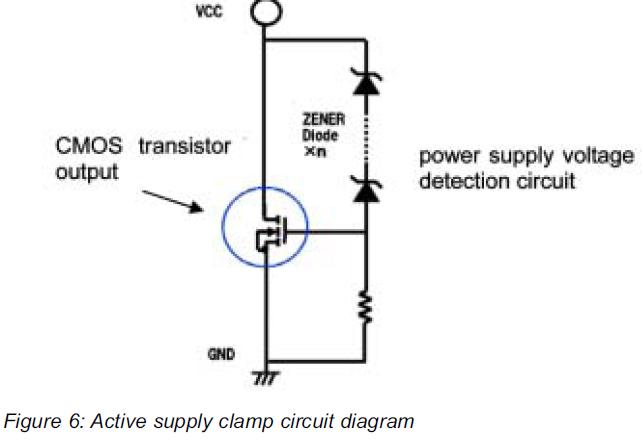
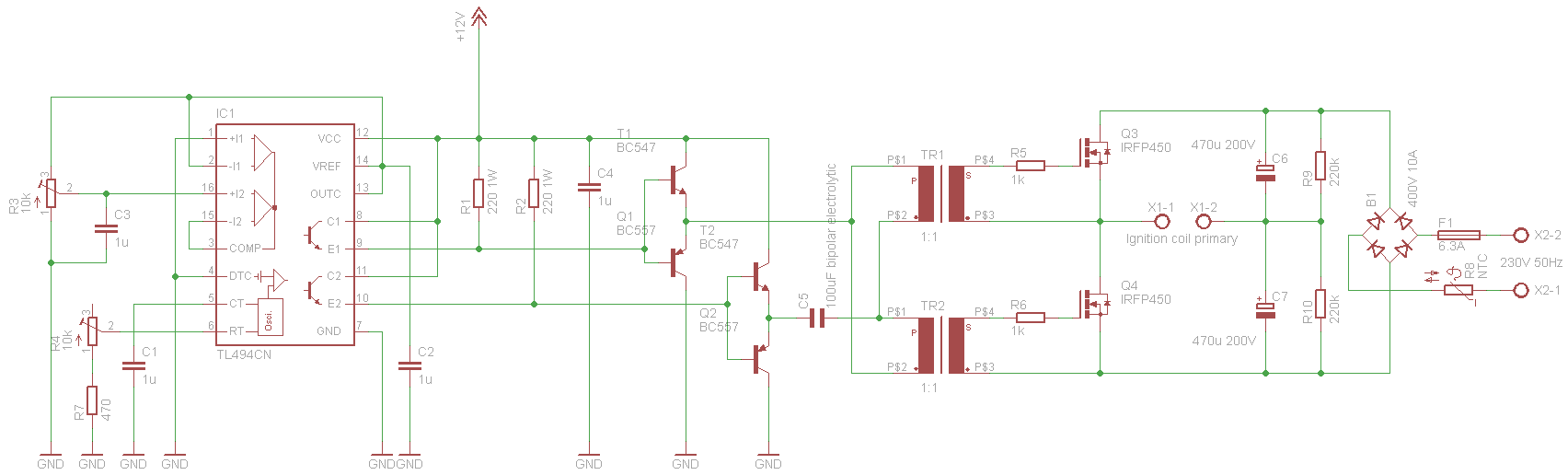
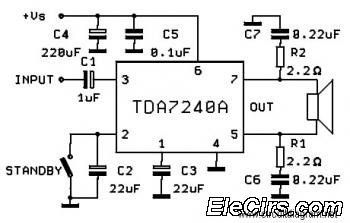
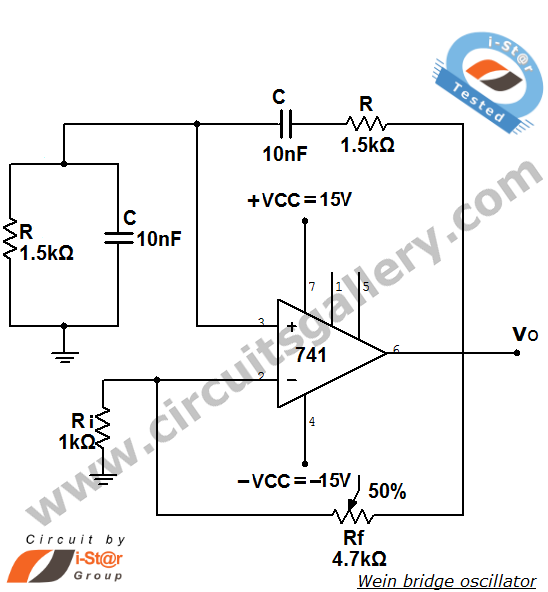
h bridge
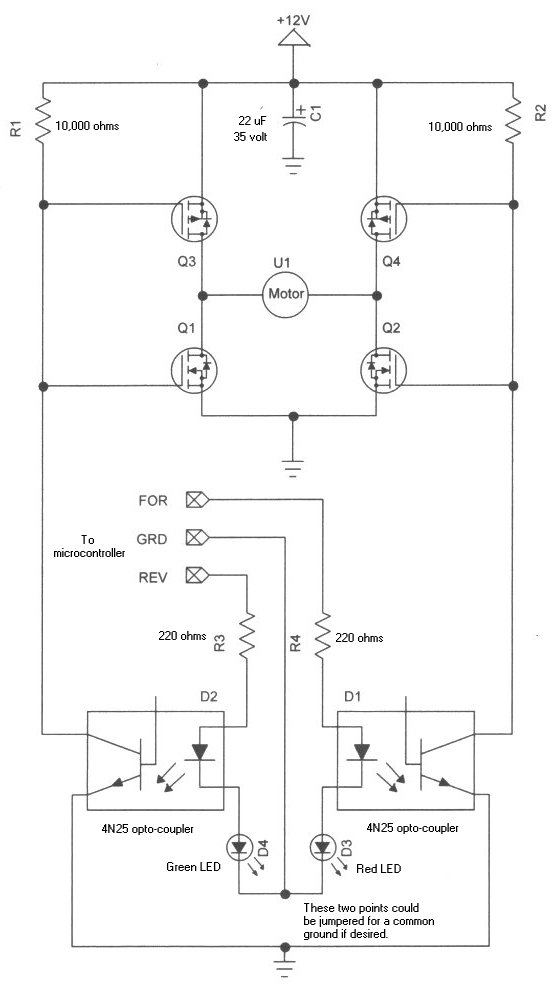
Learning how to use power MOSFETs by building an H-bridge motor control.
The H-bridge motor control circuit is an essential configuration for driving DC motors in both forward and reverse directions. It utilizes four power MOSFETs arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for bidirectional control of the motor.
In this setup, two pairs of MOSFETs are used: one pair for controlling the current flow in one direction and the other pair for the opposite direction. The gates of the MOSFETs are driven by a microcontroller or a PWM signal, enabling precise control over the motor speed and direction.
The operation of the H-bridge can be summarized as follows: when the upper left and lower right MOSFETs are turned on, the current flows through the motor in one direction, causing it to rotate clockwise. Conversely, when the upper right and lower left MOSFETs are activated, the current reverses, and the motor rotates counterclockwise.
To prevent short circuits and ensure safe operation, it is crucial to implement dead time between switching the MOSFETs. This dead time allows one MOSFET to turn off completely before the opposite pair is activated. Additionally, flyback diodes are often included in the circuit to protect the MOSFETs from back EMF generated when the motor is de-energized.
The selection of appropriate MOSFETs is vital, as they must handle the motor's current and voltage ratings. Proper heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks or active cooling, should also be considered to maintain the reliability of the circuit during operation.
Overall, the H-bridge motor control circuit not only provides a practical application for power MOSFETs but also serves as a foundational learning tool for understanding motor control techniques in electronic design.Learning how to use power MOSFETs by building an H-bridge motor control.. 🔗 External reference
The H-bridge motor control circuit is an essential configuration for driving DC motors in both forward and reverse directions. It utilizes four power MOSFETs arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for bidirectional control of the motor.
In this setup, two pairs of MOSFETs are used: one pair for controlling the current flow in one direction and the other pair for the opposite direction. The gates of the MOSFETs are driven by a microcontroller or a PWM signal, enabling precise control over the motor speed and direction.
The operation of the H-bridge can be summarized as follows: when the upper left and lower right MOSFETs are turned on, the current flows through the motor in one direction, causing it to rotate clockwise. Conversely, when the upper right and lower left MOSFETs are activated, the current reverses, and the motor rotates counterclockwise.
To prevent short circuits and ensure safe operation, it is crucial to implement dead time between switching the MOSFETs. This dead time allows one MOSFET to turn off completely before the opposite pair is activated. Additionally, flyback diodes are often included in the circuit to protect the MOSFETs from back EMF generated when the motor is de-energized.
The selection of appropriate MOSFETs is vital, as they must handle the motor's current and voltage ratings. Proper heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks or active cooling, should also be considered to maintain the reliability of the circuit during operation.
Overall, the H-bridge motor control circuit not only provides a practical application for power MOSFETs but also serves as a foundational learning tool for understanding motor control techniques in electronic design.Learning how to use power MOSFETs by building an H-bridge motor control.. 🔗 External reference