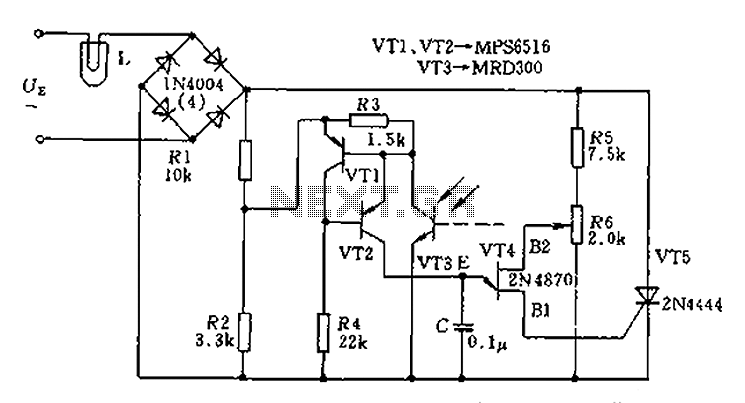
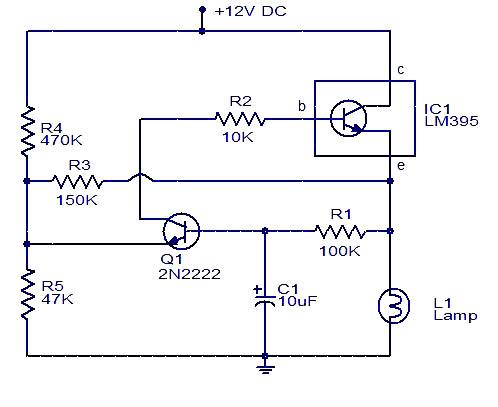
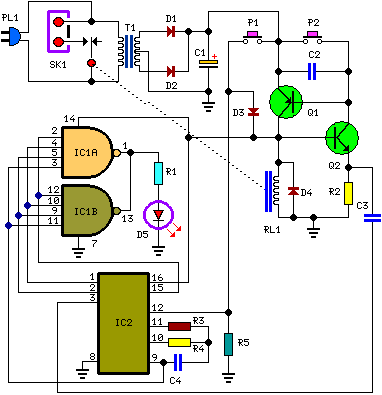
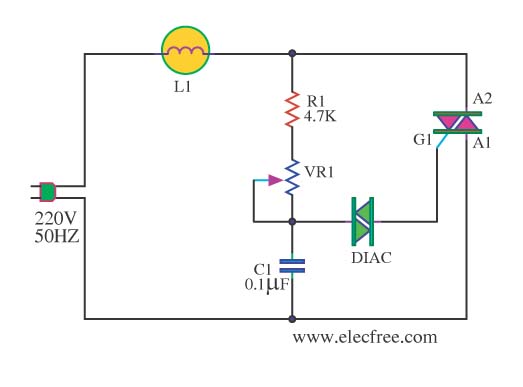
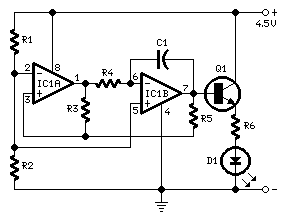
Halogen Lamp Dimmer With Soft Start

Most dimmers utilize pulse width modulation (PWM) to regulate the amount of power supplied to the lamp. Those that are packaged with a switch faceplate...
Dimmers that employ pulse width modulation (PWM) function by rapidly turning the power supplied to the lamp on and off at a frequency that is imperceptible to the human eye. The ratio of the on-time to the off-time, known as the duty cycle, determines the average power delivered to the lamp, thus controlling its brightness. A higher duty cycle results in a brighter light, while a lower duty cycle dims the light.
In a typical PWM dimmer circuit, a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM controller generates the switching signal. This signal is then used to drive a power transistor or MOSFET, which acts as a switch for the load (the lamp). The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for filtering and protection diodes to prevent back EMF from inductive loads.
Furthermore, dimmers that come with a switch faceplate often incorporate user-friendly features, such as tactile feedback or visual indicators, to enhance the user experience. These faceplates may also house additional circuitry to facilitate features like remote control operation or integration with smart home systems, allowing for more advanced control over lighting environments.
In summary, PWM dimmers represent an efficient means of controlling light intensity, providing flexibility and energy savings while maintaining a simple user interface. The implementation of such dimming technology can vary, but the fundamental principles of PWM remain consistent across different designs.Most dimmers use pulse width modulation (PWM) to control the amount of power that is delivered to the lamp. Those that come bundled with a switch faceplat.. 🔗 External reference
Dimmers that employ pulse width modulation (PWM) function by rapidly turning the power supplied to the lamp on and off at a frequency that is imperceptible to the human eye. The ratio of the on-time to the off-time, known as the duty cycle, determines the average power delivered to the lamp, thus controlling its brightness. A higher duty cycle results in a brighter light, while a lower duty cycle dims the light.
In a typical PWM dimmer circuit, a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM controller generates the switching signal. This signal is then used to drive a power transistor or MOSFET, which acts as a switch for the load (the lamp). The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for filtering and protection diodes to prevent back EMF from inductive loads.
Furthermore, dimmers that come with a switch faceplate often incorporate user-friendly features, such as tactile feedback or visual indicators, to enhance the user experience. These faceplates may also house additional circuitry to facilitate features like remote control operation or integration with smart home systems, allowing for more advanced control over lighting environments.
In summary, PWM dimmers represent an efficient means of controlling light intensity, providing flexibility and energy savings while maintaining a simple user interface. The implementation of such dimming technology can vary, but the fundamental principles of PWM remain consistent across different designs.Most dimmers use pulse width modulation (PWM) to control the amount of power that is delivered to the lamp. Those that come bundled with a switch faceplat.. 🔗 External reference