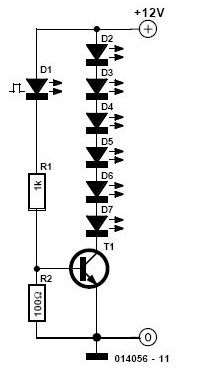
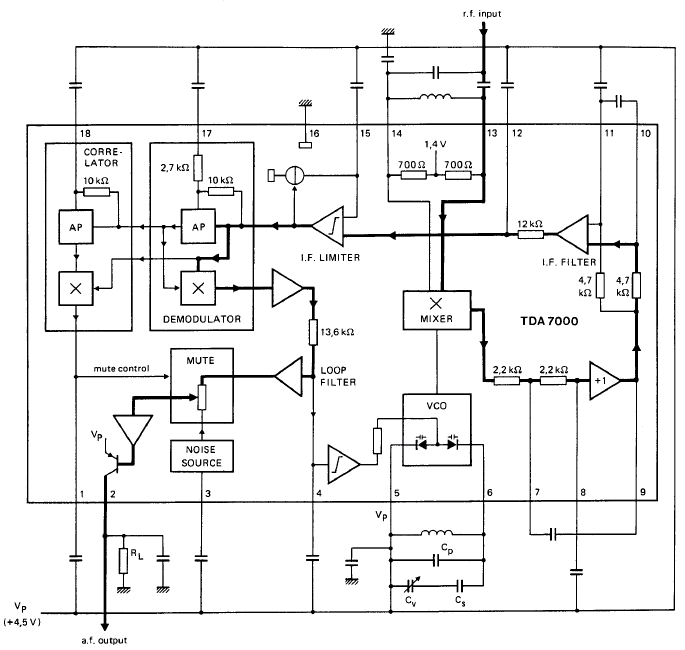
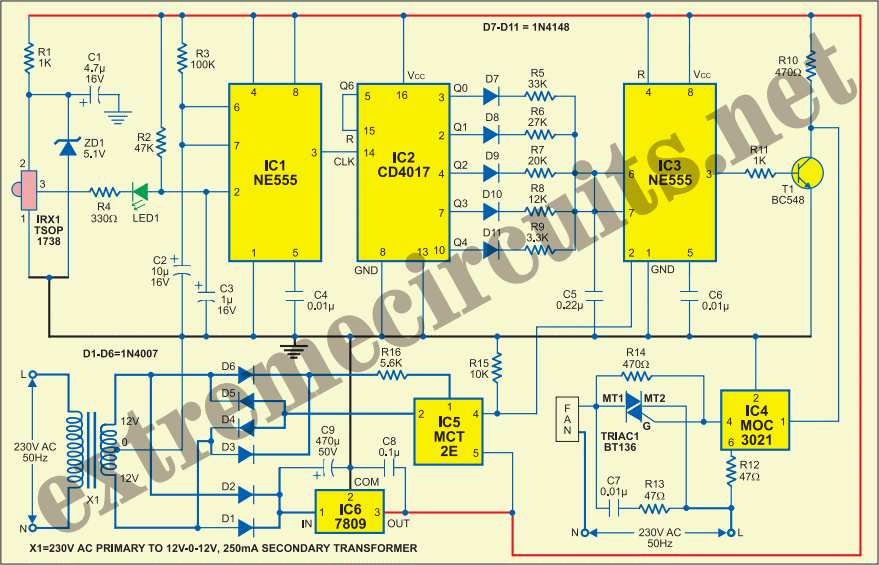
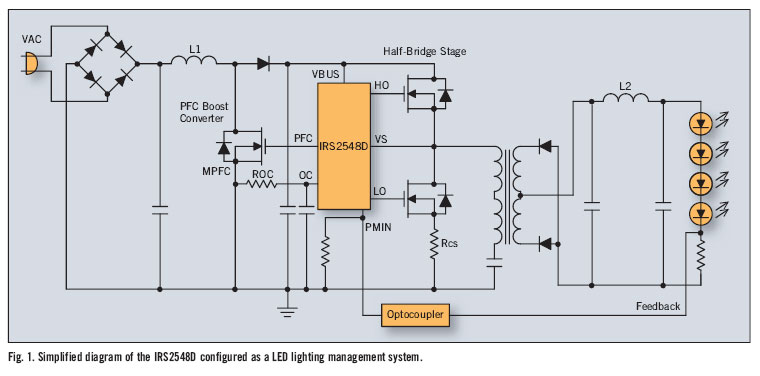
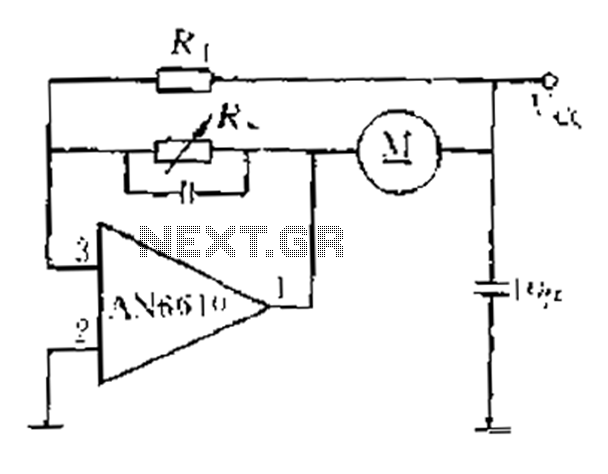
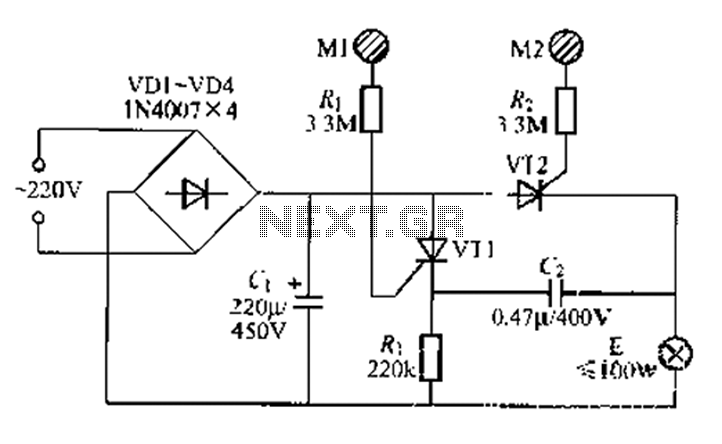
Light control relay circuit
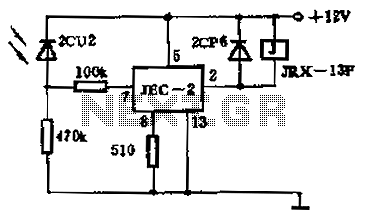
The circuit operates as a photoelectric switch utilizing a photoresistor. It exhibits high sensitivity, particularly in controlling a light relay. Under low illumination, the transistor (VT) remains non-conductive. When the illumination reaches a certain threshold, the resistance of the photoresistor decreases, allowing sufficient base current to flow into VT. This results in a significant collector current, which activates the relay.
The described photoelectric switch circuit employs a photoresistor (also known as a light-dependent resistor, LDR) as the primary sensing element. The photoresistor's resistance varies inversely with the intensity of incident light; thus, in low-light conditions, its resistance is high, preventing the base of the transistor (VT) from receiving adequate current. Consequently, the transistor remains in the off state, and no current flows through the relay coil, keeping the relay contacts open.
As the ambient light increases and surpasses a predetermined threshold, the resistance of the photoresistor decreases. This change allows a sufficient amount of current to flow into the base terminal of the transistor. The transistor enters saturation, which significantly increases the collector current. This current is sufficient to energize the relay coil, closing the relay contacts and allowing current to flow through the load connected to the relay.
The circuit typically includes additional components such as resistors to limit current and capacitors for noise filtering, ensuring stable operation. The relay can control various devices, from simple light fixtures to complex systems, depending on the design requirements. The high sensitivity of the circuit makes it suitable for applications where precise light detection is critical, such as in automatic lighting systems, security systems, and other automation applications. Proper calibration of the photoresistor and the selection of the transistor are essential for achieving optimal performance in varying lighting conditions.As a photoelectric switch with photoresistor circuit, the sensitivity is very high, as shown for the light control relay. At low illumination, VT nonconductive; when there is l ight of a certain illumination, photoresistor resistance becomes smaller, VT sufficient base current conduction, resulting in a large collector current, so that relay.
The described photoelectric switch circuit employs a photoresistor (also known as a light-dependent resistor, LDR) as the primary sensing element. The photoresistor's resistance varies inversely with the intensity of incident light; thus, in low-light conditions, its resistance is high, preventing the base of the transistor (VT) from receiving adequate current. Consequently, the transistor remains in the off state, and no current flows through the relay coil, keeping the relay contacts open.
As the ambient light increases and surpasses a predetermined threshold, the resistance of the photoresistor decreases. This change allows a sufficient amount of current to flow into the base terminal of the transistor. The transistor enters saturation, which significantly increases the collector current. This current is sufficient to energize the relay coil, closing the relay contacts and allowing current to flow through the load connected to the relay.
The circuit typically includes additional components such as resistors to limit current and capacitors for noise filtering, ensuring stable operation. The relay can control various devices, from simple light fixtures to complex systems, depending on the design requirements. The high sensitivity of the circuit makes it suitable for applications where precise light detection is critical, such as in automatic lighting systems, security systems, and other automation applications. Proper calibration of the photoresistor and the selection of the transistor are essential for achieving optimal performance in varying lighting conditions.As a photoelectric switch with photoresistor circuit, the sensitivity is very high, as shown for the light control relay. At low illumination, VT nonconductive; when there is l ight of a certain illumination, photoresistor resistance becomes smaller, VT sufficient base current conduction, resulting in a large collector current, so that relay.