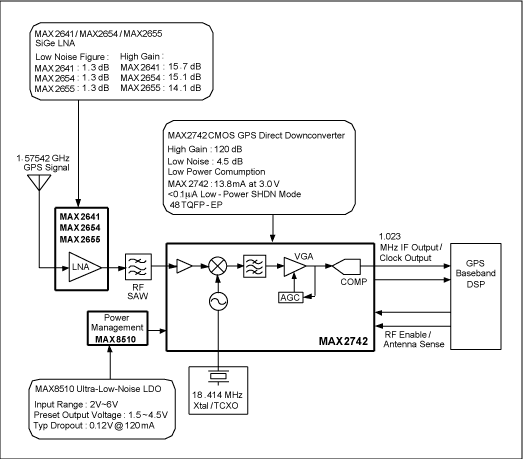
High operating voltage regulator circuit diagram
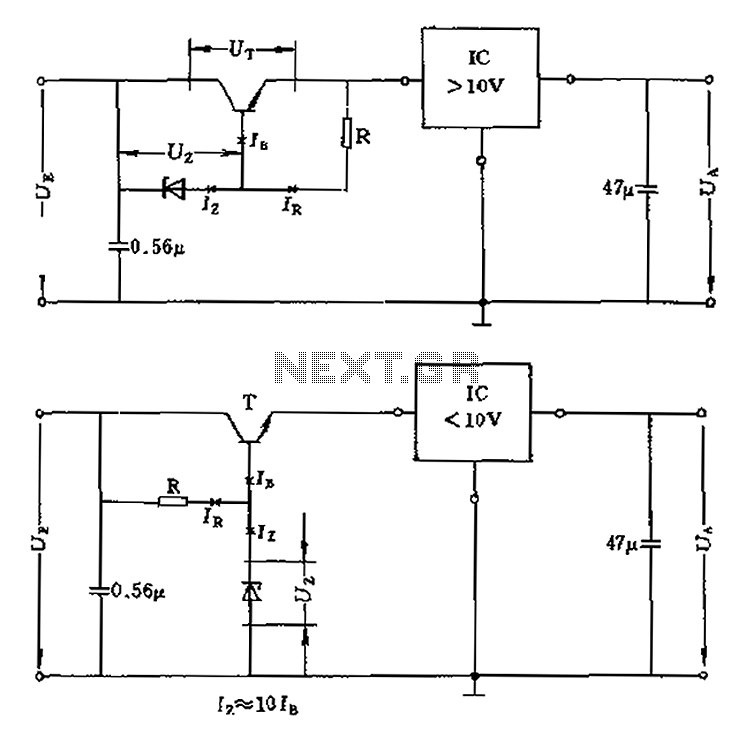
The voltage equation Ue = Ut + Ur + Ua indicates that the transistor voltage Ut will determine the maximum output voltage Ua. Additionally, Ur must be 2V. The voltage regulator's voltage value depends on the selection of Uz. In the circuit, a resistor R is chosen to meet the boundary conditions defined by the formula Ir = Iz + Ib, or the principle Ir = F10 Ibs. This integrated circuit is designed to operate at a higher voltage while functioning at a lower voltage, such as Ue = 5V. In this case, the circuit should utilize a Zener voltage that exceeds the output voltage by at least 4V (Ua). The selection of resistor R is crucial in this circuit.
The voltage regulation circuit operates based on the principles of transistor behavior and Zener diode regulation. The equation Ue = Ut + Ur + Ua outlines the relationship between the input voltage (Ue), the transistor voltage drop (Ut), the reference voltage (Ur), and the output voltage (Ua). The maximum output voltage (Ua) is influenced by the transistor voltage (Ut), which is a critical parameter for ensuring the circuit's efficiency.
In the design of this voltage regulator, the Zener diode plays a pivotal role. The Zener voltage (Uz) must be selected to be at least 4V higher than the desired output voltage (Ua) to ensure stable operation. This margin allows for variations in load and input voltage while maintaining a constant output. The resistor R is selected based on the current requirements, which must satisfy the boundary conditions of the circuit. The relationship Ir = Iz + Ib indicates that the current flowing through the resistor R (Ir) must equal the sum of the Zener current (Iz) and the base current (Ib) of the transistor.
When designing the circuit for a lower input voltage, such as Ue = 5V, careful consideration must be given to the components selected to ensure that they can handle the operational constraints. The integrated circuit utilized in this design is optimized for higher operating voltages, thus enabling it to function effectively even when the input voltage is significantly lower.
In summary, the design of the voltage regulator requires meticulous selection of the Zener voltage and resistor values to achieve the desired output voltage while ensuring stability and performance across varying conditions. Proper understanding of the relationships between the input voltage, transistor characteristics, and Zener diode behavior is essential for effective circuit design. By the voltage equation Ue Ut + Ur + Ua shows that the size of the transistor voltage Ut will determine the maximum output voltage Ua. At the same time there should be Ur 2V. U t voltage regulator voltage value depends on the choice of Uz. Figure a resistor R is selected to satisfy the boundary conditions Ir Iz Ib formula or principle + Ir F10 Ibs. This integrated circuit is adapted to have a higher operating voltage of the occasion, at a lower voltage, for example Ue 5V, the circuit should be used in Figure b.
Zener voltage higher than the output voltage of at least Ua4V. Resistor R selection circuit with a.
The voltage regulation circuit operates based on the principles of transistor behavior and Zener diode regulation. The equation Ue = Ut + Ur + Ua outlines the relationship between the input voltage (Ue), the transistor voltage drop (Ut), the reference voltage (Ur), and the output voltage (Ua). The maximum output voltage (Ua) is influenced by the transistor voltage (Ut), which is a critical parameter for ensuring the circuit's efficiency.
In the design of this voltage regulator, the Zener diode plays a pivotal role. The Zener voltage (Uz) must be selected to be at least 4V higher than the desired output voltage (Ua) to ensure stable operation. This margin allows for variations in load and input voltage while maintaining a constant output. The resistor R is selected based on the current requirements, which must satisfy the boundary conditions of the circuit. The relationship Ir = Iz + Ib indicates that the current flowing through the resistor R (Ir) must equal the sum of the Zener current (Iz) and the base current (Ib) of the transistor.
When designing the circuit for a lower input voltage, such as Ue = 5V, careful consideration must be given to the components selected to ensure that they can handle the operational constraints. The integrated circuit utilized in this design is optimized for higher operating voltages, thus enabling it to function effectively even when the input voltage is significantly lower.
In summary, the design of the voltage regulator requires meticulous selection of the Zener voltage and resistor values to achieve the desired output voltage while ensuring stability and performance across varying conditions. Proper understanding of the relationships between the input voltage, transistor characteristics, and Zener diode behavior is essential for effective circuit design. By the voltage equation Ue Ut + Ur + Ua shows that the size of the transistor voltage Ut will determine the maximum output voltage Ua. At the same time there should be Ur 2V. U t voltage regulator voltage value depends on the choice of Uz. Figure a resistor R is selected to satisfy the boundary conditions Ir Iz Ib formula or principle + Ir F10 Ibs. This integrated circuit is adapted to have a higher operating voltage of the occasion, at a lower voltage, for example Ue 5V, the circuit should be used in Figure b.
Zener voltage higher than the output voltage of at least Ua4V. Resistor R selection circuit with a.