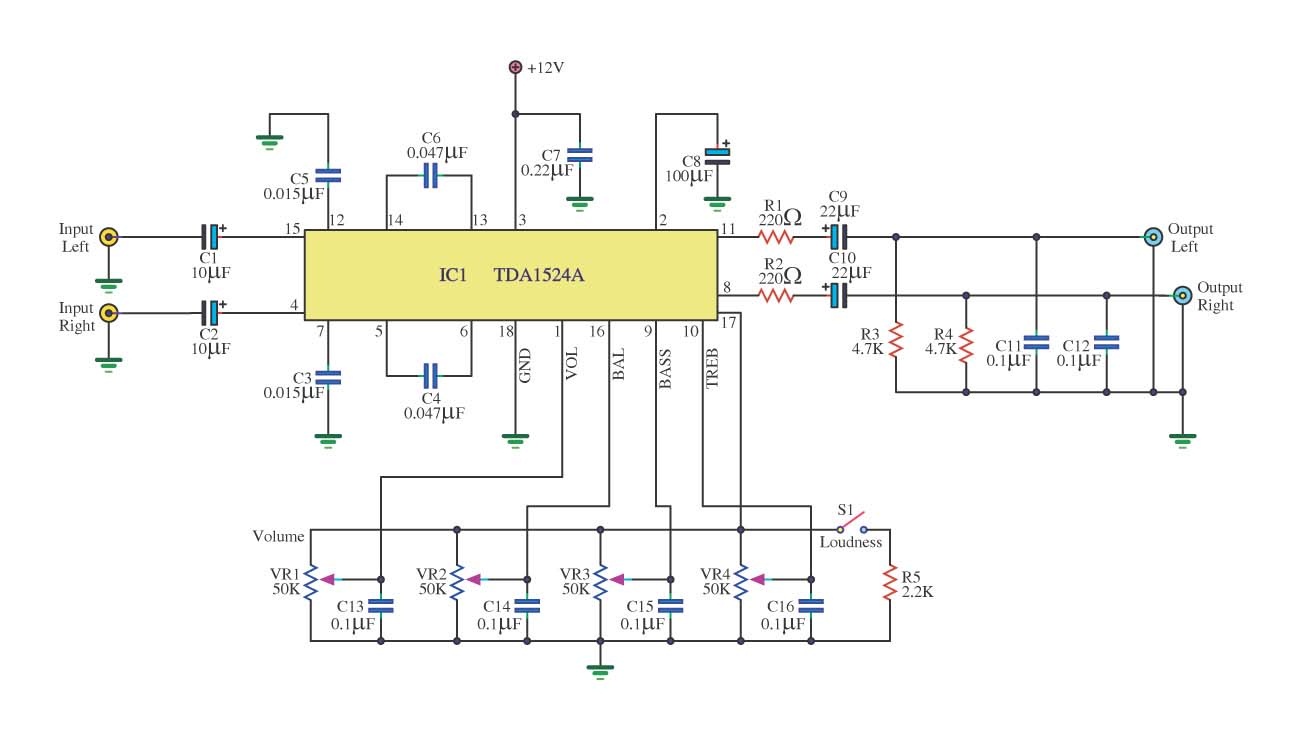
Infrared Remote Control Tester
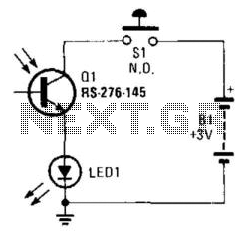
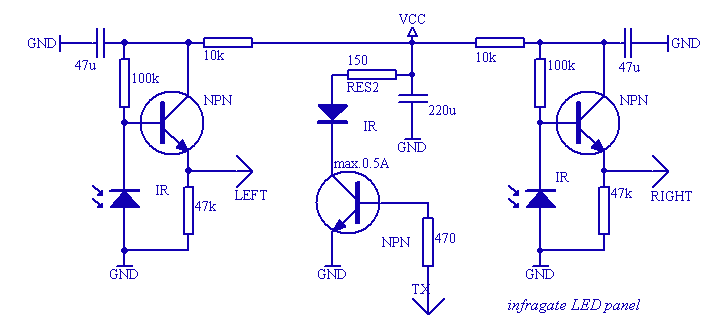
Using a battery, a phototransistor, and a visible-light LED, this simple circuit functions as a "go/no go" tester for infrared remote control devices. The illumination of the LED indicates that the phototransistor is being modulated by infrared energy.
This circuit operates on the principle of light modulation, where the infrared (IR) signal from a remote control is detected by the phototransistor. The circuit consists of a power source, typically a battery, which provides the necessary voltage for operation. The phototransistor is sensitive to infrared light, allowing it to detect signals emitted by IR remote controls.
When the remote control is activated, it emits an IR signal that is received by the phototransistor. This signal causes the phototransistor to conduct, allowing current to flow through the circuit. The flow of current is then used to illuminate a visible-light LED. The LED serves as an indicator, visually confirming that the phototransistor is receiving IR energy and that the remote control is functioning correctly.
The circuit's simplicity makes it an effective tool for testing the functionality of IR remote controls. It can be easily assembled on a breadboard or a printed circuit board (PCB) using basic electronic components. The design can also be enhanced by incorporating additional features, such as adjustable sensitivity or a more sophisticated LED indicator system, to provide more detailed feedback on the strength of the received signal. Overall, this circuit is a practical application in the field of electronics, particularly for troubleshooting and testing IR remote devices. Using a battery, a phototransistor and a visible-light LED, this simple circuit is a " "go/no go"" tester fo r IR remote control devices. The illumination of the LED indicates that Ql is being modulated by IR energy. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates on the principle of light modulation, where the infrared (IR) signal from a remote control is detected by the phototransistor. The circuit consists of a power source, typically a battery, which provides the necessary voltage for operation. The phototransistor is sensitive to infrared light, allowing it to detect signals emitted by IR remote controls.
When the remote control is activated, it emits an IR signal that is received by the phototransistor. This signal causes the phototransistor to conduct, allowing current to flow through the circuit. The flow of current is then used to illuminate a visible-light LED. The LED serves as an indicator, visually confirming that the phototransistor is receiving IR energy and that the remote control is functioning correctly.
The circuit's simplicity makes it an effective tool for testing the functionality of IR remote controls. It can be easily assembled on a breadboard or a printed circuit board (PCB) using basic electronic components. The design can also be enhanced by incorporating additional features, such as adjustable sensitivity or a more sophisticated LED indicator system, to provide more detailed feedback on the strength of the received signal. Overall, this circuit is a practical application in the field of electronics, particularly for troubleshooting and testing IR remote devices. Using a battery, a phototransistor and a visible-light LED, this simple circuit is a " "go/no go"" tester fo r IR remote control devices. The illumination of the LED indicates that Ql is being modulated by IR energy. 🔗 External reference