electronic dice circuit
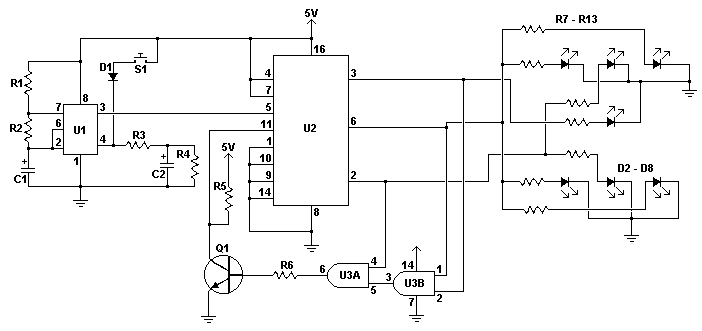
An electronic dice is a classic introductory project for individuals interested in electronics. It consists of a timer, counter, and several LEDs, forming a circuit that adds an engaging element to traditional board games. When the switch is activated, a 555 timer configured in astable mode generates pulses to a BCD counter, which illuminates a series of LEDs arranged to represent the faces of a die. Two AND gates are employed to reset the count back to one whenever the BCD output reaches seven. Consequently, although the circuit is not genuinely random, the natural bounce from the pushbutton and the typical human reaction time, which is much slower than the oscillator's frequency, create an output that appears random.
The electronic dice circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode, which produces a continuous square wave output. This output serves as the clock signal for the BCD counter, typically a 74HC390 or similar IC, which counts from 0 to 9 in binary-coded decimal format. The counter is connected to a series of LEDs through a resistor network to limit the current and prevent damage to the LEDs. The arrangement of the LEDs simulates the faces of a die, with outputs corresponding to the values 1 through 6.
To ensure the output does not exceed the maximum value of 6, the two AND gates are strategically placed in the circuit. They monitor the BCD output, and when the count reaches seven, they send a reset signal to the BCD counter, forcing it back to one. This mechanism prevents the circuit from displaying an invalid die face.
The overall design can be enhanced by incorporating additional components, such as a debouncing circuit for the pushbutton switch, which would help to eliminate any unwanted multiple counts caused by mechanical bounce. Furthermore, a capacitor can be added to the 555 timer circuit to adjust the timing interval, allowing for customization of the dice rolling speed.
In summary, this electronic dice project combines fundamental electronic components, such as timers, counters, and logic gates, to create an engaging and interactive device that can enhance traditional gaming experiences. The design's simplicity and reliance on basic electronic principles make it an ideal project for beginners in the field of electronics.An electronic dice is a classic first project for those getting interested in electronics. A timer, counter and a few LEDs makes a circuit that can also add a new twist to some old boring board games. When the switch is pressed, a 555 timer in astable mode pulses a BCD counter which lights up a series of LEDs wired to mimic a dice.
Two AND gates a re used to reset the count back to one whenever the BCD output is seven. Thus, the circuit is not truly random but the natural bounce present in a pushbutton and the normal human ability to operate much slower then the oscillator make the output of the circuit seem random. 🔗 External reference
The electronic dice circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode, which produces a continuous square wave output. This output serves as the clock signal for the BCD counter, typically a 74HC390 or similar IC, which counts from 0 to 9 in binary-coded decimal format. The counter is connected to a series of LEDs through a resistor network to limit the current and prevent damage to the LEDs. The arrangement of the LEDs simulates the faces of a die, with outputs corresponding to the values 1 through 6.
To ensure the output does not exceed the maximum value of 6, the two AND gates are strategically placed in the circuit. They monitor the BCD output, and when the count reaches seven, they send a reset signal to the BCD counter, forcing it back to one. This mechanism prevents the circuit from displaying an invalid die face.
The overall design can be enhanced by incorporating additional components, such as a debouncing circuit for the pushbutton switch, which would help to eliminate any unwanted multiple counts caused by mechanical bounce. Furthermore, a capacitor can be added to the 555 timer circuit to adjust the timing interval, allowing for customization of the dice rolling speed.
In summary, this electronic dice project combines fundamental electronic components, such as timers, counters, and logic gates, to create an engaging and interactive device that can enhance traditional gaming experiences. The design's simplicity and reliance on basic electronic principles make it an ideal project for beginners in the field of electronics.An electronic dice is a classic first project for those getting interested in electronics. A timer, counter and a few LEDs makes a circuit that can also add a new twist to some old boring board games. When the switch is pressed, a 555 timer in astable mode pulses a BCD counter which lights up a series of LEDs wired to mimic a dice.
Two AND gates a re used to reset the count back to one whenever the BCD output is seven. Thus, the circuit is not truly random but the natural bounce present in a pushbutton and the normal human ability to operate much slower then the oscillator make the output of the circuit seem random. 🔗 External reference