Fire Alarm Using Thermistor circuit
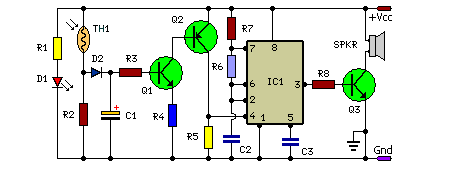
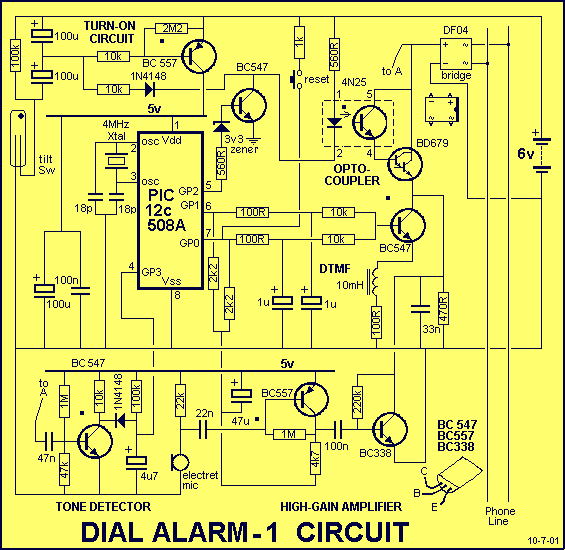
In this fire alarm circuit, a thermistor functions as the heat sensor. As the temperature rises, its resistance diminishes, and conversely, when the temperature falls, its resistance increases. At standard temperature, the resistance of the thermistor (TH1) is approximately kilo-ohms, which decreases to a few ohms when the temperature exceeds 100 °C. The circuit utilizes commonly available components and can be easily assembled on any general-purpose PCB.
The fire alarm circuit operates on the principle of temperature monitoring through the thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature changes. The thermistor is positioned in an environment where it can effectively sense heat, such as near potential fire sources.
When the ambient temperature rises due to a fire, the thermistor's resistance decreases, leading to an increase in current flow through the circuit. This change in current can be detected by a comparator or a microcontroller, which is configured to trigger an alarm when the current exceeds a certain threshold.
The circuit may include additional components such as a power supply, typically a 5V or 12V source, a comparator IC like the LM393, and a buzzer or alarm indicator. The thermistor is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor, allowing for a measurable voltage change that corresponds to the resistance change in the thermistor.
To ensure reliability, the circuit can be designed with hysteresis to prevent false alarms due to minor temperature fluctuations. This is achieved by incorporating feedback from the output of the comparator back to the input, creating a stable threshold for activation.
Overall, this fire alarm circuit is designed for ease of construction and reliability, making it suitable for various applications in fire detection systems. It is essential to follow safety standards and guidelines during assembly and installation to ensure effective operation in real-world scenarios.In this fire alarm circuit, a Thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases, its resistance decreases, and vice versa. At normal temperature, the resistance of the Thermistor (TH1) is approximately kilo-ohms, which reduces to a few ohms as the temperature increases beyond 100 C. The circuit uses readily available components and can be easily constructed on any general-purpose PCB..
🔗 External reference
The fire alarm circuit operates on the principle of temperature monitoring through the thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature changes. The thermistor is positioned in an environment where it can effectively sense heat, such as near potential fire sources.
When the ambient temperature rises due to a fire, the thermistor's resistance decreases, leading to an increase in current flow through the circuit. This change in current can be detected by a comparator or a microcontroller, which is configured to trigger an alarm when the current exceeds a certain threshold.
The circuit may include additional components such as a power supply, typically a 5V or 12V source, a comparator IC like the LM393, and a buzzer or alarm indicator. The thermistor is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor, allowing for a measurable voltage change that corresponds to the resistance change in the thermistor.
To ensure reliability, the circuit can be designed with hysteresis to prevent false alarms due to minor temperature fluctuations. This is achieved by incorporating feedback from the output of the comparator back to the input, creating a stable threshold for activation.
Overall, this fire alarm circuit is designed for ease of construction and reliability, making it suitable for various applications in fire detection systems. It is essential to follow safety standards and guidelines during assembly and installation to ensure effective operation in real-world scenarios.In this fire alarm circuit, a Thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases, its resistance decreases, and vice versa. At normal temperature, the resistance of the Thermistor (TH1) is approximately kilo-ohms, which reduces to a few ohms as the temperature increases beyond 100 C. The circuit uses readily available components and can be easily constructed on any general-purpose PCB..
🔗 External reference