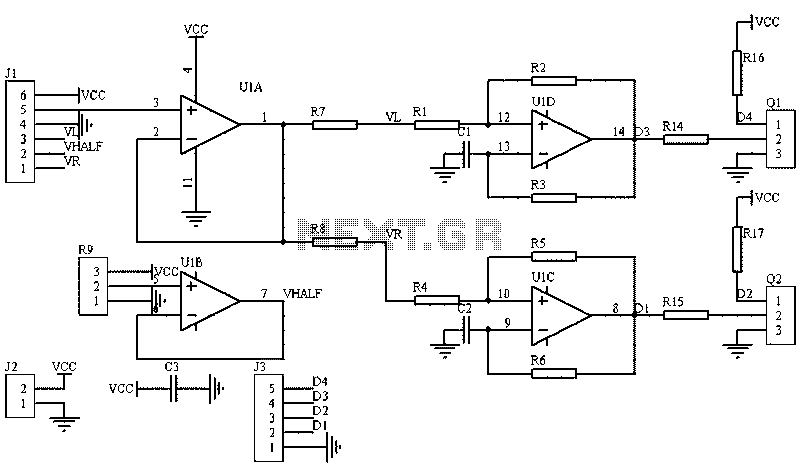
External protection signal generator by a circuit diagram TDA4866
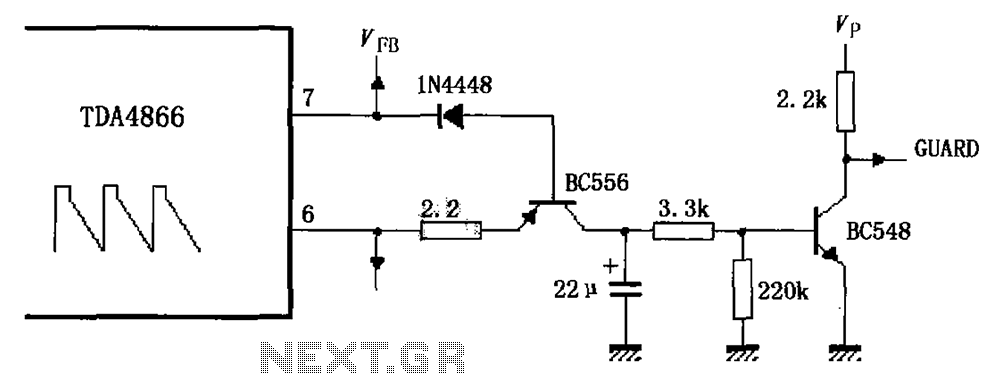
As illustrated in FIG TDA4866, the circuit consists of an external signal generator circuit protection. The internal protection circuit's role is to manage control, while the external protection circuit performs its functions. During normal operation, the vertical amplitude of the output signal is higher, causing the BC556 transistor to turn on. At the same time, the base current of the BC548 transistor is activated, allowing it to function as a low-level output indicator. Conversely, when the circuit is not functioning correctly, the vertical amplitude of the output signal decreases, resulting in the BC556 transistor turning off. In this state, the BC548 transistor receives no base current and also turns off, leading to a high output signal that indicates an error in operation.
The TDA4866 circuit is designed to ensure the integrity and reliability of the signal generation process through its dual-layer protection mechanism. The external signal generator circuit protection serves as a primary defense against potential signal anomalies or external disturbances that may affect the overall operation. The internal protection circuit is tasked with monitoring and controlling the performance of the system, ensuring that any deviations from expected operational parameters are promptly addressed.
The BC556 transistor plays a crucial role in amplifying the output signal during normal conditions. When the vertical amplitude of the output signal is within the acceptable range, the BC556 is activated, allowing for efficient signal amplification. The BC548 transistor, meanwhile, functions as a low-level output indicator, providing a visual or electronic cue to the system's operational status. This transistor is designed to turn on when the base current is sufficient, indicating that the system is functioning as intended.
In scenarios where the circuit encounters issues, the behavior of the transistors changes significantly. A drop in the vertical amplitude of the output signal signifies a malfunction, prompting the BC556 transistor to deactivate. This action is critical as it prevents further amplification of a potentially faulty signal. Simultaneously, the lack of base current to the BC548 transistor causes it to turn off, resulting in a high output signal that serves as an error indication. This dual response mechanism is vital for maintaining the reliability of the circuit and preventing damage due to uncontrolled conditions.
The design of the TDA4866 circuit, with its integrated protection features and transistor-based signaling, exemplifies a robust approach to signal management in electronic systems. The careful interplay between the BC556 and BC548 transistors ensures that the circuit can both amplify and indicate operational status effectively, providing essential feedback for troubleshooting and maintenance. As shown in FIG TDA4866 constituted by an external signal generator circuit protection. The role of the internal protection circuit is out of control, the external protection c ircuit functions. Vertical amplitude of the output signal during normal operation of a larger, BC556 transistor is turned on, while the base current of transistor BC548 get too turned on to work as a low-level output indication. When not working properly, the vertical amplitude of the output signal is low, transistor BC556 is turned off, while transistor BC548 no base current is turned off, the output is high as an error work instructions.
The TDA4866 circuit is designed to ensure the integrity and reliability of the signal generation process through its dual-layer protection mechanism. The external signal generator circuit protection serves as a primary defense against potential signal anomalies or external disturbances that may affect the overall operation. The internal protection circuit is tasked with monitoring and controlling the performance of the system, ensuring that any deviations from expected operational parameters are promptly addressed.
The BC556 transistor plays a crucial role in amplifying the output signal during normal conditions. When the vertical amplitude of the output signal is within the acceptable range, the BC556 is activated, allowing for efficient signal amplification. The BC548 transistor, meanwhile, functions as a low-level output indicator, providing a visual or electronic cue to the system's operational status. This transistor is designed to turn on when the base current is sufficient, indicating that the system is functioning as intended.
In scenarios where the circuit encounters issues, the behavior of the transistors changes significantly. A drop in the vertical amplitude of the output signal signifies a malfunction, prompting the BC556 transistor to deactivate. This action is critical as it prevents further amplification of a potentially faulty signal. Simultaneously, the lack of base current to the BC548 transistor causes it to turn off, resulting in a high output signal that serves as an error indication. This dual response mechanism is vital for maintaining the reliability of the circuit and preventing damage due to uncontrolled conditions.
The design of the TDA4866 circuit, with its integrated protection features and transistor-based signaling, exemplifies a robust approach to signal management in electronic systems. The careful interplay between the BC556 and BC548 transistors ensures that the circuit can both amplify and indicate operational status effectively, providing essential feedback for troubleshooting and maintenance. As shown in FIG TDA4866 constituted by an external signal generator circuit protection. The role of the internal protection circuit is out of control, the external protection c ircuit functions. Vertical amplitude of the output signal during normal operation of a larger, BC556 transistor is turned on, while the base current of transistor BC548 get too turned on to work as a low-level output indication. When not working properly, the vertical amplitude of the output signal is low, transistor BC556 is turned off, while transistor BC548 no base current is turned off, the output is high as an error work instructions.