Fire Alarm Circuit
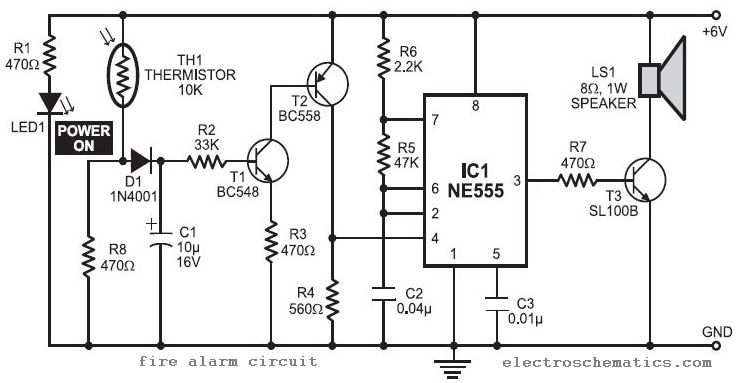
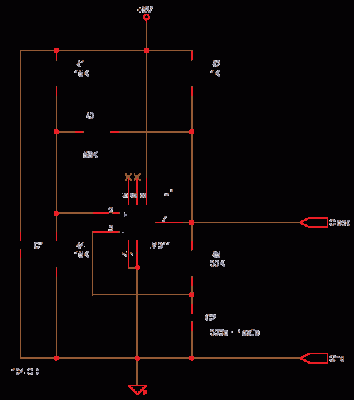
In this fire alarm circuit project, a thermistor functions as the heat sensor. When the temperature rises, its resistance decreases, and conversely, when the temperature falls, its resistance increases. Under normal conditions...
In this fire alarm circuit, the thermistor is a critical component that detects changes in temperature due to fire. The thermistor, typically a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) type, exhibits a decrease in resistance as the temperature increases. This property is essential for the circuit's ability to monitor environmental conditions effectively.
The circuit design includes a voltage divider configuration, where the thermistor is connected in series with a fixed resistor. As the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor drops, resulting in a change in voltage across the fixed resistor. This change can be monitored by a microcontroller or a comparator circuit, which can trigger an alarm or activate other safety measures when a predefined temperature threshold is exceeded.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate an operational amplifier configured as a comparator to enhance sensitivity. The output of the comparator can drive an LED indicator or a relay to activate an external alarm system. Power supply considerations are also crucial, as the circuit must operate reliably under various conditions, ensuring that it remains functional during a fire event.
To improve the overall performance, it may be beneficial to include a calibration mechanism to account for variations in thermistor characteristics and environmental factors. Furthermore, the circuit can be designed with a delay feature to prevent false alarms caused by transient temperature spikes.
Overall, this fire alarm circuit utilizing a thermistor is a practical and effective solution for detecting heat increases associated with fire hazards, providing an essential safety mechanism in residential and commercial settings.In this fire alarm circuit project, a thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases, its resistance decreases, and vice versa. At normal.. 🔗 External reference
In this fire alarm circuit, the thermistor is a critical component that detects changes in temperature due to fire. The thermistor, typically a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) type, exhibits a decrease in resistance as the temperature increases. This property is essential for the circuit's ability to monitor environmental conditions effectively.
The circuit design includes a voltage divider configuration, where the thermistor is connected in series with a fixed resistor. As the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor drops, resulting in a change in voltage across the fixed resistor. This change can be monitored by a microcontroller or a comparator circuit, which can trigger an alarm or activate other safety measures when a predefined temperature threshold is exceeded.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate an operational amplifier configured as a comparator to enhance sensitivity. The output of the comparator can drive an LED indicator or a relay to activate an external alarm system. Power supply considerations are also crucial, as the circuit must operate reliably under various conditions, ensuring that it remains functional during a fire event.
To improve the overall performance, it may be beneficial to include a calibration mechanism to account for variations in thermistor characteristics and environmental factors. Furthermore, the circuit can be designed with a delay feature to prevent false alarms caused by transient temperature spikes.
Overall, this fire alarm circuit utilizing a thermistor is a practical and effective solution for detecting heat increases associated with fire hazards, providing an essential safety mechanism in residential and commercial settings.In this fire alarm circuit project, a thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases, its resistance decreases, and vice versa. At normal.. 🔗 External reference