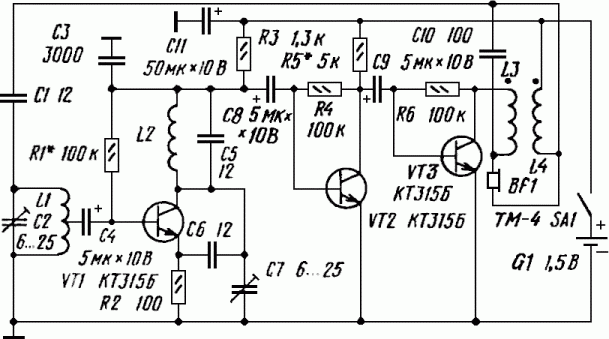
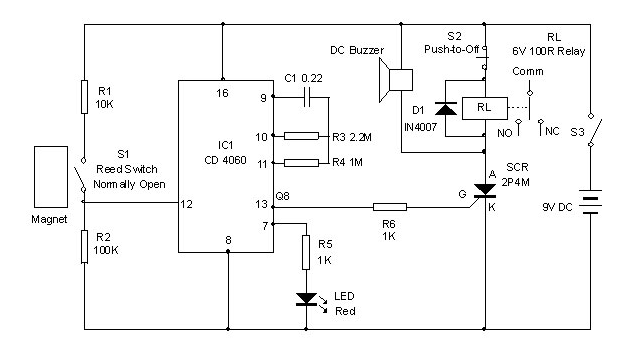
Simple high-volt supply
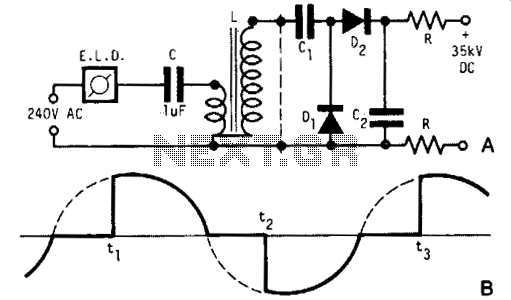
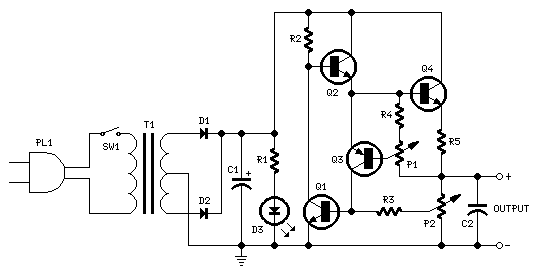
A light dimmer, a 1 µF capacitor, and a 12 V car ignition coil form a simple line-powered high-voltage generator. The current in the dimmer is illustrated in Fig. B. During the time intervals tp to t2, determined by the dimmer switch, the internal triac of the dimmer activates, allowing a very high and rapid current pulse to charge the capacitor through the primary winding of the induction coil. Consequently, at a frequency of 120 times per second for a 60 Hz line, a very high voltage pulse is generated at the secondary of the coil. To achieve a high-voltage direct current (HV DC) output, a voltage doubler circuit is employed. Diodes D1 and D2 are selenium rectifiers (TV 18 Siemens or ITT) utilized for powering television sets. High-value output shock protection resistors, labeled R, are recommended for safety.
The circuit operates by utilizing the properties of a light dimmer, which effectively modulates the amount of power delivered to the load. The dimmer's internal triac acts as a switch that controls the timing of current flow to the capacitor and subsequently to the ignition coil. When the triac is triggered, it allows a pulse of current to flow through the primary winding of the ignition coil, inducing a magnetic field. The rapid change in current creates a high-voltage pulse in the secondary winding due to the principles of electromagnetic induction.
The capacitor, rated at 1 µF, serves as a charge storage element, accumulating energy during the brief periods when the triac is conducting. This energy is then released as a high-voltage pulse at the secondary of the coil. The frequency of operation, which is linked to the AC line frequency, contributes to the generation of high-voltage pulses at a rate consistent with the line frequency.
To convert the high-voltage alternating current (AC) output from the ignition coil into a usable high-voltage direct current (DC), a voltage doubler circuit is implemented. This circuit typically consists of two diodes (D1 and D2) and two capacitors. The selenium rectifiers are chosen for their reliability and efficiency in rectifying the high-voltage output, which is essential for applications such as powering television sets.
In addition to the rectification process, the inclusion of high-value output shock protection resistors is critical for safeguarding against potential high-voltage shocks. These resistors limit the current that can flow through the circuit during fault conditions, enhancing the overall safety of the high-voltage generator setup. Proper selection of resistor values and ratings is essential to ensure effective protection while maintaining the desired performance of the high-voltage output.A light dimmer, a 1 µf capacitor and a 12 V car ignition coil form the simple line powered HV generator. The current in the dimmer is shown in Fig. B. At times tp t2, set by the dimmer switch, the inner triac of the dimmer switches on, and a very high and very fast current pulse charges the capacitor through the primary of the induction coil.
Then at a rate of 120 times per second for a 60 Hz line, a very high voltage pulse appears at the secondary of the coil. To obtain an HV dc output, use a voltage doubler. Dl and D2 are selenium rectifiers (TV 18 Siemens or ITT) used for the supply of television sets. High value output shock protection resistors, R, are recommended when suitable. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the properties of a light dimmer, which effectively modulates the amount of power delivered to the load. The dimmer's internal triac acts as a switch that controls the timing of current flow to the capacitor and subsequently to the ignition coil. When the triac is triggered, it allows a pulse of current to flow through the primary winding of the ignition coil, inducing a magnetic field. The rapid change in current creates a high-voltage pulse in the secondary winding due to the principles of electromagnetic induction.
The capacitor, rated at 1 µF, serves as a charge storage element, accumulating energy during the brief periods when the triac is conducting. This energy is then released as a high-voltage pulse at the secondary of the coil. The frequency of operation, which is linked to the AC line frequency, contributes to the generation of high-voltage pulses at a rate consistent with the line frequency.
To convert the high-voltage alternating current (AC) output from the ignition coil into a usable high-voltage direct current (DC), a voltage doubler circuit is implemented. This circuit typically consists of two diodes (D1 and D2) and two capacitors. The selenium rectifiers are chosen for their reliability and efficiency in rectifying the high-voltage output, which is essential for applications such as powering television sets.
In addition to the rectification process, the inclusion of high-value output shock protection resistors is critical for safeguarding against potential high-voltage shocks. These resistors limit the current that can flow through the circuit during fault conditions, enhancing the overall safety of the high-voltage generator setup. Proper selection of resistor values and ratings is essential to ensure effective protection while maintaining the desired performance of the high-voltage output.A light dimmer, a 1 µf capacitor and a 12 V car ignition coil form the simple line powered HV generator. The current in the dimmer is shown in Fig. B. At times tp t2, set by the dimmer switch, the inner triac of the dimmer switches on, and a very high and very fast current pulse charges the capacitor through the primary of the induction coil.
Then at a rate of 120 times per second for a 60 Hz line, a very high voltage pulse appears at the secondary of the coil. To obtain an HV dc output, use a voltage doubler. Dl and D2 are selenium rectifiers (TV 18 Siemens or ITT) used for the supply of television sets. High value output shock protection resistors, R, are recommended when suitable. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713