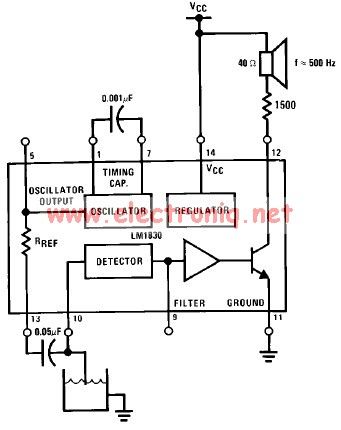
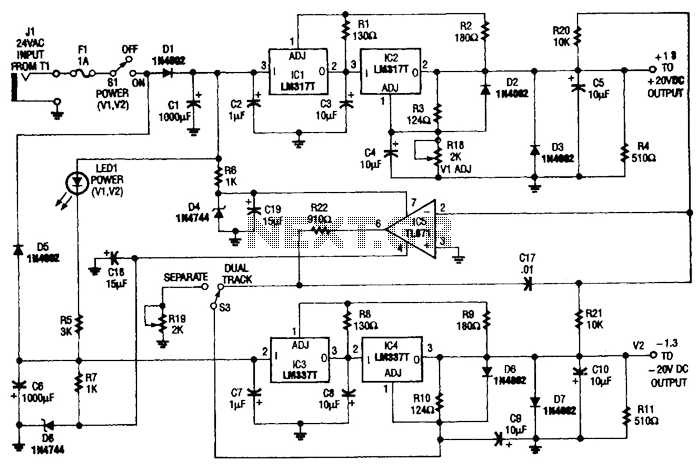
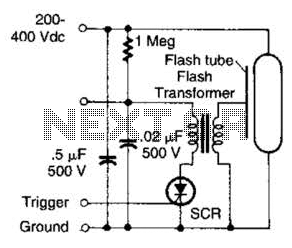
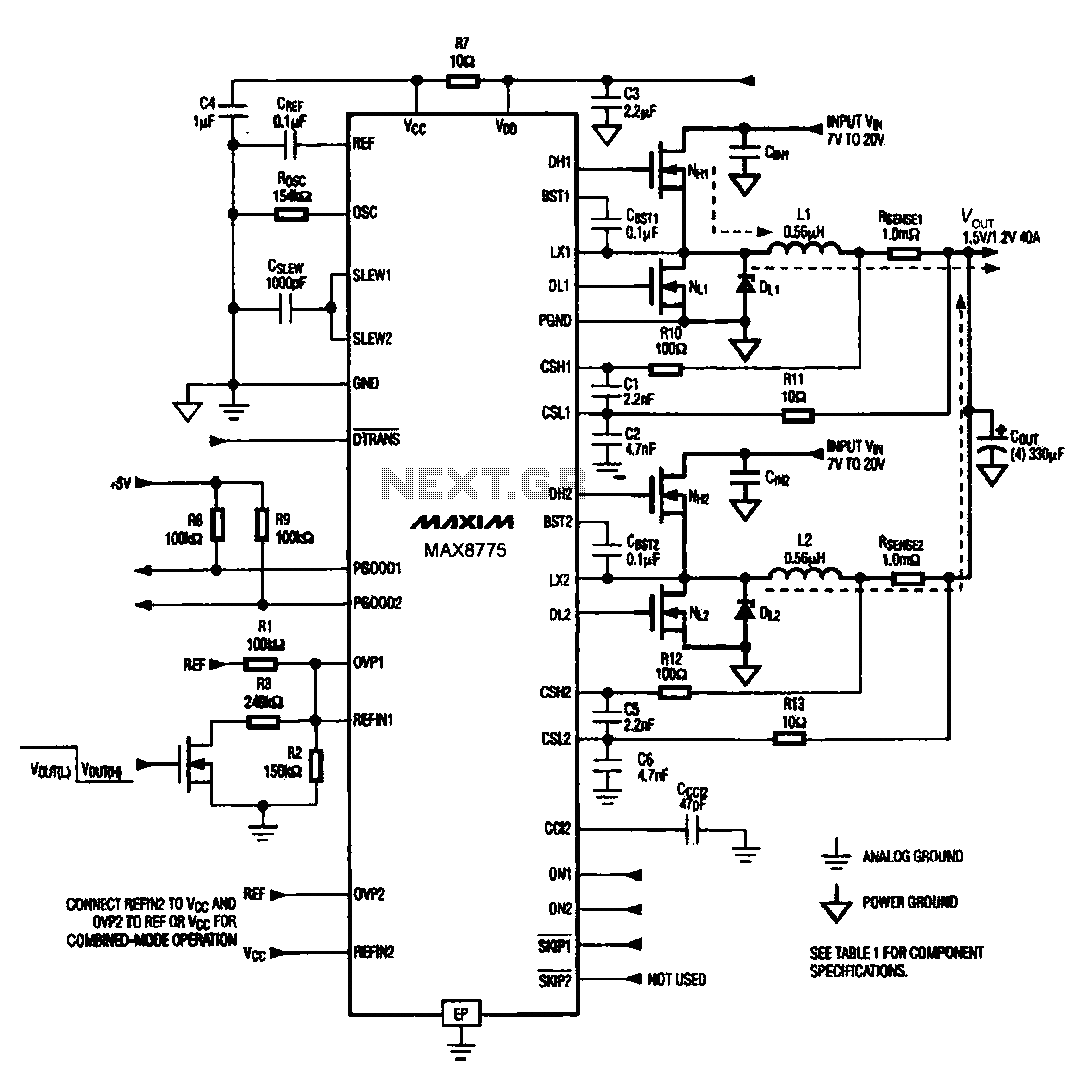
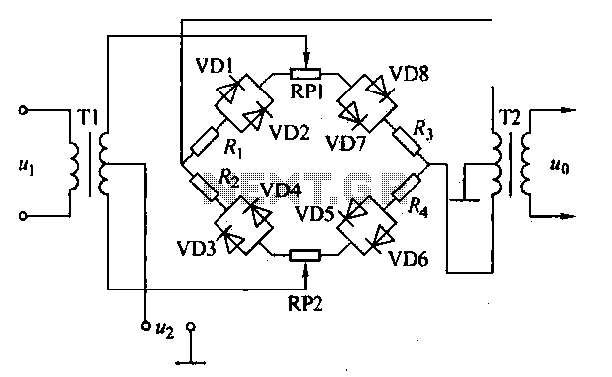
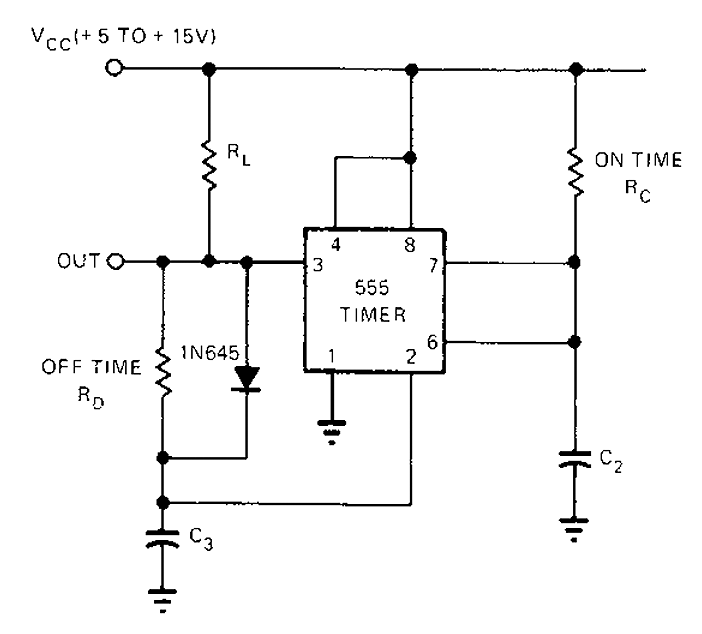
Fet Audio Mixer electronic circuit

This circuit combines two or more audio channels into a single channel (for example, converting stereo to mono). It is capable of mixing multiple channels while consuming minimal power. The schematic illustrates two inputs, but additional inputs can be incorporated by simply replicating the clearly defined sections.
The circuit employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a summing amplifier arrangement to achieve the mixing functionality. Each input channel is connected to a resistor that feeds into the inverting terminal of the op-amp. The resistors are selected to ensure that the levels of the incoming signals are appropriately balanced, preventing any single channel from dominating the output.
The output of the op-amp provides the mixed audio signal, which can then be sent to a speaker or further processed in an audio system. Power supply requirements for this circuit are minimal, typically requiring only a dual power supply (positive and negative) to operate the op-amps effectively.
By adding additional input channels, one can easily increase the number of audio sources mixed together. Care should be taken to maintain consistent resistor values across all channels to ensure uniform mixing and avoid distortion in the final output. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included near the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation.
This circuit is particularly useful in applications such as audio processing, sound reinforcement systems, and various consumer electronics where multiple audio sources need to be combined efficiently. Overall, the design is straightforward, cost-effective, and versatile for a range of audio mixing applications.This simple circuit mixes two or more channels into one channel (eg. stereo into mono). The circuit can mix as many or as few channels as you like and consumes very little power. The mixer is shown with two inputs, but you can add as many as you want by just duplicating the sections which are clearly visible on the schematic. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a summing amplifier arrangement to achieve the mixing functionality. Each input channel is connected to a resistor that feeds into the inverting terminal of the op-amp. The resistors are selected to ensure that the levels of the incoming signals are appropriately balanced, preventing any single channel from dominating the output.
The output of the op-amp provides the mixed audio signal, which can then be sent to a speaker or further processed in an audio system. Power supply requirements for this circuit are minimal, typically requiring only a dual power supply (positive and negative) to operate the op-amps effectively.
By adding additional input channels, one can easily increase the number of audio sources mixed together. Care should be taken to maintain consistent resistor values across all channels to ensure uniform mixing and avoid distortion in the final output. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included near the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation.
This circuit is particularly useful in applications such as audio processing, sound reinforcement systems, and various consumer electronics where multiple audio sources need to be combined efficiently. Overall, the design is straightforward, cost-effective, and versatile for a range of audio mixing applications.This simple circuit mixes two or more channels into one channel (eg. stereo into mono). The circuit can mix as many or as few channels as you like and consumes very little power. The mixer is shown with two inputs, but you can add as many as you want by just duplicating the sections which are clearly visible on the schematic. 🔗 External reference