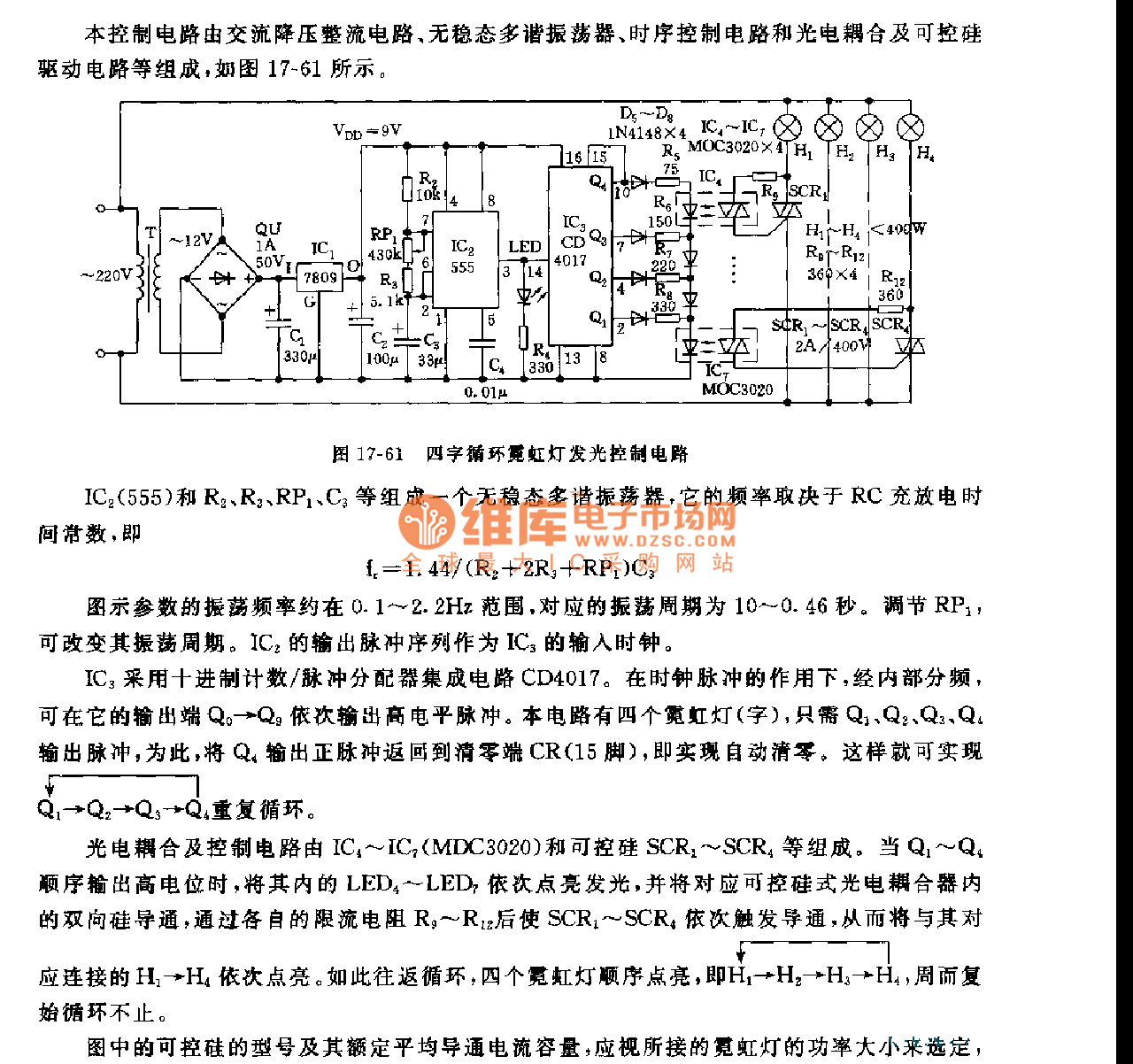
The One-shot Monostable Multivibrator Circuit
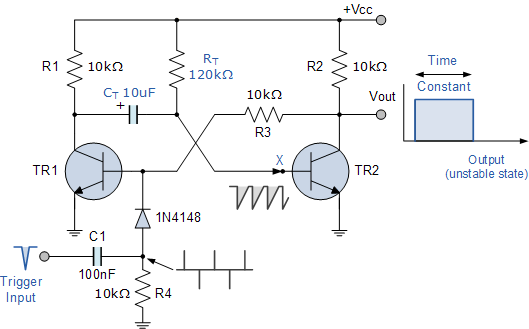
Electronics tutorial about the monostable multivibrator circuit, also known as a one-shot monostable multivibrator, used as a pulse generator circuit.
The monostable multivibrator is a crucial component in electronic circuits, functioning as a pulse generator that produces a single output pulse in response to a triggering input. This circuit is characterized by its ability to return to a stable state after a temporary output pulse, hence the term "monostable."
The typical configuration of a monostable multivibrator involves a timing resistor (R) and a timing capacitor (C) connected to a trigger input. When the circuit is triggered, the capacitor charges through the resistor, and the output pulse width is determined by the RC time constant, calculated using the formula \( T = 1.1 \times R \times C \), where \( T \) is the duration of the output pulse in seconds.
Commonly, the 555 timer IC is utilized to construct monostable multivibrators due to its versatility and ease of use. In this configuration, the trigger input is connected to pin 2 of the 555 timer, while the timing components are connected between pin 6 (threshold) and pin 3 (output). The output pulse can be used in various applications, such as debounce circuits, timers, and pulse width modulation.
In practical applications, the monostable multivibrator can be employed to generate precise timing intervals for various electronic devices, ensuring accurate signal processing and control. Its simplicity and reliability make it an essential tool for engineers and hobbyists in the field of electronics.Electronics Tutorial about the Monostable Multivibrator Circuit also known as a One-shot Monostable Multivibrator used as a Pulse Generator Circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The monostable multivibrator is a crucial component in electronic circuits, functioning as a pulse generator that produces a single output pulse in response to a triggering input. This circuit is characterized by its ability to return to a stable state after a temporary output pulse, hence the term "monostable."
The typical configuration of a monostable multivibrator involves a timing resistor (R) and a timing capacitor (C) connected to a trigger input. When the circuit is triggered, the capacitor charges through the resistor, and the output pulse width is determined by the RC time constant, calculated using the formula \( T = 1.1 \times R \times C \), where \( T \) is the duration of the output pulse in seconds.
Commonly, the 555 timer IC is utilized to construct monostable multivibrators due to its versatility and ease of use. In this configuration, the trigger input is connected to pin 2 of the 555 timer, while the timing components are connected between pin 6 (threshold) and pin 3 (output). The output pulse can be used in various applications, such as debounce circuits, timers, and pulse width modulation.
In practical applications, the monostable multivibrator can be employed to generate precise timing intervals for various electronic devices, ensuring accurate signal processing and control. Its simplicity and reliability make it an essential tool for engineers and hobbyists in the field of electronics.Electronics Tutorial about the Monostable Multivibrator Circuit also known as a One-shot Monostable Multivibrator used as a Pulse Generator Circuit.. 🔗 External reference