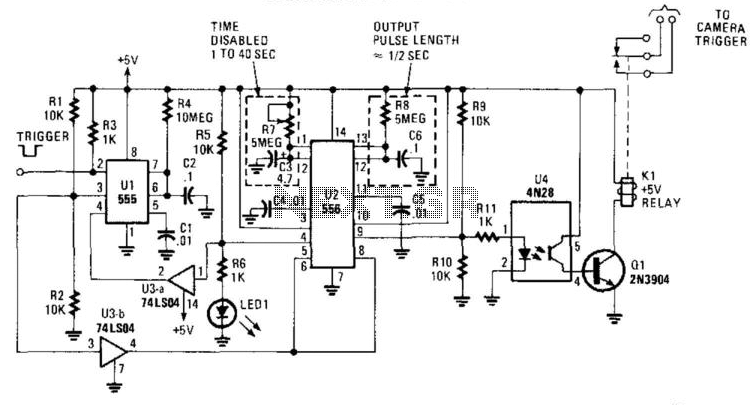
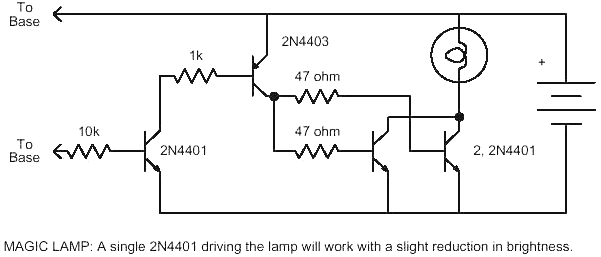
Infa-Red Remote Control circuit
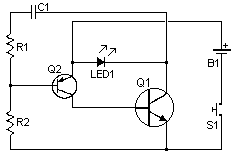
This remote transmits a tone using an infrared LED. This tone is decoded by the receiver. Since the receiver only switches when it "hears" the tone, there are no accidental activations.
The described circuit consists of a remote control unit and a corresponding receiver unit. The remote control utilizes an infrared (IR) LED to emit a modulated signal, which encodes a specific tone. This modulation allows the receiver to distinguish the intended signal from background noise or interference, ensuring accurate communication between the two devices.
The infrared LED in the remote is driven by a microcontroller or a dedicated tone generator circuit. The modulation frequency can be selected based on the application requirements, typically falling within the range of 30 kHz to 40 kHz. The choice of frequency is crucial as it must be compatible with the receiver's detection capabilities.
On the receiving end, an infrared photodiode or phototransistor is employed to detect the incoming IR signal. This component is connected to a signal processing circuit that includes a band-pass filter, which helps to isolate the desired modulation frequency from any ambient light or other noise sources. When the receiver detects the specific tone, it activates a switching mechanism, such as a relay or a transistor, to perform the intended action, such as turning on a device or triggering an event.
The design ensures that the receiver only activates upon receiving the correct tone, thereby preventing accidental activations caused by false signals. This feature enhances the reliability and efficiency of the remote control system, making it suitable for various applications, including home automation, security systems, and remote operation of electronic devices.his remote transmits a tone using an infa-red LED. This tone is decoded by the receiver. Since the receiver only switches when it "hears" the tone, there are no accidental activations.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit consists of a remote control unit and a corresponding receiver unit. The remote control utilizes an infrared (IR) LED to emit a modulated signal, which encodes a specific tone. This modulation allows the receiver to distinguish the intended signal from background noise or interference, ensuring accurate communication between the two devices.
The infrared LED in the remote is driven by a microcontroller or a dedicated tone generator circuit. The modulation frequency can be selected based on the application requirements, typically falling within the range of 30 kHz to 40 kHz. The choice of frequency is crucial as it must be compatible with the receiver's detection capabilities.
On the receiving end, an infrared photodiode or phototransistor is employed to detect the incoming IR signal. This component is connected to a signal processing circuit that includes a band-pass filter, which helps to isolate the desired modulation frequency from any ambient light or other noise sources. When the receiver detects the specific tone, it activates a switching mechanism, such as a relay or a transistor, to perform the intended action, such as turning on a device or triggering an event.
The design ensures that the receiver only activates upon receiving the correct tone, thereby preventing accidental activations caused by false signals. This feature enhances the reliability and efficiency of the remote control system, making it suitable for various applications, including home automation, security systems, and remote operation of electronic devices.his remote transmits a tone using an infa-red LED. This tone is decoded by the receiver. Since the receiver only switches when it "hears" the tone, there are no accidental activations.. 🔗 External reference