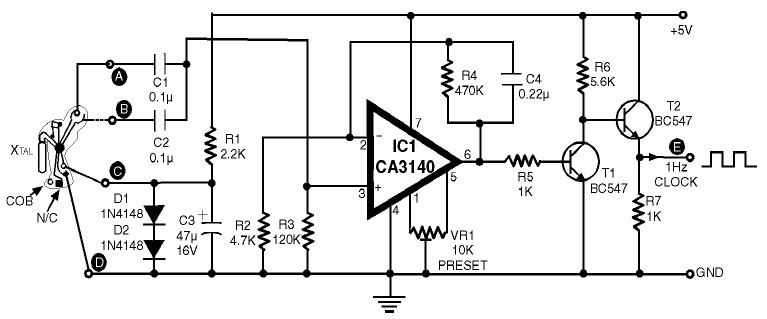
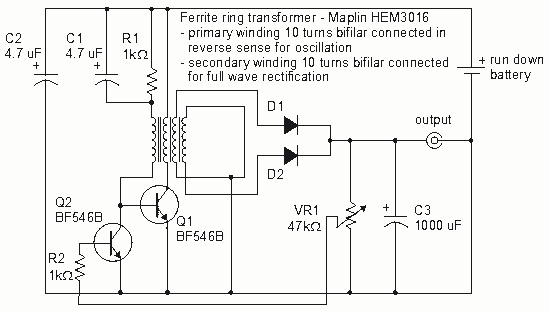
Single-junction transistor trigger circuit 2
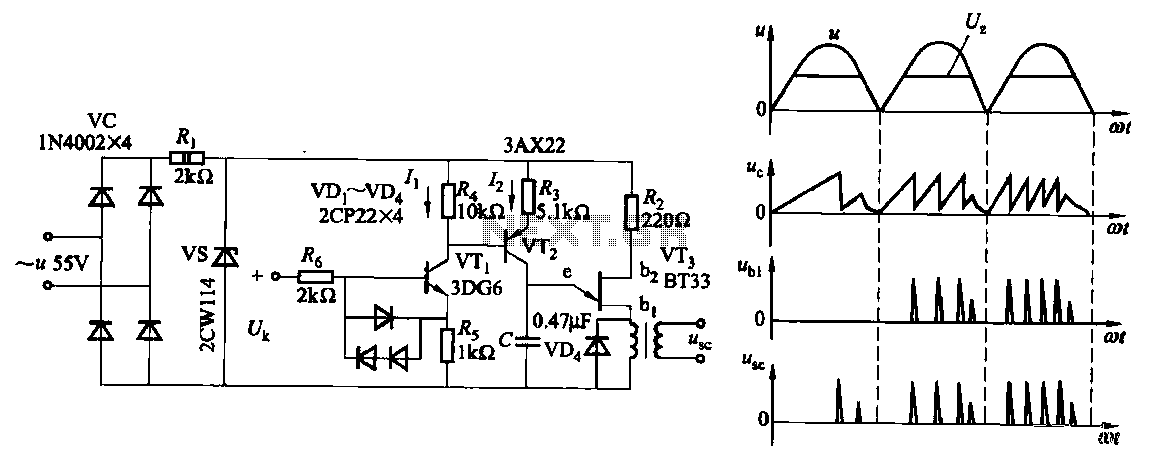
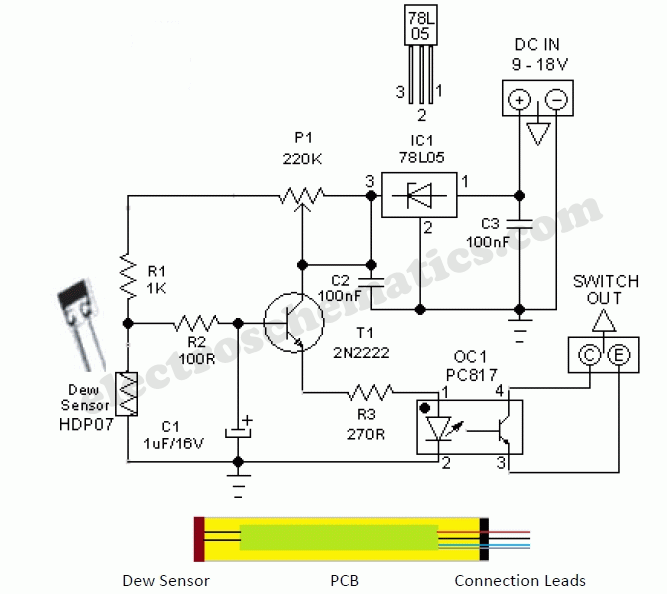
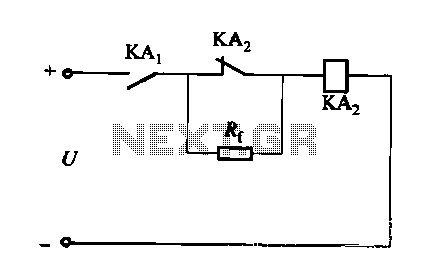
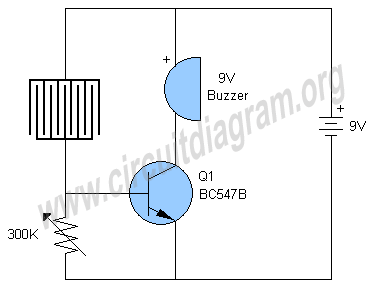
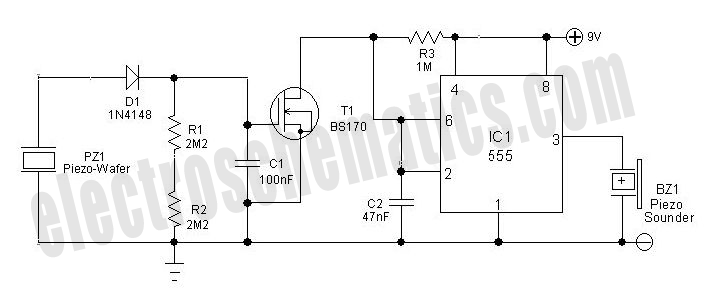
Due to the increased level of the transistor amplifier circuit, the control circuit's performance in Figure 16-6 is more sensitive and can accept input control signals superimposed on others (such as voltage, current, and speed feedback signals) to meet system requirements.
The transistor amplifier circuit, as illustrated in Figure 16-6, showcases a heightened sensitivity that enhances the control circuit's performance. This sensitivity allows the circuit to effectively process multiple input control signals simultaneously. These signals can include voltage levels, current readings, and speed feedback, which are crucial for various applications in electronic systems.
The design of the control circuit incorporates a transistor amplifier that is configured to amplify the desired control signals while filtering out noise and interference. This is achieved through careful selection of transistor characteristics, biasing conditions, and feedback mechanisms. The circuit may utilize operational amplifiers in conjunction with transistors to achieve the desired gain and bandwidth, ensuring that the circuit remains responsive to changes in the input signals.
The ability to superimpose multiple control signals enables the system to operate under various conditions and respond dynamically to feedback. For instance, in a motor control application, the control circuit can simultaneously process speed feedback and current measurements to adjust the voltage supplied to the motor, thereby optimizing performance and efficiency.
Overall, the transistor amplifier circuit serves as a critical component in modern electronic systems, providing the necessary sensitivity and versatility to handle complex control tasks.Due to the increased level of transistor amplifier circuit, the control circuit of Figure 16-6 performance more than plus sensitive, and can input control signal superimposed o n the other (such as voltage, current, speed feedback signal) to meet system requirements.
The transistor amplifier circuit, as illustrated in Figure 16-6, showcases a heightened sensitivity that enhances the control circuit's performance. This sensitivity allows the circuit to effectively process multiple input control signals simultaneously. These signals can include voltage levels, current readings, and speed feedback, which are crucial for various applications in electronic systems.
The design of the control circuit incorporates a transistor amplifier that is configured to amplify the desired control signals while filtering out noise and interference. This is achieved through careful selection of transistor characteristics, biasing conditions, and feedback mechanisms. The circuit may utilize operational amplifiers in conjunction with transistors to achieve the desired gain and bandwidth, ensuring that the circuit remains responsive to changes in the input signals.
The ability to superimpose multiple control signals enables the system to operate under various conditions and respond dynamically to feedback. For instance, in a motor control application, the control circuit can simultaneously process speed feedback and current measurements to adjust the voltage supplied to the motor, thereby optimizing performance and efficiency.
Overall, the transistor amplifier circuit serves as a critical component in modern electronic systems, providing the necessary sensitivity and versatility to handle complex control tasks.Due to the increased level of transistor amplifier circuit, the control circuit of Figure 16-6 performance more than plus sensitive, and can input control signal superimposed o n the other (such as voltage, current, speed feedback signal) to meet system requirements.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713