intercom circuit
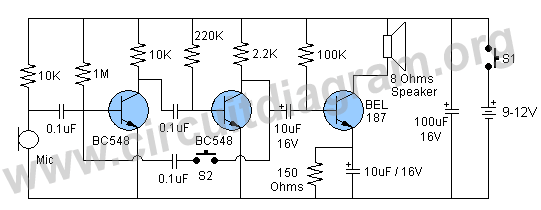
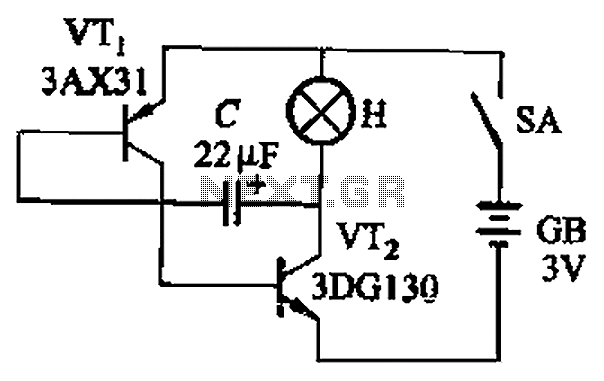
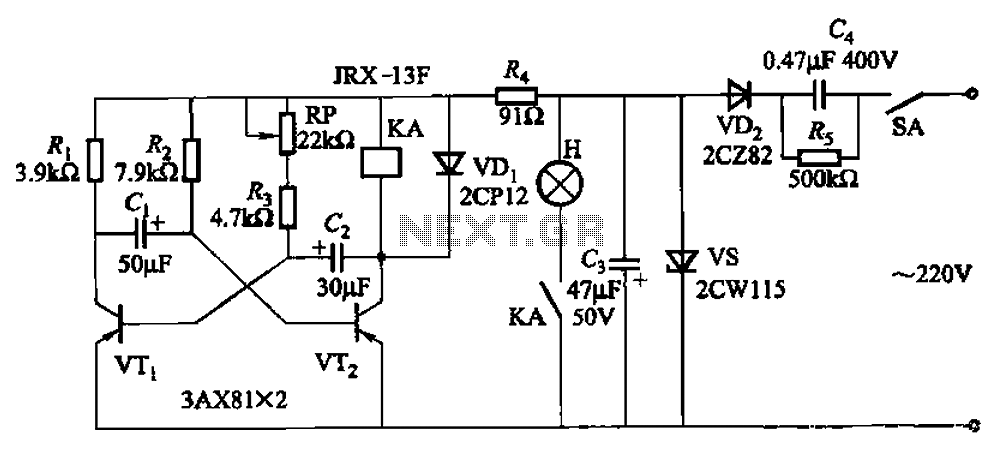
A high-quality and straightforward intercom circuit utilizing only three transistors. By pressing switch S2, the circuit generates ringing signals. To create a two-way intercom, two identical circuits can be constructed and combined as illustrated in diagram 2. The circuit's current consumption is minimal.
This intercom circuit operates effectively with minimal components, demonstrating the efficiency of using three transistors in its design. The primary function of the circuit is to generate ringing signals when switch S2 is activated, allowing for communication between two or more stations.
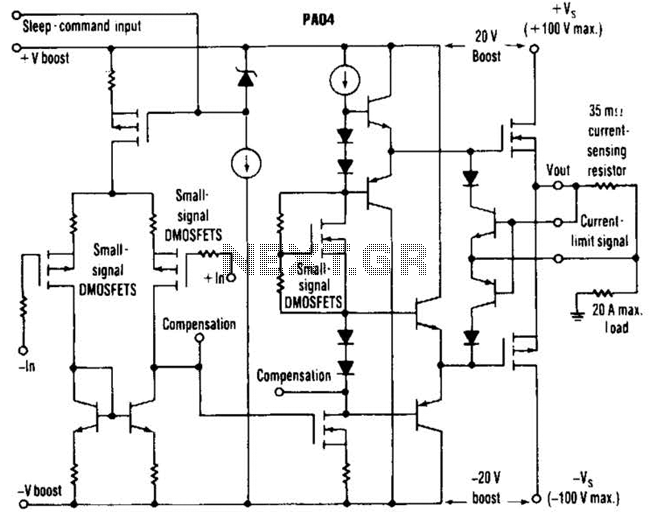
The circuit can be divided into two main sections: the transmitter and the receiver. Each section employs one transistor for amplification and two additional transistors for signal processing and switching. The transistors are typically configured in a common emitter arrangement, which provides the necessary gain for the audio signals.
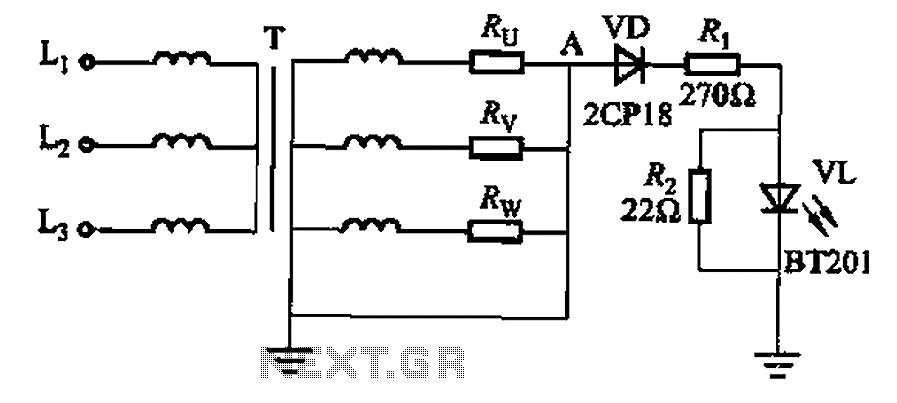
For a two-way intercom system, two identical circuits are required. Each circuit can be connected to a common power supply and linked via audio lines, allowing for seamless communication. The intercom can be enhanced with additional features such as volume control, which can be implemented using variable resistors in the audio path.
Current consumption is an important factor in the design, especially for battery-operated systems. The transistors should be selected based on their low quiescent current characteristics to ensure the circuit remains energy-efficient. When designing the layout, careful consideration should be given to component placement to minimize noise and ensure clear audio quality.
In summary, this intercom circuit design is not only straightforward and cost-effective but also scalable, allowing for multiple intercom stations to be added as needed while maintaining high audio fidelity and low power consumption.A very good quality and simple intercom circuit using only three transistors. By pressing the switch S2 the circuit will generate ring signals. For making two way intercom make two identical circuits and combine them as shown in diagram 2. The current consumption of the circuit 🔗 External reference
This intercom circuit operates effectively with minimal components, demonstrating the efficiency of using three transistors in its design. The primary function of the circuit is to generate ringing signals when switch S2 is activated, allowing for communication between two or more stations.
The circuit can be divided into two main sections: the transmitter and the receiver. Each section employs one transistor for amplification and two additional transistors for signal processing and switching. The transistors are typically configured in a common emitter arrangement, which provides the necessary gain for the audio signals.
For a two-way intercom system, two identical circuits are required. Each circuit can be connected to a common power supply and linked via audio lines, allowing for seamless communication. The intercom can be enhanced with additional features such as volume control, which can be implemented using variable resistors in the audio path.
Current consumption is an important factor in the design, especially for battery-operated systems. The transistors should be selected based on their low quiescent current characteristics to ensure the circuit remains energy-efficient. When designing the layout, careful consideration should be given to component placement to minimize noise and ensure clear audio quality.
In summary, this intercom circuit design is not only straightforward and cost-effective but also scalable, allowing for multiple intercom stations to be added as needed while maintaining high audio fidelity and low power consumption.A very good quality and simple intercom circuit using only three transistors. By pressing the switch S2 the circuit will generate ring signals. For making two way intercom make two identical circuits and combine them as shown in diagram 2. The current consumption of the circuit 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713