In-Car Charger And Switcher Circuit For SLA Battery circuit
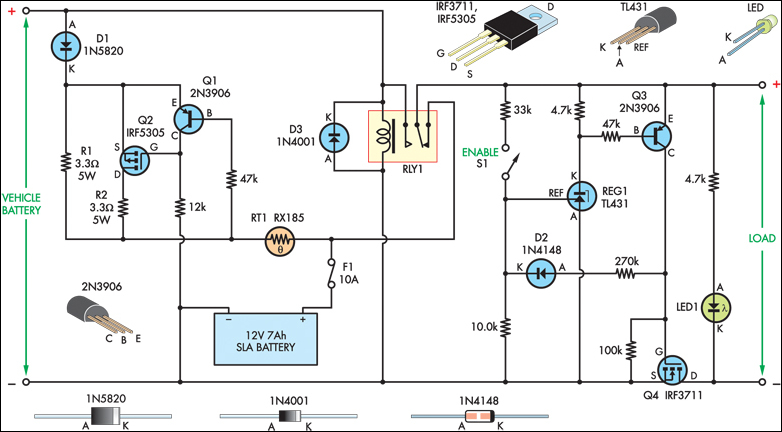
The SLA battery is charged from the vehicle's battery. When the engine is running, the voltage remains fairly constant, which greatly simplifies the charging circuit. If the SLA battery is fully charged, any further charging current from the vehicle battery is limited by a 3.3W 5W resistor (R1). If the SLA battery is deeply discharged, the voltage drop across this resistor will be enough to bias on PNP transistor Q1. This will turn on P-channel MOSFET Q2, providing further charging current via R2, effectively becoming a two-step charger.
The circuit operates by utilizing the vehicle's battery to charge a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery while the engine is running. The design leverages the relatively stable voltage output of the vehicle's alternator, which simplifies the charging process. The charging circuit includes a resistor (R1) rated at 3.3W to 5W, which serves to limit the charging current when the SLA battery reaches its full charge. This resistor prevents overcharging and protects the battery from damage due to excessive current.
In scenarios where the SLA battery is deeply discharged, the voltage drop across resistor R1 becomes significant enough to activate the base of the PNP transistor Q1. This activation leads to the conduction of Q1, which in turn triggers the P-channel MOSFET Q2. The MOSFET then allows additional charging current to flow through a secondary resistor (R2) connected in series. This configuration effectively creates a two-step charging system, where the initial charging phase is controlled by R1 and the secondary phase is managed by the MOSFET and R2.
The two-step charging approach is beneficial as it allows for a more controlled and efficient charging process, reducing the risk of battery damage and extending the overall life of the SLA battery. The design is particularly useful in automotive applications, where maintaining battery health is crucial for reliability and performance. The circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an ideal solution for integrating SLA batteries into vehicle electrical systems.The SLA battery is charged from the vehicle s battery. When the engine is running, the voltage remains fairly constant, which greatly simplifies the charging circuit. If the SLA battery is fully charged, any further charging current from the vehicle battery is limited by a 3.3W 5W resistor (R1).
If the SLA battery is deeply discharged, the voltage drop across this resistor will be enough to bias on PNP transistor Q1. This will turn on P-channel Mosfet Q2 and it will provide further charging current via R2, effectively becoming a 2-step charger..
🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the vehicle's battery to charge a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery while the engine is running. The design leverages the relatively stable voltage output of the vehicle's alternator, which simplifies the charging process. The charging circuit includes a resistor (R1) rated at 3.3W to 5W, which serves to limit the charging current when the SLA battery reaches its full charge. This resistor prevents overcharging and protects the battery from damage due to excessive current.
In scenarios where the SLA battery is deeply discharged, the voltage drop across resistor R1 becomes significant enough to activate the base of the PNP transistor Q1. This activation leads to the conduction of Q1, which in turn triggers the P-channel MOSFET Q2. The MOSFET then allows additional charging current to flow through a secondary resistor (R2) connected in series. This configuration effectively creates a two-step charging system, where the initial charging phase is controlled by R1 and the secondary phase is managed by the MOSFET and R2.
The two-step charging approach is beneficial as it allows for a more controlled and efficient charging process, reducing the risk of battery damage and extending the overall life of the SLA battery. The design is particularly useful in automotive applications, where maintaining battery health is crucial for reliability and performance. The circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an ideal solution for integrating SLA batteries into vehicle electrical systems.The SLA battery is charged from the vehicle s battery. When the engine is running, the voltage remains fairly constant, which greatly simplifies the charging circuit. If the SLA battery is fully charged, any further charging current from the vehicle battery is limited by a 3.3W 5W resistor (R1).
If the SLA battery is deeply discharged, the voltage drop across this resistor will be enough to bias on PNP transistor Q1. This will turn on P-channel Mosfet Q2 and it will provide further charging current via R2, effectively becoming a 2-step charger..
🔗 External reference