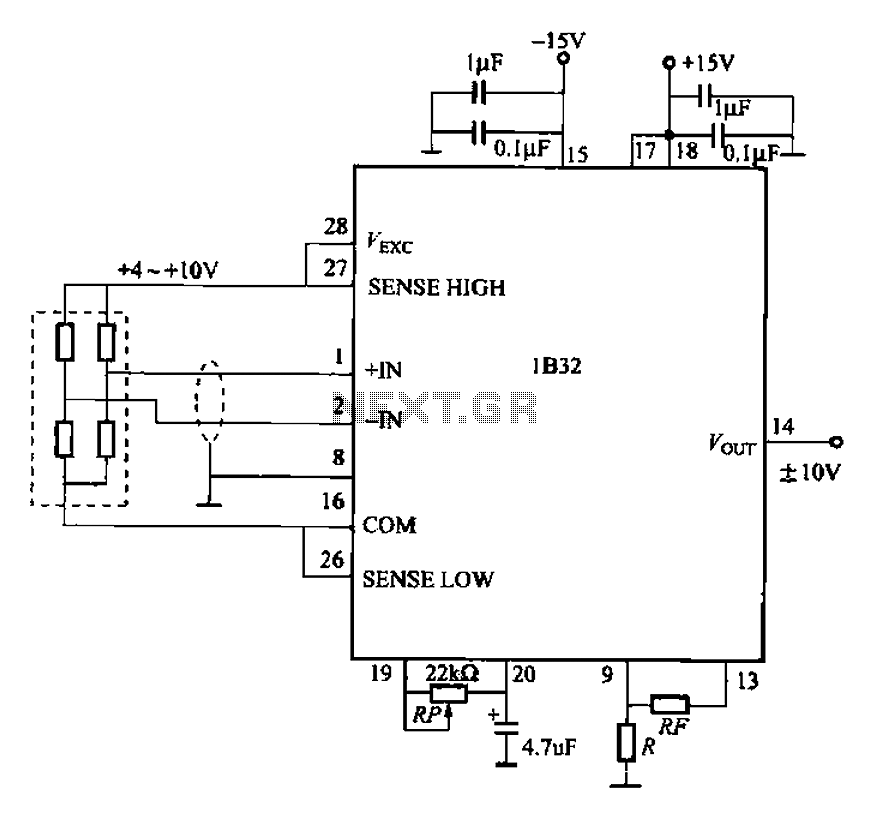
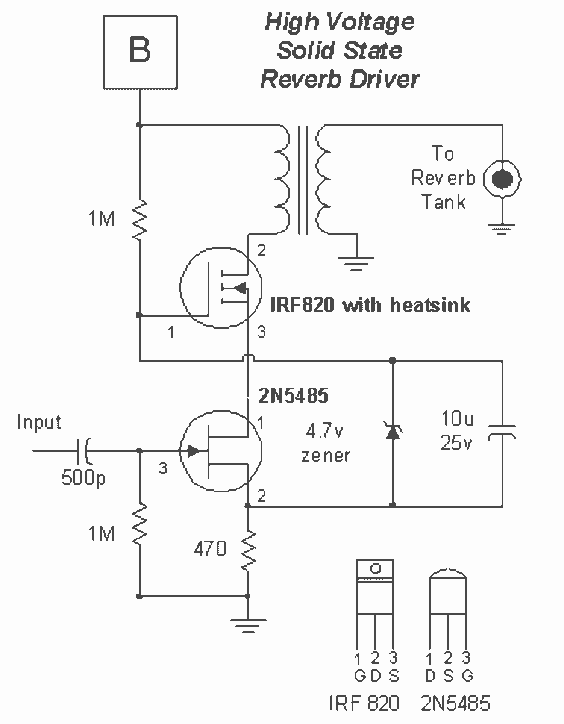
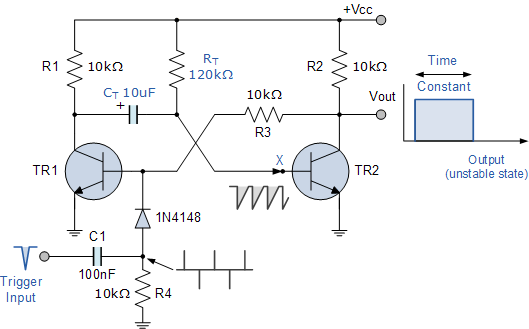
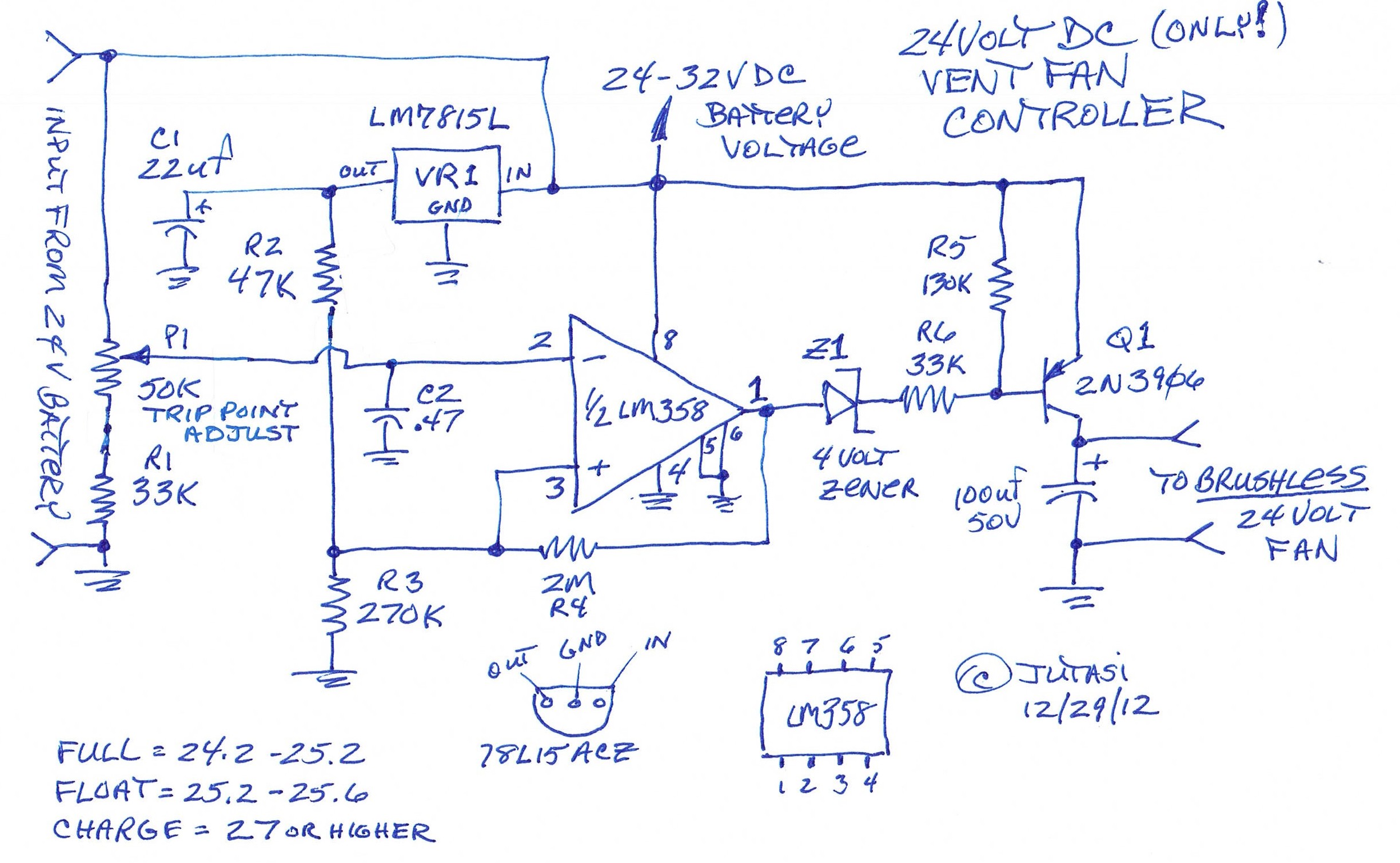
Efficient Laser Supply Circuit
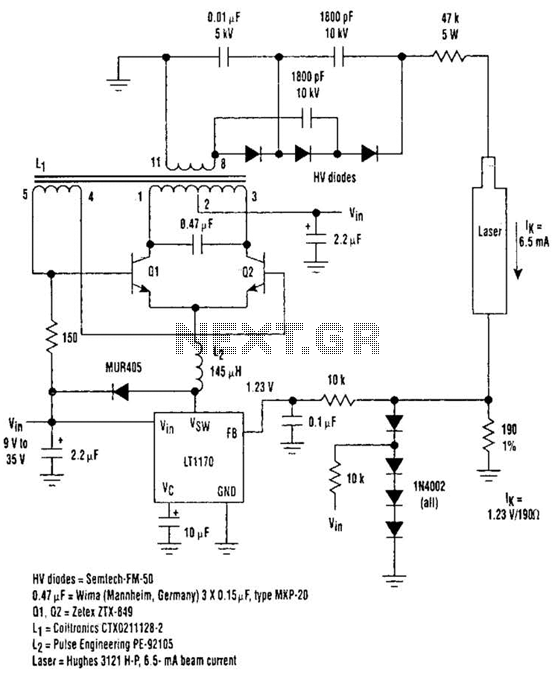
Driving Helium-Neon lasers can be greatly simplified using this power supply configuration. When power is applied, the laser does not conduct, and the voltage across the 190-ohm resistor is zero. However, a resonant circuit and a voltage tripler then produce over 10 kV to activate the laser. More: HV diodes = Semiech-FM-50, 0.47 µF = Wima (Mannheim, Germany), 3 x 0.15 µF, type MXP-20, Q1 = Zelex ZTX-849, L1 = Coiltronics CTX0211128-2, L2 = Pulse Engineering PE-92105, Laser = Hughes 3121H-P, 6.5 mA beam current.
The described power supply configuration for driving Helium-Neon lasers utilizes a combination of components to achieve the necessary high voltage for laser activation. The circuit begins with a resonant circuit that is designed to store and release energy efficiently, enabling a rapid rise in voltage. The initial state of the laser is non-conductive, which is indicated by the zero voltage across the 190-ohm resistor when power is first applied.
The resonant circuit typically consists of inductors and capacitors, which are tuned to resonate at a specific frequency. In this configuration, the voltage tripler plays a crucial role, as it multiplies the input voltage to generate the high voltages required for the laser operation. The output from the voltage tripler can exceed 10 kV, which is essential for initiating the discharge in the Helium-Neon laser.
The components specified for this configuration include high-voltage diodes such as the Semiech-FM-50, which are capable of handling the high reverse voltages encountered in the circuit. The capacitors used, including the Wima 0.47 µF and three 0.15 µF capacitors of type MXP-20, are selected for their voltage ratings and capacitance values to ensure stability and performance during operation.
Transistor Q1, identified as the Zelex ZTX-849, serves as a switching element that controls the flow of current in the circuit. The inductors L1 (Coiltronics CTX0211128-2) and L2 (Pulse Engineering PE-92105) are critical for the resonant behavior and energy storage in the circuit. Finally, the laser itself, a Hughes 3121H-P, operates at a beam current of 6.5 mA, which is necessary for producing the desired laser output.
This power supply configuration effectively combines these components to create a reliable and efficient means of driving Helium-Neon lasers, ensuring that the high voltage required for operation is generated safely and effectively. Driving Helium-Neon Lasers can be simplified considerably using This power-supply configuration. When power is applied, the laser doesn`t conduct and the voltage across the 190- resistor is zero. However, a resonant circuit and a voltage tripler then produces over 10 kV to turn on the laser. HV diodes = Semiech-FM-50, 0.47 uf = Wima (Mannheim, Germany) 3 x 0.15uf, type MXP-20, Ql,OZ = Zelex ZTX-849, Li = Coitlromcs CTX0211128-2, L2 = Puise Engineering PE-92105, Laser = Hughes 3121H-P, 6.5- mA beam current. 🔗 External reference
The described power supply configuration for driving Helium-Neon lasers utilizes a combination of components to achieve the necessary high voltage for laser activation. The circuit begins with a resonant circuit that is designed to store and release energy efficiently, enabling a rapid rise in voltage. The initial state of the laser is non-conductive, which is indicated by the zero voltage across the 190-ohm resistor when power is first applied.
The resonant circuit typically consists of inductors and capacitors, which are tuned to resonate at a specific frequency. In this configuration, the voltage tripler plays a crucial role, as it multiplies the input voltage to generate the high voltages required for the laser operation. The output from the voltage tripler can exceed 10 kV, which is essential for initiating the discharge in the Helium-Neon laser.
The components specified for this configuration include high-voltage diodes such as the Semiech-FM-50, which are capable of handling the high reverse voltages encountered in the circuit. The capacitors used, including the Wima 0.47 µF and three 0.15 µF capacitors of type MXP-20, are selected for their voltage ratings and capacitance values to ensure stability and performance during operation.
Transistor Q1, identified as the Zelex ZTX-849, serves as a switching element that controls the flow of current in the circuit. The inductors L1 (Coiltronics CTX0211128-2) and L2 (Pulse Engineering PE-92105) are critical for the resonant behavior and energy storage in the circuit. Finally, the laser itself, a Hughes 3121H-P, operates at a beam current of 6.5 mA, which is necessary for producing the desired laser output.
This power supply configuration effectively combines these components to create a reliable and efficient means of driving Helium-Neon lasers, ensuring that the high voltage required for operation is generated safely and effectively. Driving Helium-Neon Lasers can be simplified considerably using This power-supply configuration. When power is applied, the laser doesn`t conduct and the voltage across the 190- resistor is zero. However, a resonant circuit and a voltage tripler then produces over 10 kV to turn on the laser. HV diodes = Semiech-FM-50, 0.47 uf = Wima (Mannheim, Germany) 3 x 0.15uf, type MXP-20, Ql,OZ = Zelex ZTX-849, Li = Coitlromcs CTX0211128-2, L2 = Puise Engineering PE-92105, Laser = Hughes 3121H-P, 6.5- mA beam current. 🔗 External reference