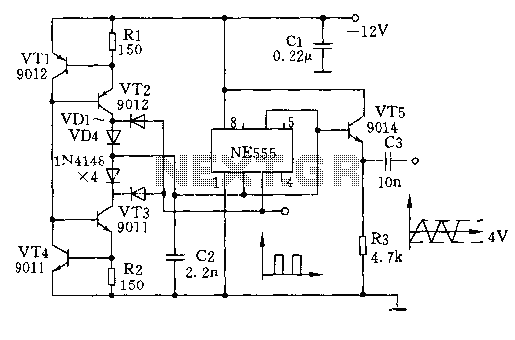
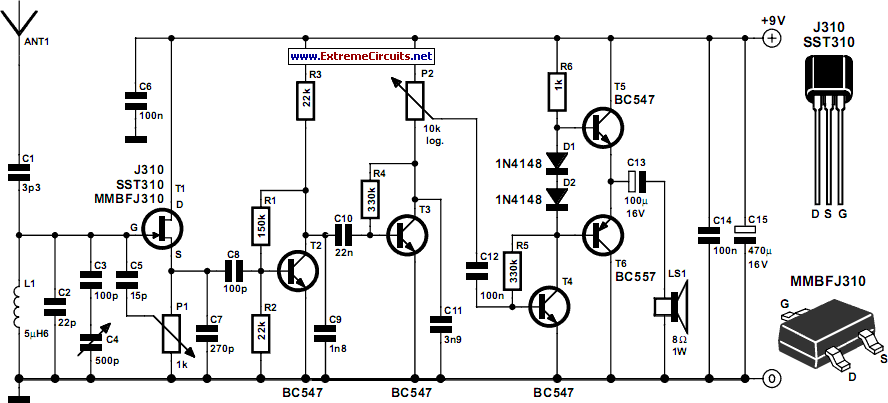
HOLTEK 9200B & 9170B DTMF Generator & Receiver
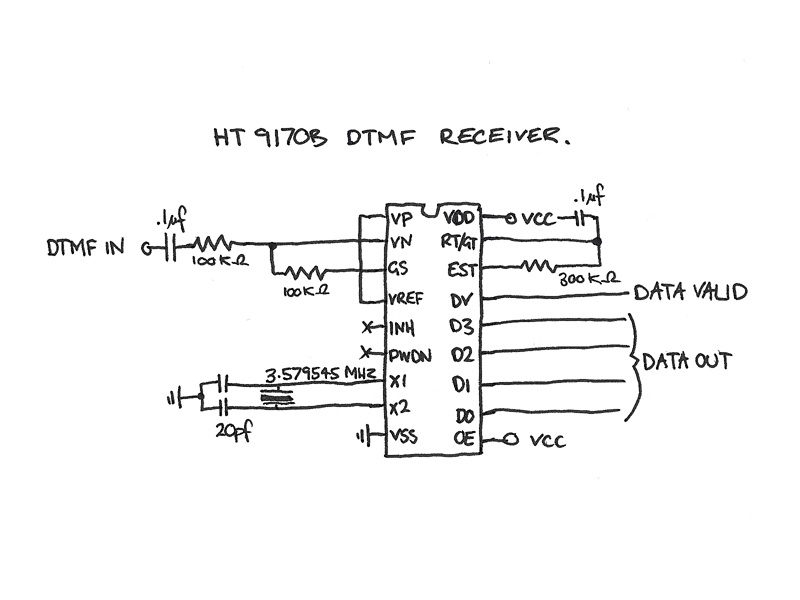
The four data lines from the Keypad Interface connect directly to the data inputs of the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator (pins 6, 7, 8, and 9). The Inverted Chip Enable output from the Keypad Interface is connected to the Chip Enable Input of the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator (pin 1). When the Chip Enable line is at logic 0, a DTMF tone is generated from the DTMF output (pin 13) relative to ground. This is an active low input, meaning that a logic 0 will enable the chip. The DTMF output is then routed to the DTMF input line of the Holtek 9170B DTMF Receiver. When a tone is detected, the Data Valid output (pin 15) goes high. Additionally, the DTMF tone is decoded into a 4-bit binary number on the output lines (pins 11, 12, 13, and 14).
The circuit described involves a Keypad Interface that serves as an input mechanism for the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator. The data lines from the keypad are essential for transmitting the pressed key information, which is encoded into DTMF tones by the generator. The connection to the data inputs (pins 6, 7, 8, and 9) allows the generator to interpret the keypad inputs directly.
The Chip Enable input (pin 1) is crucial for the operation of the DTMF generator. When this pin is held at a logic low state (0 volts), the generator becomes active and starts producing the corresponding DTMF tones. The output of the DTMF generator is then fed to the DTMF input of the Holtek 9170B DTMF Receiver, which is responsible for decoding the generated tones back into a digital format.
The receiver's functionality is indicated by the Data Valid output (pin 15), which transitions to a high state when a valid tone is detected. This output can be utilized to trigger further processing or actions within the system. Furthermore, the DTMF tones are decoded into a 4-bit binary number, available on output lines (pins 11, 12, 13, and 14), facilitating straightforward integration with digital logic circuits or microcontrollers for further processing or display.
In summary, this circuit effectively bridges the input from a keypad interface to DTMF tone generation and decoding, allowing for efficient communication and data processing within electronic systems that utilize DTMF signaling.The 4 data lines from the Keypad Interface go straight into the data inputs of the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator (pins 6, 7, 8 & 9), and the Inverted Chip Enable output on the Keypad Interface goes into the Chip Enable Input on the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator (pin1). When the Chip Enable line is at logic 0, a DTMF tone is generated from the DTMF out put (pin 13) with respect to ground. This is an `Active Low` input so logic 0 will enable the chip. The DTMF output is then taken to the DTMF input line of the Holtek 9170B DTMF Receiver. When a tone is present, the Data Valid output goes high (pin 15). Also the DTMF tone will be decoded to a 4 bit binary number on the output lines (pins 11, 12, 13 and 14). 🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves a Keypad Interface that serves as an input mechanism for the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator. The data lines from the keypad are essential for transmitting the pressed key information, which is encoded into DTMF tones by the generator. The connection to the data inputs (pins 6, 7, 8, and 9) allows the generator to interpret the keypad inputs directly.
The Chip Enable input (pin 1) is crucial for the operation of the DTMF generator. When this pin is held at a logic low state (0 volts), the generator becomes active and starts producing the corresponding DTMF tones. The output of the DTMF generator is then fed to the DTMF input of the Holtek 9170B DTMF Receiver, which is responsible for decoding the generated tones back into a digital format.
The receiver's functionality is indicated by the Data Valid output (pin 15), which transitions to a high state when a valid tone is detected. This output can be utilized to trigger further processing or actions within the system. Furthermore, the DTMF tones are decoded into a 4-bit binary number, available on output lines (pins 11, 12, 13, and 14), facilitating straightforward integration with digital logic circuits or microcontrollers for further processing or display.
In summary, this circuit effectively bridges the input from a keypad interface to DTMF tone generation and decoding, allowing for efficient communication and data processing within electronic systems that utilize DTMF signaling.The 4 data lines from the Keypad Interface go straight into the data inputs of the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator (pins 6, 7, 8 & 9), and the Inverted Chip Enable output on the Keypad Interface goes into the Chip Enable Input on the Holtek 9200B DTMF Generator (pin1). When the Chip Enable line is at logic 0, a DTMF tone is generated from the DTMF out put (pin 13) with respect to ground. This is an `Active Low` input so logic 0 will enable the chip. The DTMF output is then taken to the DTMF input line of the Holtek 9170B DTMF Receiver. When a tone is present, the Data Valid output goes high (pin 15). Also the DTMF tone will be decoded to a 4 bit binary number on the output lines (pins 11, 12, 13 and 14). 🔗 External reference