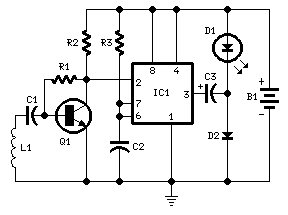
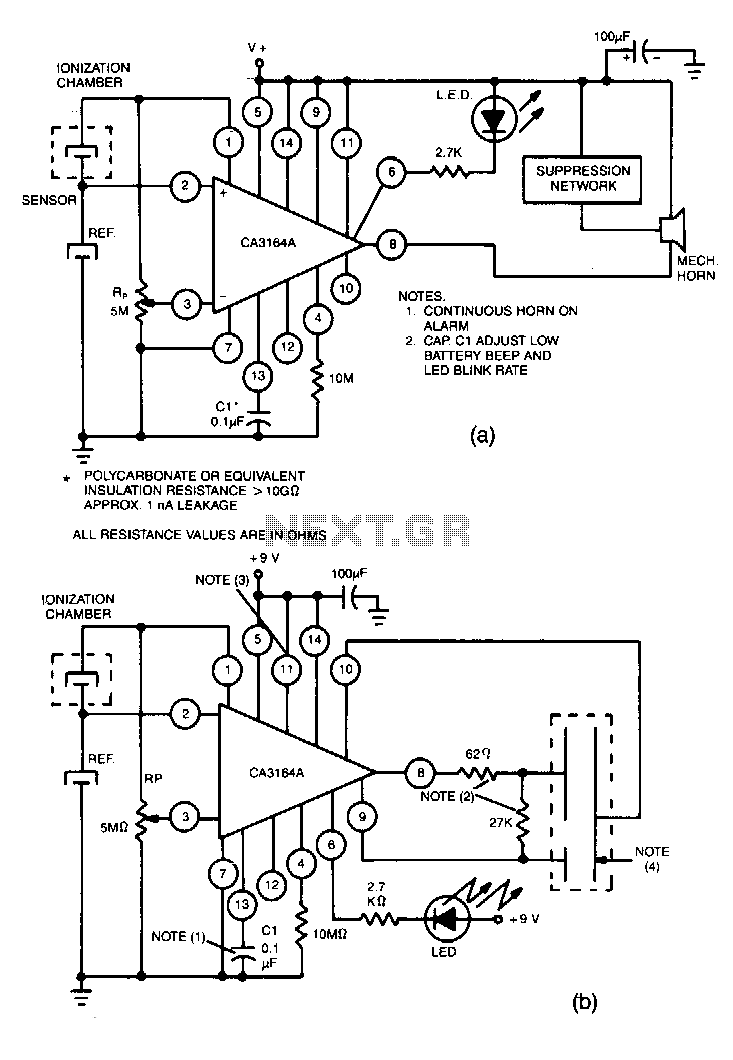
Infra-red Level Detector
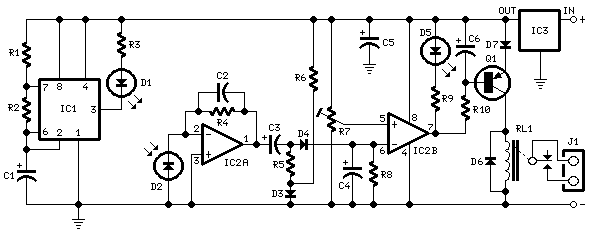
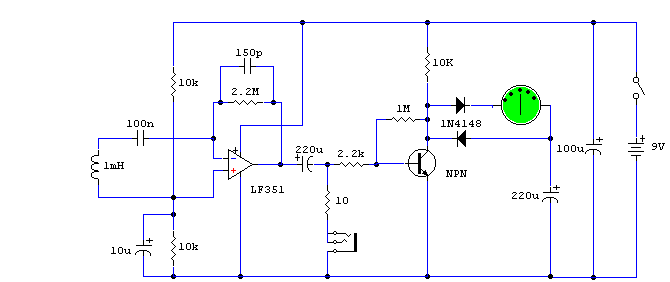
This circuit is useful in liquids level or proximity detection. It operates detecting the distance from the target by reflection of an infra-red beam. It can safely detect the level of a liquid in a tank without any contact with the liquid itself. The device's range can be set from a couple of cm to about 50 cm by means of a trimmer. Range can vary, depending on infra-red transmitting and receiving LEDs used and is mostly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces lower greatly the device's sensitivity.
The circuit utilizes an infrared LED as the transmitter and a photodiode or phototransistor as the receiver. When the infrared beam emitted by the LED strikes a reflective surface, it is reflected back towards the receiver. The distance to the target can be calculated based on the time taken for the reflected beam to return or by measuring the intensity of the received signal, which varies with distance.
A trimmer potentiometer is included in the circuit to adjust the sensitivity and range of detection. By varying the resistance, the circuit can be calibrated to detect objects at desired distances, ranging from a few centimeters up to approximately 50 centimeters.
The choice of infrared LEDs is crucial, as different wavelengths may have varying degrees of reflection based on the target surface. For example, light-colored surfaces reflect infrared light more effectively than dark surfaces, which can significantly impact detection performance. Therefore, careful consideration should be given to the application environment and the properties of the surfaces being detected.
The circuit may also include a microcontroller or comparator circuit to process the signal from the photodiode, providing a digital output that can trigger alarms or control other devices based on the detected distance. This allows for integration with other systems, enhancing its versatility in applications such as liquid level monitoring in tanks, proximity sensing in automation, or safety systems where non-contact detection is essential.
In summary, this infrared-based circuit design offers a reliable and non-invasive method for detecting liquid levels or proximity, with adjustable sensitivity and a range that can be tailored to specific applications.This circuit is useful in liquids level or proximity detection. It operates detecting the distance from the target by reflection of an infra-red beam. It can safely detect the level of a liquid in a tank without any contact with the liquid itself. The device`s range can be set from a couple of cm. to about 50 cm. by means of a trimmer. Range can vary, depending on infra-red transmitting and receiving LEDs used and is mostly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces lower greatly the device`s sensitivity. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an infrared LED as the transmitter and a photodiode or phototransistor as the receiver. When the infrared beam emitted by the LED strikes a reflective surface, it is reflected back towards the receiver. The distance to the target can be calculated based on the time taken for the reflected beam to return or by measuring the intensity of the received signal, which varies with distance.
A trimmer potentiometer is included in the circuit to adjust the sensitivity and range of detection. By varying the resistance, the circuit can be calibrated to detect objects at desired distances, ranging from a few centimeters up to approximately 50 centimeters.
The choice of infrared LEDs is crucial, as different wavelengths may have varying degrees of reflection based on the target surface. For example, light-colored surfaces reflect infrared light more effectively than dark surfaces, which can significantly impact detection performance. Therefore, careful consideration should be given to the application environment and the properties of the surfaces being detected.
The circuit may also include a microcontroller or comparator circuit to process the signal from the photodiode, providing a digital output that can trigger alarms or control other devices based on the detected distance. This allows for integration with other systems, enhancing its versatility in applications such as liquid level monitoring in tanks, proximity sensing in automation, or safety systems where non-contact detection is essential.
In summary, this infrared-based circuit design offers a reliable and non-invasive method for detecting liquid levels or proximity, with adjustable sensitivity and a range that can be tailored to specific applications.This circuit is useful in liquids level or proximity detection. It operates detecting the distance from the target by reflection of an infra-red beam. It can safely detect the level of a liquid in a tank without any contact with the liquid itself. The device`s range can be set from a couple of cm. to about 50 cm. by means of a trimmer. Range can vary, depending on infra-red transmitting and receiving LEDs used and is mostly affected by the color of the reflecting surface. Black surfaces lower greatly the device`s sensitivity. 🔗 External reference