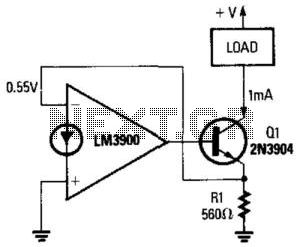
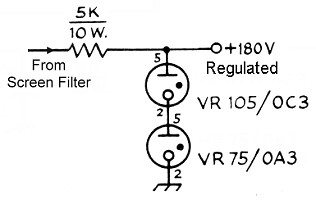
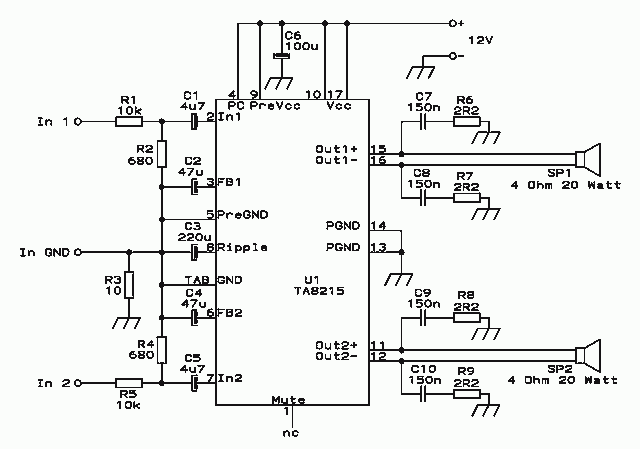
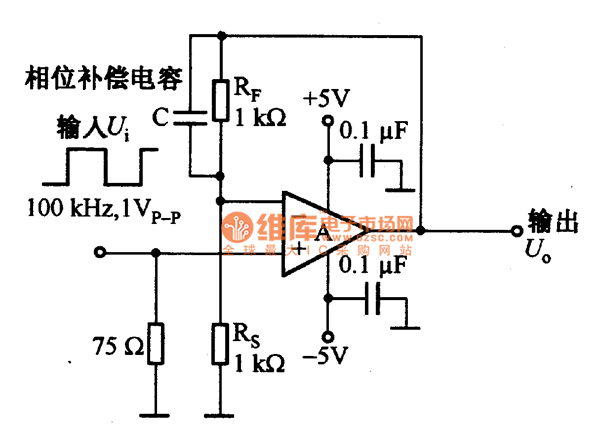
Heavy-duty power supply regulates either voltage current or power
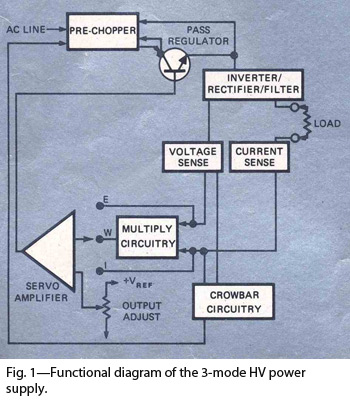
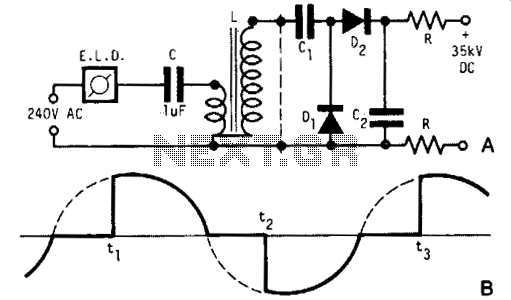
By combining switching and series-pass techniques, the designer of this high-voltage supply achieved 0.01% regulation at power levels up to 100W.
The high-voltage power supply employs a hybrid approach that integrates both switching and series-pass regulation methods to achieve exceptional performance. The switching technique is utilized for its efficiency, allowing for high power conversion with minimal heat generation. This is particularly advantageous in high-voltage applications where thermal management is critical.
The series-pass element serves to fine-tune the output voltage, providing precise regulation. This combination allows the supply to maintain an output voltage within 0.01% of the desired level, even under varying load conditions. The design is capable of delivering up to 100 watts of power, making it suitable for demanding applications that require stable and reliable high-voltage sources.
In practical terms, the circuit likely includes a high-frequency switching regulator that steps down the input voltage to a manageable level, followed by a linear regulator that ensures tight voltage regulation. Components such as high-voltage MOSFETs or BJTs may be employed in the series-pass section to handle the power levels effectively. Additionally, feedback mechanisms are crucial for monitoring the output voltage and adjusting the control signals to maintain regulation.
The design may also incorporate protection features such as over-voltage and over-current protection to safeguard both the power supply and the connected load. Proper filtering and decoupling capacitors are essential to minimize ripple and noise, ensuring a clean output voltage.
Overall, this high-voltage supply design represents a sophisticated balance between efficiency and precision, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as telecommunications, medical equipment, and industrial automation.By combining switching and series-pass techniques, this high-voltage supply`s designer achieved 0.01% regulation at power levels to 100W.. 🔗 External reference
The high-voltage power supply employs a hybrid approach that integrates both switching and series-pass regulation methods to achieve exceptional performance. The switching technique is utilized for its efficiency, allowing for high power conversion with minimal heat generation. This is particularly advantageous in high-voltage applications where thermal management is critical.
The series-pass element serves to fine-tune the output voltage, providing precise regulation. This combination allows the supply to maintain an output voltage within 0.01% of the desired level, even under varying load conditions. The design is capable of delivering up to 100 watts of power, making it suitable for demanding applications that require stable and reliable high-voltage sources.
In practical terms, the circuit likely includes a high-frequency switching regulator that steps down the input voltage to a manageable level, followed by a linear regulator that ensures tight voltage regulation. Components such as high-voltage MOSFETs or BJTs may be employed in the series-pass section to handle the power levels effectively. Additionally, feedback mechanisms are crucial for monitoring the output voltage and adjusting the control signals to maintain regulation.
The design may also incorporate protection features such as over-voltage and over-current protection to safeguard both the power supply and the connected load. Proper filtering and decoupling capacitors are essential to minimize ripple and noise, ensuring a clean output voltage.
Overall, this high-voltage supply design represents a sophisticated balance between efficiency and precision, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as telecommunications, medical equipment, and industrial automation.By combining switching and series-pass techniques, this high-voltage supply`s designer achieved 0.01% regulation at power levels to 100W.. 🔗 External reference