Fully Adjustable Power Supply
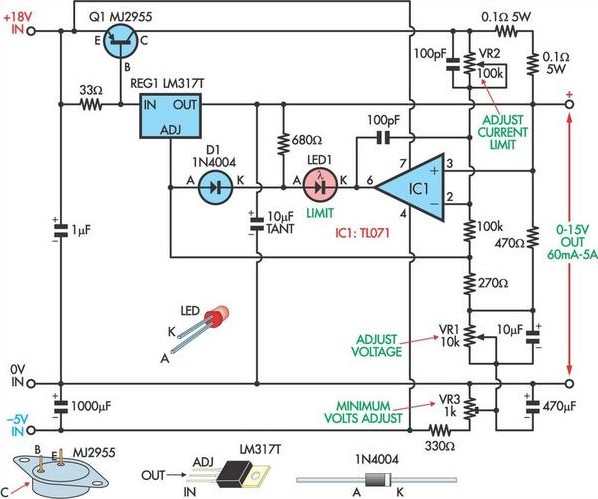
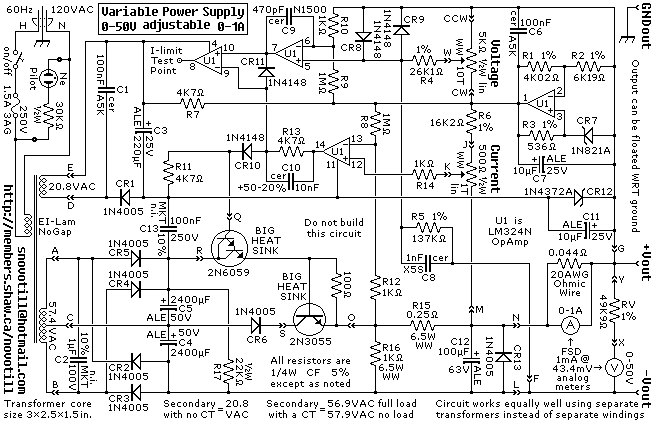
This circuit, based on a National Semiconductor application note, utilizes an LM317 3-terminal regulator (REG1) due to its integrated over-current and over-temperature protection features. The output current is amplified to slightly over 5A using the MJ2955 transistor (Q1). The output voltage is adjustable by varying the voltage at the ADJ terminal of REG1 with a 10 kΩ potentiometer (VR1) connected through a 270Ω resistor. Current limiting is implemented using op amp IC1 as a comparator, which monitors the voltage across two 0.1Ω current sensing resistors. When this voltage exceeds a threshold set by potentiometer VR2, the output of IC1 goes low, reducing the voltage at the adjust pin of REG1 and consequently lowering the output voltage. An LED (LED1) indicates when current limiting is in effect. The 10 kΩ voltage adjust potentiometer (VR1) is connected to -5V instead of 0V, allowing the output voltage to be adjusted down to 0V rather than the standard 1.2V minimum of an LM317. Trimpot VR3 is used to set the minimum output voltage to approximately +100mV. It is important to note that the -5V rail should be regulated using an LM7905 or similar device. The LM317 regulator and Q1 must be mounted on the same heatsink to optimize the thermal management of REG1.
This circuit design effectively combines the functionality of an adjustable voltage regulator with current limiting capabilities, making it suitable for applications requiring precise voltage control and protection against overcurrent conditions. The LM317 serves as the primary voltage regulation component, while the MJ2955 transistor provides the necessary current amplification to exceed typical output limits. The use of a potentiometer for voltage adjustment allows for user-friendly customization of the output voltage, while the current sensing resistors ensure that the circuit can respond dynamically to load changes.
The inclusion of an op-amp comparator for current limiting enhances the reliability of the circuit, protecting both the regulator and the load from excessive current conditions. The design choice of employing a -5V reference voltage allows for a wider range of output voltage adjustment, which is particularly beneficial in applications where lower voltage levels are required. The LED indicator serves as a visual cue for the user, signaling when the circuit is operating in a current limiting mode.
Proper thermal management is critical in this design, necessitating the mounting of the LM317 and MJ2955 on a shared heatsink. This ensures that both components can effectively dissipate heat, maintaining operational stability and preventing thermal shutdown. Overall, this circuit provides a robust solution for adjustable power supply applications, balancing performance with safety features.Based on a National Semiconductor application note, this circuit uses an LM317 3-terminal regulator (REG1), chosen because of its built-in over-current and over-temperature protection. Its output is boosted up to just over 5A by the MJ2955 transistor (Q1). The output voltage is varied by adjusting the voltage on REG1`s ADJ terminal using VR1 (a 10 kO potentiometer), via the 270O resistor. Adjustable current limiting is provided by op amp IC1, used as a comparator, which monitors the voltage across the 0. 1O current sensing resistors. Once this voltage exceeds a level set by potentiometer VR2, then its output goes low, dragging down the adjust pin of REG1 and thus the output voltage.
LED1 illuminates when current limiting is occurring. The 10kO voltage adjust potentiometer (VR1) has one side connected to -5V instead of 0V so that the output voltage can be varied down to 0V instead of 1. 2V (normal limit of an LM317). Trimpot VR3 is adjusted to set the minimum output voltage to +100mV or so. Note that because the -5V rail is used as a reference, it should be regulated using an LM7905 or similar.
The LM317 3-terminal regulator and Q1 should be mounted on the same heatsink to take advantage of REG1`s thermal control. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design effectively combines the functionality of an adjustable voltage regulator with current limiting capabilities, making it suitable for applications requiring precise voltage control and protection against overcurrent conditions. The LM317 serves as the primary voltage regulation component, while the MJ2955 transistor provides the necessary current amplification to exceed typical output limits. The use of a potentiometer for voltage adjustment allows for user-friendly customization of the output voltage, while the current sensing resistors ensure that the circuit can respond dynamically to load changes.
The inclusion of an op-amp comparator for current limiting enhances the reliability of the circuit, protecting both the regulator and the load from excessive current conditions. The design choice of employing a -5V reference voltage allows for a wider range of output voltage adjustment, which is particularly beneficial in applications where lower voltage levels are required. The LED indicator serves as a visual cue for the user, signaling when the circuit is operating in a current limiting mode.
Proper thermal management is critical in this design, necessitating the mounting of the LM317 and MJ2955 on a shared heatsink. This ensures that both components can effectively dissipate heat, maintaining operational stability and preventing thermal shutdown. Overall, this circuit provides a robust solution for adjustable power supply applications, balancing performance with safety features.Based on a National Semiconductor application note, this circuit uses an LM317 3-terminal regulator (REG1), chosen because of its built-in over-current and over-temperature protection. Its output is boosted up to just over 5A by the MJ2955 transistor (Q1). The output voltage is varied by adjusting the voltage on REG1`s ADJ terminal using VR1 (a 10 kO potentiometer), via the 270O resistor. Adjustable current limiting is provided by op amp IC1, used as a comparator, which monitors the voltage across the 0. 1O current sensing resistors. Once this voltage exceeds a level set by potentiometer VR2, then its output goes low, dragging down the adjust pin of REG1 and thus the output voltage.
LED1 illuminates when current limiting is occurring. The 10kO voltage adjust potentiometer (VR1) has one side connected to -5V instead of 0V so that the output voltage can be varied down to 0V instead of 1. 2V (normal limit of an LM317). Trimpot VR3 is adjusted to set the minimum output voltage to +100mV or so. Note that because the -5V rail is used as a reference, it should be regulated using an LM7905 or similar.
The LM317 3-terminal regulator and Q1 should be mounted on the same heatsink to take advantage of REG1`s thermal control. 🔗 External reference