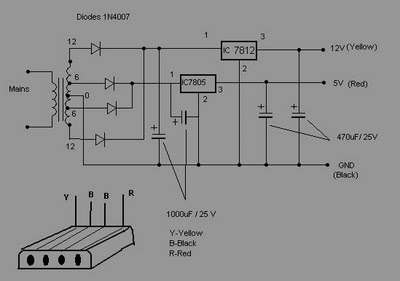
Free Running Oscillator Circuit

This circuit is an oscillator utilizing astable mode operation, based on the 555 timer integrated circuit (IC). It functions as a free-running oscillator. The operation begins when the capacitor (C) charges towards 2/3 of the supply voltage (V+) through resistors Ra and Rb. Once the voltage across capacitor C reaches this threshold level, the discharge output at pin 7 activates, causing capacitor C to discharge. The use of a CMOS 555 timer IC allows for a wide frequency range while minimizing voltage spikes and power dissipation. The selection of resistor values Ra and Rb is constrained by the input leakage specifications at pins 7, 2, and 6.
The described circuit operates in astable mode, which means it continuously oscillates between high and low states without requiring any external triggering. The 555 timer IC is a versatile component that can be configured in various modes, with astable operation being one of the most common applications. In this configuration, the timer generates a square wave output, which can be utilized for various applications such as clock pulses, tone generation, or LED flashing.
In the circuit, the timing interval is determined by the values of resistors Ra and Rb, as well as the capacitance of capacitor C. The frequency of oscillation (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(Ra + 2Rb)C} \]
This equation shows that the frequency is inversely proportional to the total resistance and the capacitance. Therefore, selecting appropriate values for Ra, Rb, and C is crucial for achieving the desired frequency of oscillation.
The 555 timer operates by charging and discharging the capacitor through the resistors. Initially, when the circuit is powered, capacitor C begins charging through Ra and Rb. As the voltage across C reaches 2/3 V+, the 555 timer's internal comparator triggers the discharge pin (pin 7), which connects C to ground, allowing it to discharge rapidly. The capacitor's discharge causes the output (pin 3) to go low, and the cycle repeats as the capacitor charges again.
Utilizing a CMOS version of the 555 timer can enhance the circuit's performance by providing lower power consumption, reduced voltage spikes, and higher frequency capabilities. This makes it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power efficiency is paramount.
In summary, this astable oscillator circuit using a 555 timer IC is a simple yet effective design for generating continuous square wave signals. Proper selection of component values is essential for achieving the desired oscillation frequency while ensuring reliable operation within the specified limits of the 555 timer IC.This is a circuit for oscillator using astable mode operation. The basic oscillatior is using 555 timer IC. This circuit is also give mode free running oscillator. This is the figure of the circuit. Operation of the circuit is begin, when initialy by capacitor C charged towards 2/3 V+ with Ra and Rb. When voltage on C reaches that threshold level, the discharge output in pin 7 is turning on to discharging C. Using CMOS 555 timer IC is a very wide frequency at very low of voltage spikes and dissipation can be achieved. Selections of values the Ra and Rb is limited by input leakage specification at time in pin 7, 2, and 6.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates in astable mode, which means it continuously oscillates between high and low states without requiring any external triggering. The 555 timer IC is a versatile component that can be configured in various modes, with astable operation being one of the most common applications. In this configuration, the timer generates a square wave output, which can be utilized for various applications such as clock pulses, tone generation, or LED flashing.
In the circuit, the timing interval is determined by the values of resistors Ra and Rb, as well as the capacitance of capacitor C. The frequency of oscillation (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(Ra + 2Rb)C} \]
This equation shows that the frequency is inversely proportional to the total resistance and the capacitance. Therefore, selecting appropriate values for Ra, Rb, and C is crucial for achieving the desired frequency of oscillation.
The 555 timer operates by charging and discharging the capacitor through the resistors. Initially, when the circuit is powered, capacitor C begins charging through Ra and Rb. As the voltage across C reaches 2/3 V+, the 555 timer's internal comparator triggers the discharge pin (pin 7), which connects C to ground, allowing it to discharge rapidly. The capacitor's discharge causes the output (pin 3) to go low, and the cycle repeats as the capacitor charges again.
Utilizing a CMOS version of the 555 timer can enhance the circuit's performance by providing lower power consumption, reduced voltage spikes, and higher frequency capabilities. This makes it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power efficiency is paramount.
In summary, this astable oscillator circuit using a 555 timer IC is a simple yet effective design for generating continuous square wave signals. Proper selection of component values is essential for achieving the desired oscillation frequency while ensuring reliable operation within the specified limits of the 555 timer IC.This is a circuit for oscillator using astable mode operation. The basic oscillatior is using 555 timer IC. This circuit is also give mode free running oscillator. This is the figure of the circuit. Operation of the circuit is begin, when initialy by capacitor C charged towards 2/3 V+ with Ra and Rb. When voltage on C reaches that threshold level, the discharge output in pin 7 is turning on to discharging C. Using CMOS 555 timer IC is a very wide frequency at very low of voltage spikes and dissipation can be achieved. Selections of values the Ra and Rb is limited by input leakage specification at time in pin 7, 2, and 6.
🔗 External reference