Function Generator Circuit
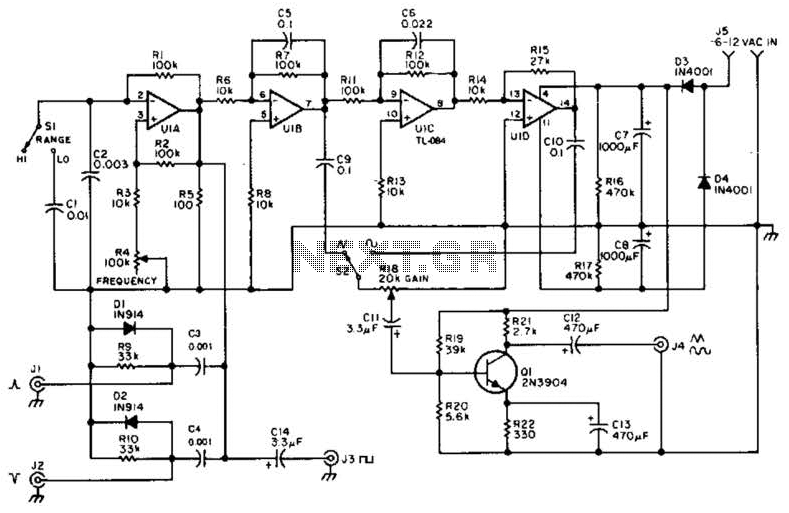
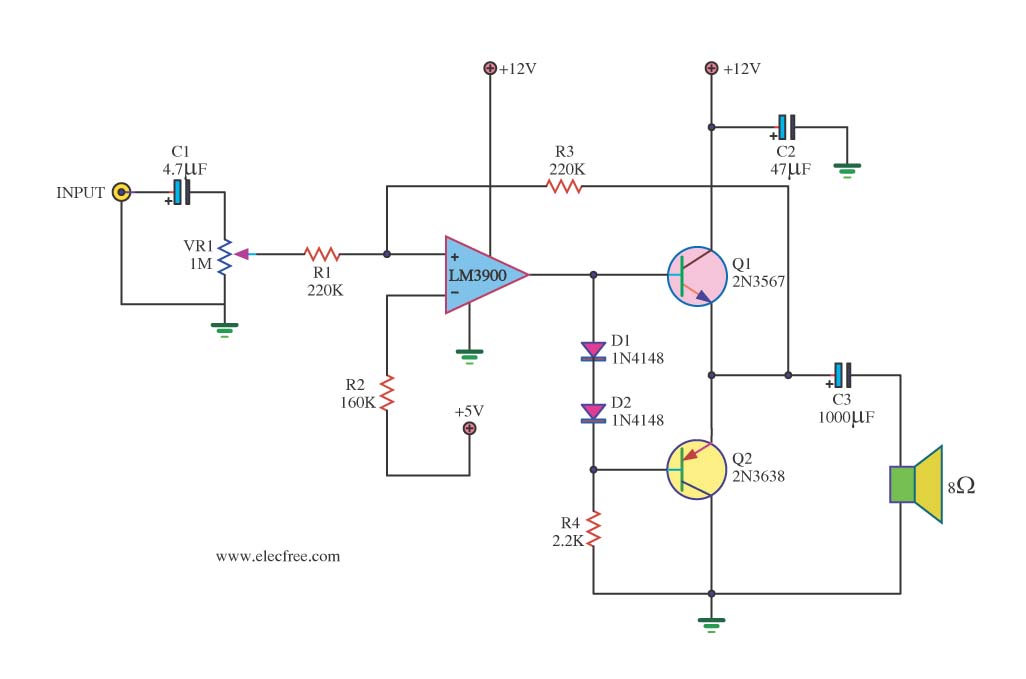
A quad op-amp serves as the core component of this function generator. U1A produces a square wave, which is outputted to J8. J1 and J2 are pulse outputs derived from differentiating the square wave. The integrator U1B creates a triangle wave, which is then shaped to produce a sine wave. Additionally, Q1 functions as an output amplifier.
The function generator circuit utilizes a quad operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration, which is essential for generating various waveform outputs. The op-amp U1A is configured to produce a square wave signal. This square wave is then directed to output terminal J8, where it can be utilized for further processing or testing.
To obtain pulse outputs, the circuit differentiates the square wave signal. This differentiation is achieved through additional circuitry connected to the outputs J1 and J2. These outputs provide sharp pulse signals that can be employed in various applications, such as timing circuits or digital signal processing.
The op-amp U1B is configured as an integrator, which takes the square wave input and generates a triangle wave output. This triangle wave is crucial for the subsequent shaping process that transforms it into a sine wave. The sine wave output is often required in applications such as audio signal generation or analog modulation.
The output stage of the circuit includes Q1, which acts as an output amplifier. This component is responsible for boosting the signal strength of the generated waveforms, ensuring they can drive loads effectively without significant signal degradation. The overall design emphasizes versatility and precision, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications. A quad op amp makes up the heart of this function generator. Ul-a generates a square wave, and outputs this to J8. J1 and J2 are pulse outputs obtained by differentiating the square wave. Integrator Ul-b generates a triangle-wave shaper to obtain a sine wave. Ql is an output- amplifier. 🔗 External reference
The function generator circuit utilizes a quad operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration, which is essential for generating various waveform outputs. The op-amp U1A is configured to produce a square wave signal. This square wave is then directed to output terminal J8, where it can be utilized for further processing or testing.
To obtain pulse outputs, the circuit differentiates the square wave signal. This differentiation is achieved through additional circuitry connected to the outputs J1 and J2. These outputs provide sharp pulse signals that can be employed in various applications, such as timing circuits or digital signal processing.
The op-amp U1B is configured as an integrator, which takes the square wave input and generates a triangle wave output. This triangle wave is crucial for the subsequent shaping process that transforms it into a sine wave. The sine wave output is often required in applications such as audio signal generation or analog modulation.
The output stage of the circuit includes Q1, which acts as an output amplifier. This component is responsible for boosting the signal strength of the generated waveforms, ensuring they can drive loads effectively without significant signal degradation. The overall design emphasizes versatility and precision, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications. A quad op amp makes up the heart of this function generator. Ul-a generates a square wave, and outputs this to J8. J1 and J2 are pulse outputs obtained by differentiating the square wave. Integrator Ul-b generates a triangle-wave shaper to obtain a sine wave. Ql is an output- amplifier. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713