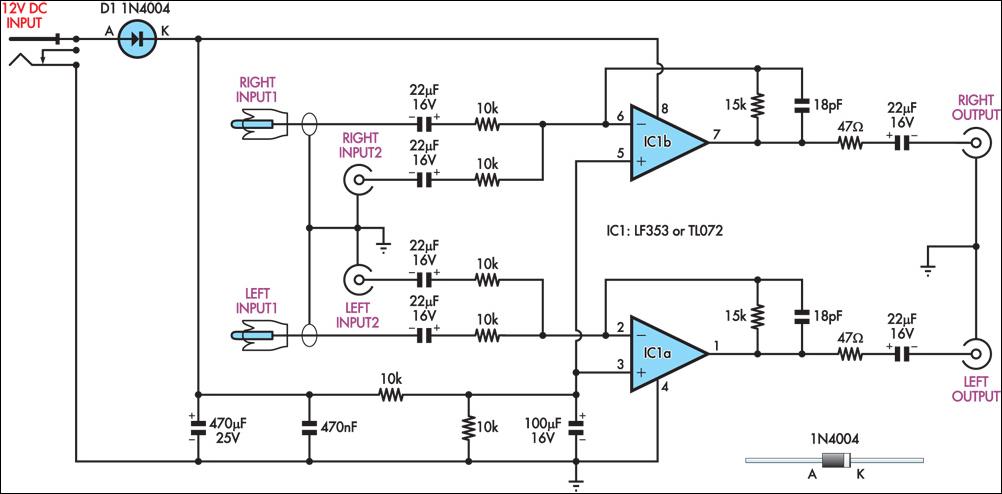
This circuit combines two separate line-level stereo (L & R) signals into one stereo (L & R) output, eliminating the need to switch between two pairs of input signals. It is utilized in a scenario where the stereo audio from a TV receiver and a DVD player are fed into an external amplifier. The necessity for this circuit emerged due to a design peculiarity in the TV receiver. The TV features four A/V inputs and one A/V output. Inputs AV1-AV3 accept composite or S-video along with stereo audio, which are directed to the TV's A/V output. In contrast, AV4 accepts Component video (Y/Pb/Pr) with stereo audio; however, its audio (and video) signals are not routed to the TV's A/V output. The Y/Pb/Pr input was selected for the DVD player due to its superior video quality, while the audio is sent to an external amplifier for enhanced reproduction. Manual switching was found inconvenient, leading to the development of this design. In operation, the DVD player's audio is connected in parallel to TV AV4 and one pair of inputs on the combining amplifier, while the TV audio output connects to the other input pair. The amplifier's output is then sent to the external audio amplifier. There is no conflict between the two audio inputs, as when AV4 (DVD player) is selected, there is no TV audio output. In all other modes, the DVD player is inactive. The circuit exhibits a voltage gain of 1.5 times (3.5 dB), which can be adjusted by changing the two 15 kΩ resistors. The input impedance is 10 kΩ, and the outputs are isolated from cable and amplifier input capacitance using 47 Ω series resistors. The circuit can be powered by a regulated 12V DC plug pack.
This circuit employs a combining amplifier to facilitate the merging of audio signals from two distinct sources, specifically designed for scenarios where manual switching of audio inputs is impractical. The design incorporates two stereo inputs: one from the TV's audio output and the other from the DVD player's audio output, ensuring seamless integration without audio conflicts.
The combining amplifier is configured to maintain a consistent voltage gain of 1.5, allowing for a slight amplification of the audio signals while preserving the integrity of the original sound. The gain can be adjusted by replacing the two 15 kΩ resistors with resistors of different values, providing flexibility in audio output levels based on user requirements or the specific characteristics of the connected audio devices.
The input impedance of the circuit is set at 10 kΩ, which is compatible with standard line-level audio outputs, ensuring minimal loading on the audio sources. To prevent potential issues with cable capacitance or amplifier input capacitance affecting the audio quality, 47 Ω series resistors are incorporated at the output stage. This isolation helps to maintain signal integrity and reduce the risk of distortion.
Powering the circuit is straightforward, as it utilizes a regulated 12V DC power supply. This design choice ensures stable operation and minimizes the risk of noise and interference from the power source, which is crucial in maintaining high-quality audio performance.
Overall, this circuit represents an effective solution for combining audio signals from multiple sources, providing convenience and enhanced audio reproduction capabilities in home entertainment setups.This circuit takes two separate line-level stereo (L & R) signals and combines them into one stereo (L & R) output, thus avoiding the need to switch between two pairs of input signals. In the author`s application, it is used to feed the stereo audio from a TV receiver and a DVD player into an external amplifier.
The need for the circuit arose beca use of a design peculiarity in the TV receiver. The TV has four A/V inputs and one A/V output. AV1-AV3 accept composite or S-video plus stereo audio inputs and these feed into the TV`s A/V output. AV4 accepts Component video (Y/Pb/Pr) plus stereo audio but unlike AV1-AV3, its audio (and video) signals are not fed to the TV A/V output.
The Y/Pb/Pr input was chosen for use with the DVD player because of its superior video quality, while the audio was to be fed to an external amplifier for improved reproduction. However, manual switching was inconvenient, hence the genesis of this design. In use, the DVD player audio is fed in parallel to TV AV4 and to one input pair of the combining amplifier, while the TV audio output feeds the other input pair.
The amplifier output goes to the external audio amplifier. There is no conflict between the two audio inputs because when AV4 (DVD player) is selected, there is no TV audio output. In all other modes, the DVD player is off. As shown, the circuit has a voltage gain of 1. 5 times (3. 5dB) but this can be altered as required by changing the two 15kW resistors. Input impedance is 10kW and the outputs are isolated from cable and amplifier input capacitance with 47W series resistors.
The circuit can be powered from a regulated 12V DC plugpack. 🔗 External reference
This circuit employs a combining amplifier to facilitate the merging of audio signals from two distinct sources, specifically designed for scenarios where manual switching of audio inputs is impractical. The design incorporates two stereo inputs: one from the TV's audio output and the other from the DVD player's audio output, ensuring seamless integration without audio conflicts.
The combining amplifier is configured to maintain a consistent voltage gain of 1.5, allowing for a slight amplification of the audio signals while preserving the integrity of the original sound. The gain can be adjusted by replacing the two 15 kΩ resistors with resistors of different values, providing flexibility in audio output levels based on user requirements or the specific characteristics of the connected audio devices.
The input impedance of the circuit is set at 10 kΩ, which is compatible with standard line-level audio outputs, ensuring minimal loading on the audio sources. To prevent potential issues with cable capacitance or amplifier input capacitance affecting the audio quality, 47 Ω series resistors are incorporated at the output stage. This isolation helps to maintain signal integrity and reduce the risk of distortion.
Powering the circuit is straightforward, as it utilizes a regulated 12V DC power supply. This design choice ensures stable operation and minimizes the risk of noise and interference from the power source, which is crucial in maintaining high-quality audio performance.
Overall, this circuit represents an effective solution for combining audio signals from multiple sources, providing convenience and enhanced audio reproduction capabilities in home entertainment setups.This circuit takes two separate line-level stereo (L & R) signals and combines them into one stereo (L & R) output, thus avoiding the need to switch between two pairs of input signals. In the author`s application, it is used to feed the stereo audio from a TV receiver and a DVD player into an external amplifier.
The need for the circuit arose beca use of a design peculiarity in the TV receiver. The TV has four A/V inputs and one A/V output. AV1-AV3 accept composite or S-video plus stereo audio inputs and these feed into the TV`s A/V output. AV4 accepts Component video (Y/Pb/Pr) plus stereo audio but unlike AV1-AV3, its audio (and video) signals are not fed to the TV A/V output.
The Y/Pb/Pr input was chosen for use with the DVD player because of its superior video quality, while the audio was to be fed to an external amplifier for improved reproduction. However, manual switching was inconvenient, hence the genesis of this design. In use, the DVD player audio is fed in parallel to TV AV4 and to one input pair of the combining amplifier, while the TV audio output feeds the other input pair.
The amplifier output goes to the external audio amplifier. There is no conflict between the two audio inputs because when AV4 (DVD player) is selected, there is no TV audio output. In all other modes, the DVD player is off. As shown, the circuit has a voltage gain of 1. 5 times (3. 5dB) but this can be altered as required by changing the two 15kW resistors. Input impedance is 10kW and the outputs are isolated from cable and amplifier input capacitance with 47W series resistors.
The circuit can be powered from a regulated 12V DC plugpack. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713