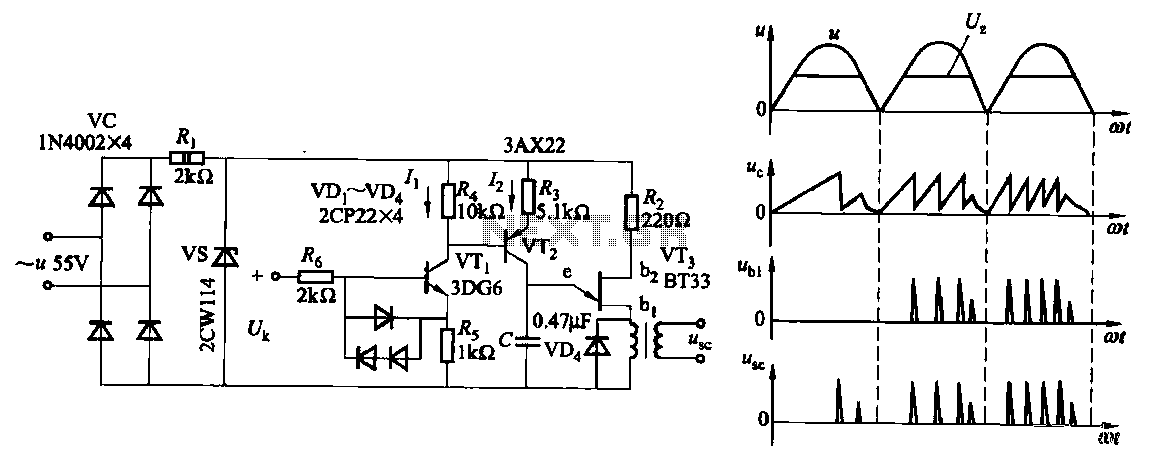
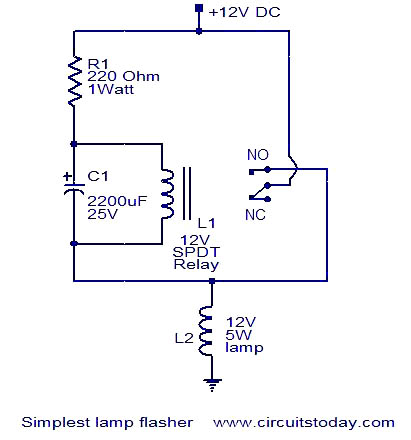
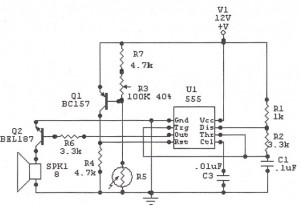
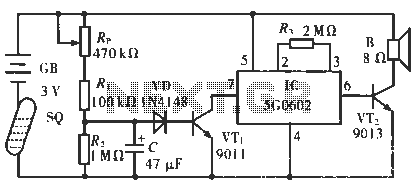
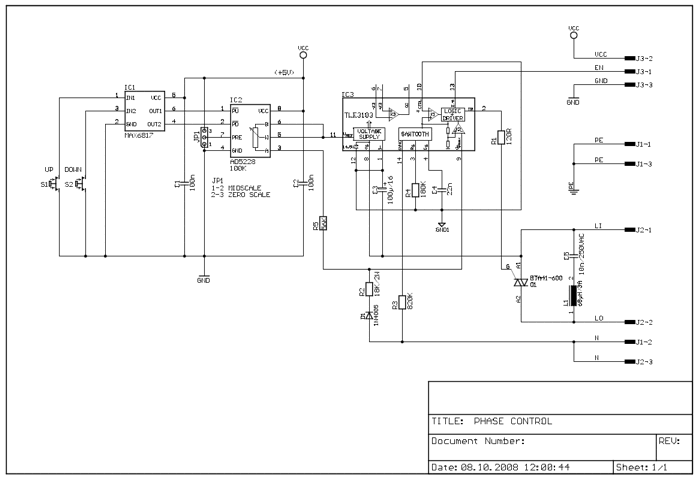
electronic marx circuit and gas
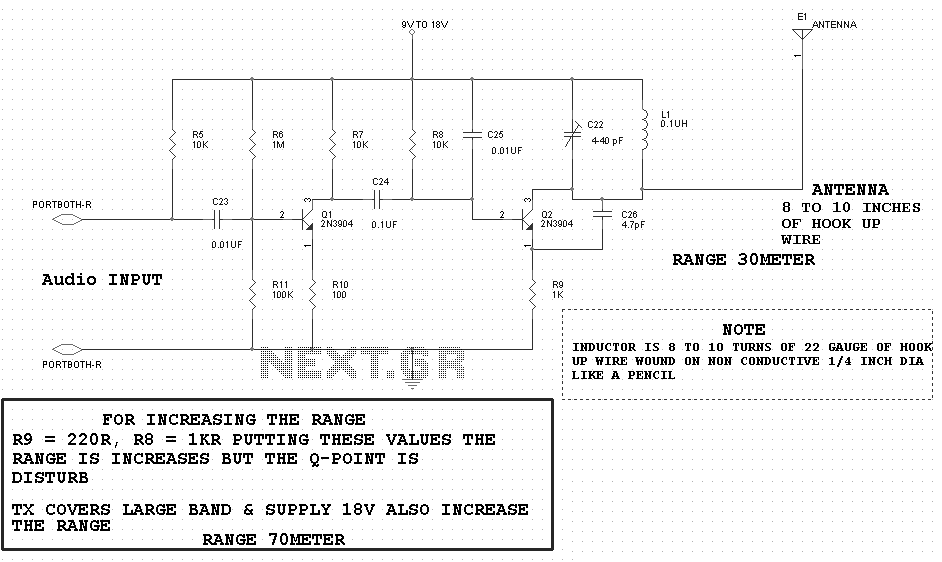
Writing about multiple circuits in Marx, an entire new set has been discovered, referred to as "the" Marx Generator. There are diagrams available, along with a useful quote: "The main advantage of the Marx circuit configuration over a more direct approach to charging is that it overcomes..."
The Marx generator is a type of electrical circuit used to generate high-voltage pulses. It consists of a series of capacitors and spark gaps arranged in a specific configuration to achieve rapid charging and discharging. The basic principle involves charging multiple capacitors in parallel and then discharging them in series, which results in a high-voltage output.
In a typical Marx generator setup, several capacitors are connected to a common voltage source. Each capacitor charges up to the source voltage. Once the capacitors are fully charged, the spark gaps are triggered, creating a conductive path between them. This allows the stored energy in the capacitors to discharge through the spark gaps in series, effectively adding the voltages of each capacitor together. The result is a much higher voltage pulse than what would be possible with a single capacitor alone.
The configuration of the Marx generator allows for precise control over the timing of the discharge, which is crucial for applications such as high-voltage testing, pulsed power applications, and electromagnetic pulse (EMP) generation. Additionally, the ability to scale the generator by adding more capacitors and spark gaps provides flexibility in designing circuits for specific high-voltage requirements.
The advantages of the Marx generator include its simplicity, efficiency in generating high-voltage pulses, and the ability to produce short-duration, high-energy outputs. It is commonly used in research laboratories, industrial applications, and as a component in various high-voltage experiments. Understanding the operational principles and configuration of the Marx generator is essential for engineers and researchers working in fields that require high-voltage technology.Writing about multiple circuits in Marx, I have just discovered (shame for not knowing this) an entire new set - indeed, billed as `the` Marx Generator. There are, of course, also diagrams, and a useful quote: `The main advantage of the Marx circuit configuration over a more direct approach to charging is that it overcomes..
🔗 External reference
The Marx generator is a type of electrical circuit used to generate high-voltage pulses. It consists of a series of capacitors and spark gaps arranged in a specific configuration to achieve rapid charging and discharging. The basic principle involves charging multiple capacitors in parallel and then discharging them in series, which results in a high-voltage output.
In a typical Marx generator setup, several capacitors are connected to a common voltage source. Each capacitor charges up to the source voltage. Once the capacitors are fully charged, the spark gaps are triggered, creating a conductive path between them. This allows the stored energy in the capacitors to discharge through the spark gaps in series, effectively adding the voltages of each capacitor together. The result is a much higher voltage pulse than what would be possible with a single capacitor alone.
The configuration of the Marx generator allows for precise control over the timing of the discharge, which is crucial for applications such as high-voltage testing, pulsed power applications, and electromagnetic pulse (EMP) generation. Additionally, the ability to scale the generator by adding more capacitors and spark gaps provides flexibility in designing circuits for specific high-voltage requirements.
The advantages of the Marx generator include its simplicity, efficiency in generating high-voltage pulses, and the ability to produce short-duration, high-energy outputs. It is commonly used in research laboratories, industrial applications, and as a component in various high-voltage experiments. Understanding the operational principles and configuration of the Marx generator is essential for engineers and researchers working in fields that require high-voltage technology.Writing about multiple circuits in Marx, I have just discovered (shame for not knowing this) an entire new set - indeed, billed as `the` Marx Generator. There are, of course, also diagrams, and a useful quote: `The main advantage of the Marx circuit configuration over a more direct approach to charging is that it overcomes..
🔗 External reference