12V-220V Modified Sine-wave Inverter Circuit
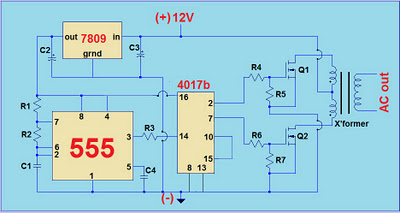
This project involves a simple 12V to 220V modified sine-wave inverter utilizing a 555 timer IC and a CD4017 decade counter. The inverter is capable of delivering 300W of continuous power and approximately 500W of maximum power output for short durations. It serves effectively as an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). The inverter is driven by the 555 timer and the CD4017 decade counter. The 555 timer generates pulses at a frequency that is four times the desired output frequency. For instance, to achieve a 60Hz output, the timer frequency must be set to 240Hz (4 times 60Hz). For a 50Hz output, the timer frequency should be 200Hz. Various combinations of resistors R1, R2, and capacitor C1 can be used to obtain the desired frequency with the help of a 555 timer calculator. The LM7809 voltage regulator is employed to protect the 555 timer and the CD4017 from voltage spikes and transients that may affect their operation and stability. Alternative regulator ICs such as LM7808, LM7806, or LM7805 can also be utilized, provided the output voltage is 5V or higher to ensure proper functioning of the MOSFETs Q1 and Q2. The accompanying diagram illustrates the comparison between modified and pure sine waves, both of which share the same peak and RMS values.
Part List (60Hz, 220V):
- R1 – 20 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- R2 – 20 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- R3 – 1.2 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- R4, R6 – 560 ohms, 1/4W
- R5, R7 – 5.6 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- C1 – 100nF capacitor
- C2 – 10uF electrolytic capacitor, rated 16V
- C3 – 470uF electrolytic capacitor, rated 16V
- C4 – 100nF capacitor
- Q1, Q2 – IRFZ44N or similar N-channel power MOSFET
- Transformer – 10V-0V-10V to 220V transformer (minimum 500VA if required)
- LM7809 – IC voltage regulator
- LM555 – timer IC
- CD4017b – 5-stage Johnson counter
- 12V – 12V lead-acid battery
The inverter circuit operates by using the 555 timer in astable mode, which generates a square wave output. This square wave is then processed by the CD4017 decade counter, which divides the frequency to produce a modified sine wave output. The output from the CD4017 is used to drive the gates of the N-channel MOSFETs (Q1 and Q2), which act as switches to control the power delivered to the transformer. The transformer steps up the voltage from 12V to 220V, enabling the inverter to supply power to standard AC loads.
The choice of components is crucial for ensuring the inverter's performance. The resistors and capacitors in the timing circuit determine the frequency of the output waveform, while the MOSFETs must be selected based on their voltage and current ratings to handle the load effectively. The use of an appropriate transformer is also essential to ensure that the inverter can supply sufficient power without overheating or saturating.
In summary, this inverter design is a practical solution for converting low-voltage DC power into high-voltage AC power, suitable for various applications, particularly as a backup power source. Proper attention to component selection and circuit design ensures reliable operation and efficiency.This project is a simple 12V to 220V modified sine-wave inverter using 555 timer IC and CD4017 decade counter. This inverter can deliver 300W continuous power and around 500W max power output (short period). A very good inverter for uninterruptible power supply (UPS). The driver of the inverter is the 555 timer and 4017 decade counter. 555 timer generate pulses at a frequency of four times the desired output frequency. For example, if you want a 60Hz output, the timer frequency must be equal to 240Hz (4*60Hz). For 50Hz output, 200Hz is the output of 555. You can try different combination of R1, R2, and C1 to obtain the desired frequency by using the 555 calculator. The use of LM7809 regulator is to protect the 555 and 4017 from voltage spikes and transients that can influence their operation and stability.
You can use LM7808, LM7806, or 7805 regulator or any regulator IC available at hand. But take note that the regulator output must be 5V and above to make sure that you can drive the Mosfet Q1, and Q2. The diagram below is the comparison of modified and pure sine wave. Both have the same peak value and RMS value. Part List (60Hz, 220V): R1 – 20 kilo-ohms 1/4W R2 – 20 kilo-ohms 1/4W R3 – 1.2 kilo-ohms 1/4W R4, R6 – 560 ohms 1/4W R5, R7 – 5.6 kilo-ohms 1/4W C1 – 100nF capacitor C2 – 10uF electrolytic capacitor rated 16V C3 – 470uF electrolytic capacitor rated 16V C4 – 100nF capacitor Q1, Q2 – IRFZ44N or similar N-channel power Mosfet X’former – 10V-0V-10V to 220V transformer (minimum 500VA if required) LM7809 – IC regulator LM555 – timer IC CD4017b – 5-stage Johnson counter 12V – 12V lead acid battery
🔗 External reference
Part List (60Hz, 220V):
- R1 – 20 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- R2 – 20 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- R3 – 1.2 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- R4, R6 – 560 ohms, 1/4W
- R5, R7 – 5.6 kilo-ohms, 1/4W
- C1 – 100nF capacitor
- C2 – 10uF electrolytic capacitor, rated 16V
- C3 – 470uF electrolytic capacitor, rated 16V
- C4 – 100nF capacitor
- Q1, Q2 – IRFZ44N or similar N-channel power MOSFET
- Transformer – 10V-0V-10V to 220V transformer (minimum 500VA if required)
- LM7809 – IC voltage regulator
- LM555 – timer IC
- CD4017b – 5-stage Johnson counter
- 12V – 12V lead-acid battery
The inverter circuit operates by using the 555 timer in astable mode, which generates a square wave output. This square wave is then processed by the CD4017 decade counter, which divides the frequency to produce a modified sine wave output. The output from the CD4017 is used to drive the gates of the N-channel MOSFETs (Q1 and Q2), which act as switches to control the power delivered to the transformer. The transformer steps up the voltage from 12V to 220V, enabling the inverter to supply power to standard AC loads.
The choice of components is crucial for ensuring the inverter's performance. The resistors and capacitors in the timing circuit determine the frequency of the output waveform, while the MOSFETs must be selected based on their voltage and current ratings to handle the load effectively. The use of an appropriate transformer is also essential to ensure that the inverter can supply sufficient power without overheating or saturating.
In summary, this inverter design is a practical solution for converting low-voltage DC power into high-voltage AC power, suitable for various applications, particularly as a backup power source. Proper attention to component selection and circuit design ensures reliable operation and efficiency.This project is a simple 12V to 220V modified sine-wave inverter using 555 timer IC and CD4017 decade counter. This inverter can deliver 300W continuous power and around 500W max power output (short period). A very good inverter for uninterruptible power supply (UPS). The driver of the inverter is the 555 timer and 4017 decade counter. 555 timer generate pulses at a frequency of four times the desired output frequency. For example, if you want a 60Hz output, the timer frequency must be equal to 240Hz (4*60Hz). For 50Hz output, 200Hz is the output of 555. You can try different combination of R1, R2, and C1 to obtain the desired frequency by using the 555 calculator. The use of LM7809 regulator is to protect the 555 and 4017 from voltage spikes and transients that can influence their operation and stability.
You can use LM7808, LM7806, or 7805 regulator or any regulator IC available at hand. But take note that the regulator output must be 5V and above to make sure that you can drive the Mosfet Q1, and Q2. The diagram below is the comparison of modified and pure sine wave. Both have the same peak value and RMS value. Part List (60Hz, 220V): R1 – 20 kilo-ohms 1/4W R2 – 20 kilo-ohms 1/4W R3 – 1.2 kilo-ohms 1/4W R4, R6 – 560 ohms 1/4W R5, R7 – 5.6 kilo-ohms 1/4W C1 – 100nF capacitor C2 – 10uF electrolytic capacitor rated 16V C3 – 470uF electrolytic capacitor rated 16V C4 – 100nF capacitor Q1, Q2 – IRFZ44N or similar N-channel power Mosfet X’former – 10V-0V-10V to 220V transformer (minimum 500VA if required) LM7809 – IC regulator LM555 – timer IC CD4017b – 5-stage Johnson counter 12V – 12V lead acid battery
🔗 External reference