Infrared Receiver for PC Schematic andCircuit
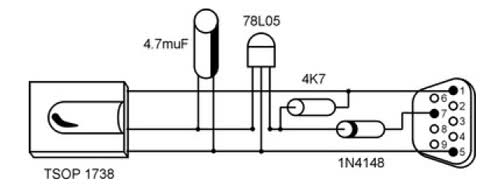
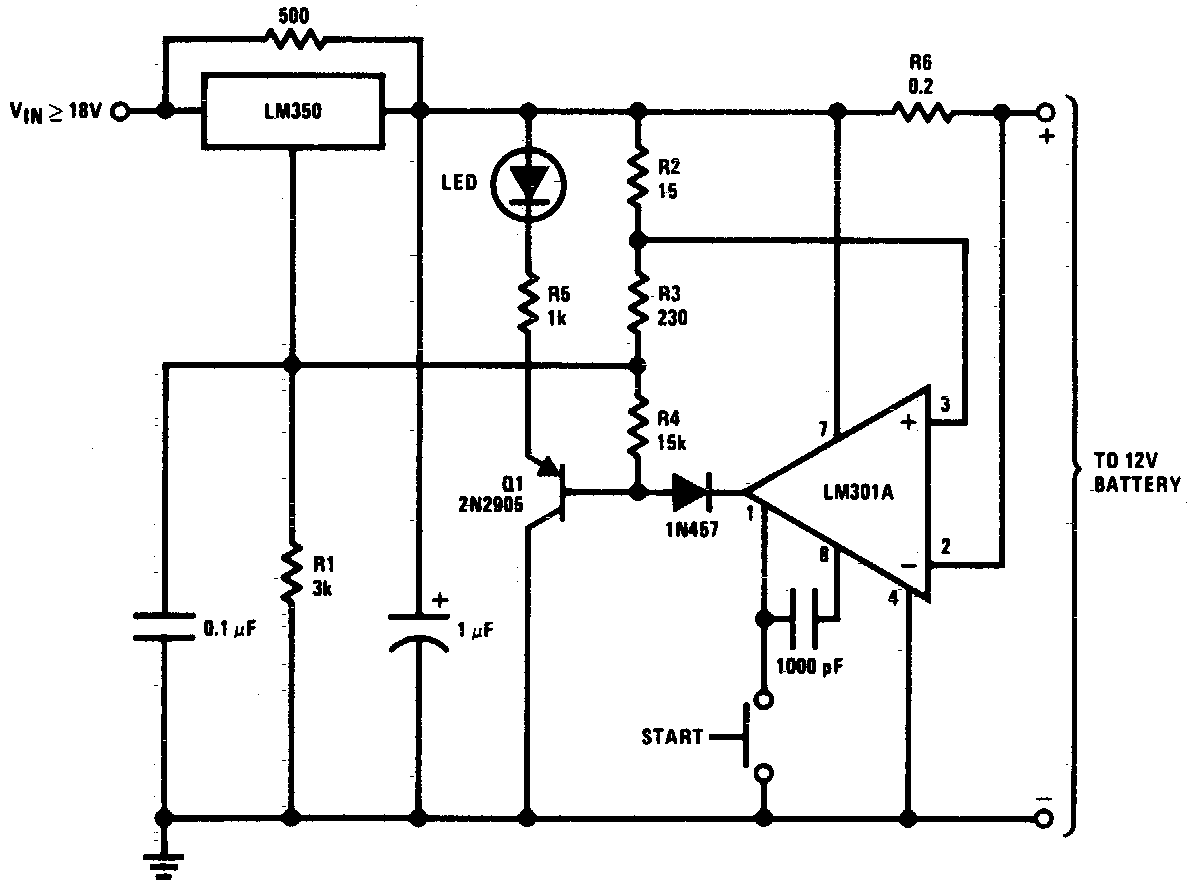
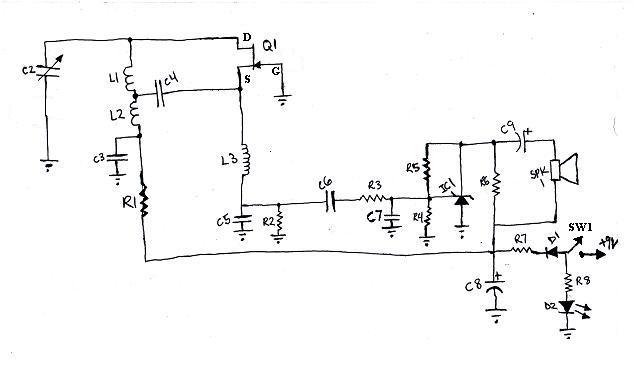
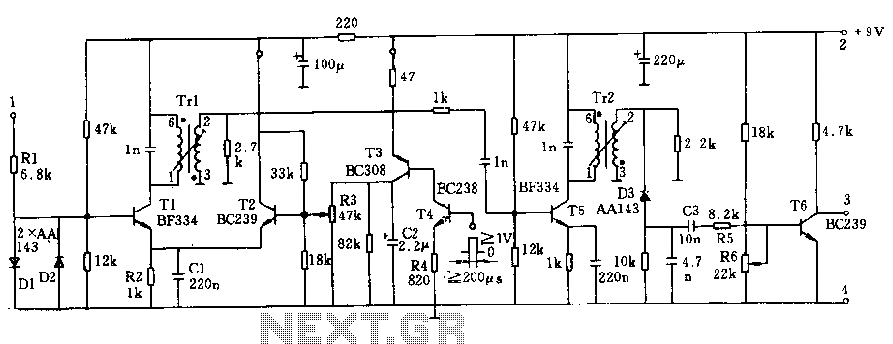
It is unusual that personal computers are not equipped with a standard remote control interface. Many motherboards feature an IRDA port; however, this port is not compatible with the 38 kHz frequencies commonly used by regular remote controls. Fortunately, WinLIRC offers a solution: with a few components and some software, it is possible to create a custom infrared receiver. This setup allows for remote control of any application on the PC from a distance of up to 30 meters. Constructing the receiver does not require advanced electronics knowledge; basic soldering skills are sufficient. To build the receiver, connect the components as illustrated in the circuit diagram. For those who are not confident in their soldering abilities, local TV or audio service centers can assist with assembly for a small fee.
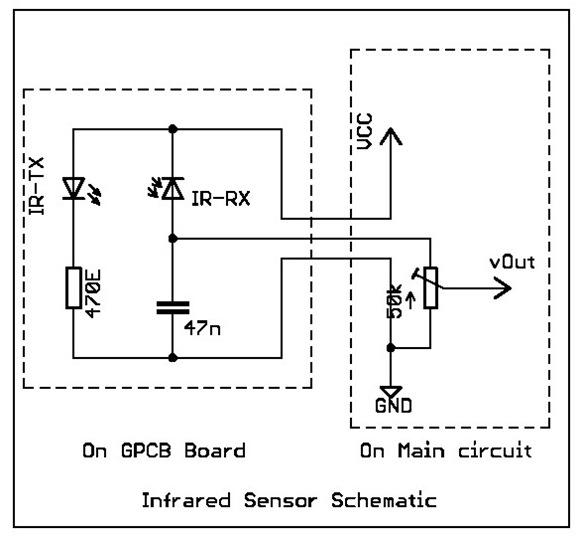
The infrared receiver circuit typically includes a few key components: an infrared receiver module, such as the TSOP4838, which is designed to receive 38 kHz modulated signals. This module is connected to a microcontroller, often a simple Arduino or similar device, which processes the signals received from the remote control. The microcontroller is programmed to interpret the commands sent by the remote, translating them into actions that control various applications on the PC.
Power supply considerations are important; the circuit usually requires a stable voltage source, typically 5V, which can be derived from the USB port of the computer. The output of the infrared receiver module is connected to one of the digital input pins of the microcontroller. The software, often utilizing the WinLIRC library, is responsible for mapping the received signals to specific commands or keystrokes that the PC can recognize.
It is important to ensure that the receiver is positioned correctly and unobstructed to maintain a reliable line of sight with the remote control. Additionally, the range of the receiver can be influenced by the environment, so it may be necessary to test and adjust the placement for optimal performance. Overall, this project provides a practical and cost-effective way to enhance the functionality of a personal computer through remote control capabilities.Actually it`s very strange why PC`s aren`t equipped with a standard remote control interface. A lot of motherboards are equipped with an IRDA port but this isn`t compatible with the frequencies (38 kHz) used in regular remote controls. But WinLIRC comes to the rescue: with just a few components and a little bit of software we can make our own IR-r
eceiver. We will be able to control every application on our pc from a distance up to 30 meters. And to make a receiver you need not be a graduate in electronics. Some basic soldering skills would suffice! Making the receiver: Connect the components as shown in the circuit diagram (Fig 2). If you are not good at soldering get it done from local TV/audio service center. I`ve seen people who have done this for me for Rs. 50. But since I`ve learned a bit of soldering I do it myself nowadays. If you see unrelated pdf files with the description or copyrighted material published, please report to us, we`ll correct/delete it it as soon as possible. NONE OF THOSE MATERIALS ARE HOSTED IN THIS SERVER NOR UPLOADED BY ME IN SOMEONE`S SERVERS. Read our DISCLAIMER for more detail. Information contained herein is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including any warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
In no event shall ANYONE be held liable for any loss of profit, special, incidental, consequential, or other similar claims. 🔗 External reference
The infrared receiver circuit typically includes a few key components: an infrared receiver module, such as the TSOP4838, which is designed to receive 38 kHz modulated signals. This module is connected to a microcontroller, often a simple Arduino or similar device, which processes the signals received from the remote control. The microcontroller is programmed to interpret the commands sent by the remote, translating them into actions that control various applications on the PC.
Power supply considerations are important; the circuit usually requires a stable voltage source, typically 5V, which can be derived from the USB port of the computer. The output of the infrared receiver module is connected to one of the digital input pins of the microcontroller. The software, often utilizing the WinLIRC library, is responsible for mapping the received signals to specific commands or keystrokes that the PC can recognize.
It is important to ensure that the receiver is positioned correctly and unobstructed to maintain a reliable line of sight with the remote control. Additionally, the range of the receiver can be influenced by the environment, so it may be necessary to test and adjust the placement for optimal performance. Overall, this project provides a practical and cost-effective way to enhance the functionality of a personal computer through remote control capabilities.Actually it`s very strange why PC`s aren`t equipped with a standard remote control interface. A lot of motherboards are equipped with an IRDA port but this isn`t compatible with the frequencies (38 kHz) used in regular remote controls. But WinLIRC comes to the rescue: with just a few components and a little bit of software we can make our own IR-r
eceiver. We will be able to control every application on our pc from a distance up to 30 meters. And to make a receiver you need not be a graduate in electronics. Some basic soldering skills would suffice! Making the receiver: Connect the components as shown in the circuit diagram (Fig 2). If you are not good at soldering get it done from local TV/audio service center. I`ve seen people who have done this for me for Rs. 50. But since I`ve learned a bit of soldering I do it myself nowadays. If you see unrelated pdf files with the description or copyrighted material published, please report to us, we`ll correct/delete it it as soon as possible. NONE OF THOSE MATERIALS ARE HOSTED IN THIS SERVER NOR UPLOADED BY ME IN SOMEONE`S SERVERS. Read our DISCLAIMER for more detail. Information contained herein is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including any warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
In no event shall ANYONE be held liable for any loss of profit, special, incidental, consequential, or other similar claims. 🔗 External reference