how to make automatic vehicle headlight
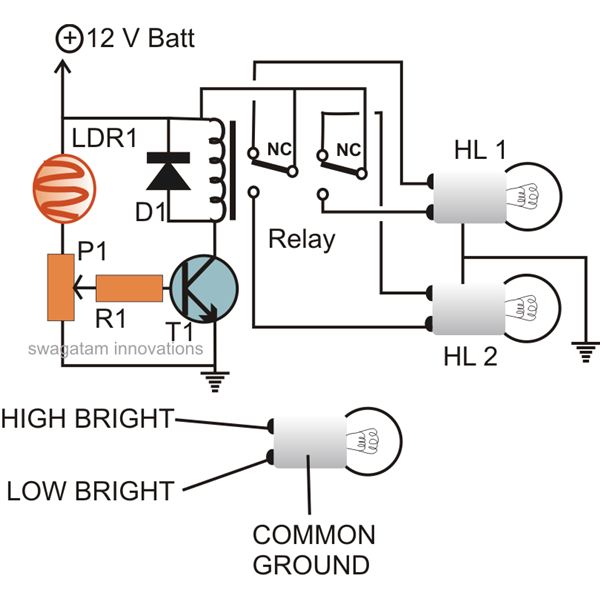
The circuit described here can be built and used in a vehicle for an automatic dipping and dimming operation of the headlamps in response to intense lights coming from opposite vehicle headlamps. This situation is often encountered while driving at night when the headlight focus from an oncoming vehicle can be blinding, making it difficult to assess the road and increasing the risk of a collision or accident. Traditionally, this issue is managed using a manual dipper switch mechanism, where the driver is prompted to "dip" the focus of their headlight, allowing the oncoming vehicle to adjust and indicating that they too should dip their vehicle lamps. However, manually performing this operation frequently can become laborious and troublesome. An automatic system can alleviate this burden, particularly in stressful driving conditions or on dangerous highways. The following diagram illustrates a simple yet effective automatic headlamp dipper or dimmer circuit. A transistor is used as a comparator, comparing the preset resistance level with the resistance level of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) relative to ground. When light from an oncoming vehicle's headlight strikes the LDR, its resistance decreases, allowing more current to flow to the base of the transistor. This causes the transistor to conduct and activate a relay, which flips the contacts to connect the host vehicle's headlamps to the dipper filament, thereby changing their intensity. The entire circuit can be enclosed in a small box and installed near the driver’s dashboard, while the LDR should be wired and positioned outside the enclosure, ideally in a corner of the windshield, to effectively detect light from oncoming vehicles as the driver would.
The automatic headlamp dipper circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) as a key component to detect incoming light. The LDR's resistance decreases when exposed to bright light, such as that from oncoming vehicle headlights. This change in resistance is crucial for the operation of the circuit. The transistor, functioning as a comparator, is connected to both the LDR and a preset resistor. When the LDR detects light, its resistance drops, which in turn increases the current flowing to the base of the transistor. The transistor, once activated, allows current to flow through its collector-emitter path, energizing the relay.
The relay serves as an electromechanical switch that controls the headlamp intensity. When the relay is activated, it changes the connection of the headlamps from the main filament to the dimmer filament, effectively "dipping" the headlights. This automatic adjustment helps prevent glare for oncoming drivers and enhances safety by allowing the driver to maintain focus on the road without the distraction of manual adjustments.
The circuit should be carefully designed to ensure that the LDR is positioned in a location that accurately represents the lighting conditions experienced by the driver. Proper enclosure of the circuit components is essential to protect against environmental factors, while ensuring that the LDR remains exposed to light sources. This design not only improves convenience for the driver but also contributes to safer driving practices during nighttime conditions. The implementation of such an automatic headlamp dimmer circuit can significantly enhance the driving experience by reducing the cognitive load on the driver, allowing for a more focused and safer journey.The circuitdescribed herecan be built and used in your vehicle for an automatic dipping and dimming operation of the headlamps, in response to the intense lights coming from an opposite vehicle headlamps. You must have come across this irritating situation while driving at night when you find the headlight focus from an opposite vehicle fallin
g straight in your eyes, making things difficult to assess, giving rise to a situation of a collision or some kind of possible accident. Such situations are normally tackled by using manual dipper switch mechanism, where the driver is prompted to "dip" the focus of his headlight, thus giving the opposite vehicle a chance to adjust his vehicle and also an indication that he too needs to "dip" his vehicle lamps.
However, doing the above operation manually, every now and then can become horribly laborious and troublesome, therefore if some kind of automatic system is Incorporated, can help to save this headache of the driver, especially while he is driving in stressful conditions and on dangerous highways. The following diagram describes a simple yet effective auto head lamp dipper or dimmer circuit. The transistor is used as a comparator, which compares the preset resistance level and the LDR resistance level with reference to ground.
Light falling over the LDR from the headlight of the vehicle coming from the front instantly lowers its resistance and allows more current to flow to the base of the transistor. The transistor conducts and activates the relay, which in turn flips the contacts such that the host vehicle`s headlamps gets connected with the dipper filament, changing its intensity.
The whole circuit may be enclosed in a small box and installed somewhere near the driver`s dashboard area, however the LDR needs to be wired and placed out of the enclosure, in some corner of the wind shield, so that it is able to "see` the light from the opposite vehicles just as the driver would see them. 🔗 External reference
The automatic headlamp dipper circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) as a key component to detect incoming light. The LDR's resistance decreases when exposed to bright light, such as that from oncoming vehicle headlights. This change in resistance is crucial for the operation of the circuit. The transistor, functioning as a comparator, is connected to both the LDR and a preset resistor. When the LDR detects light, its resistance drops, which in turn increases the current flowing to the base of the transistor. The transistor, once activated, allows current to flow through its collector-emitter path, energizing the relay.
The relay serves as an electromechanical switch that controls the headlamp intensity. When the relay is activated, it changes the connection of the headlamps from the main filament to the dimmer filament, effectively "dipping" the headlights. This automatic adjustment helps prevent glare for oncoming drivers and enhances safety by allowing the driver to maintain focus on the road without the distraction of manual adjustments.
The circuit should be carefully designed to ensure that the LDR is positioned in a location that accurately represents the lighting conditions experienced by the driver. Proper enclosure of the circuit components is essential to protect against environmental factors, while ensuring that the LDR remains exposed to light sources. This design not only improves convenience for the driver but also contributes to safer driving practices during nighttime conditions. The implementation of such an automatic headlamp dimmer circuit can significantly enhance the driving experience by reducing the cognitive load on the driver, allowing for a more focused and safer journey.The circuitdescribed herecan be built and used in your vehicle for an automatic dipping and dimming operation of the headlamps, in response to the intense lights coming from an opposite vehicle headlamps. You must have come across this irritating situation while driving at night when you find the headlight focus from an opposite vehicle fallin
g straight in your eyes, making things difficult to assess, giving rise to a situation of a collision or some kind of possible accident. Such situations are normally tackled by using manual dipper switch mechanism, where the driver is prompted to "dip" the focus of his headlight, thus giving the opposite vehicle a chance to adjust his vehicle and also an indication that he too needs to "dip" his vehicle lamps.
However, doing the above operation manually, every now and then can become horribly laborious and troublesome, therefore if some kind of automatic system is Incorporated, can help to save this headache of the driver, especially while he is driving in stressful conditions and on dangerous highways. The following diagram describes a simple yet effective auto head lamp dipper or dimmer circuit. The transistor is used as a comparator, which compares the preset resistance level and the LDR resistance level with reference to ground.
Light falling over the LDR from the headlight of the vehicle coming from the front instantly lowers its resistance and allows more current to flow to the base of the transistor. The transistor conducts and activates the relay, which in turn flips the contacts such that the host vehicle`s headlamps gets connected with the dipper filament, changing its intensity.
The whole circuit may be enclosed in a small box and installed somewhere near the driver`s dashboard area, however the LDR needs to be wired and placed out of the enclosure, in some corner of the wind shield, so that it is able to "see` the light from the opposite vehicles just as the driver would see them. 🔗 External reference