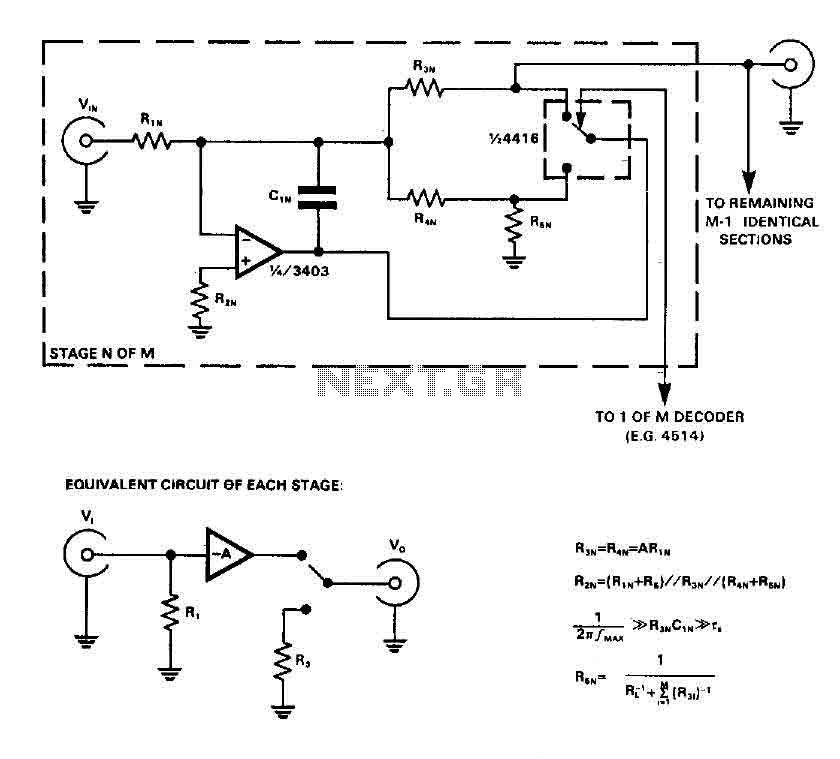
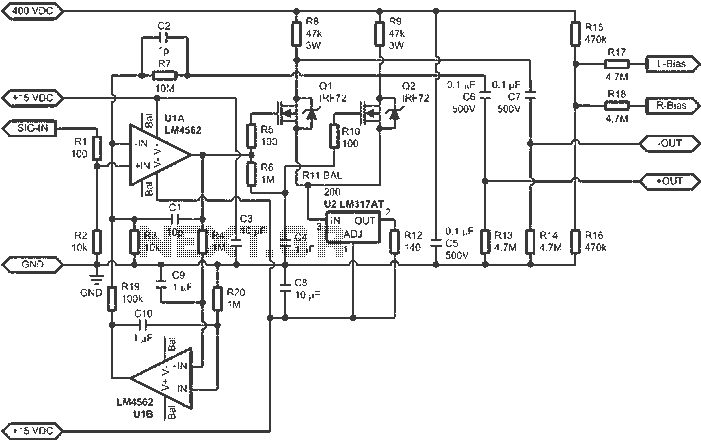
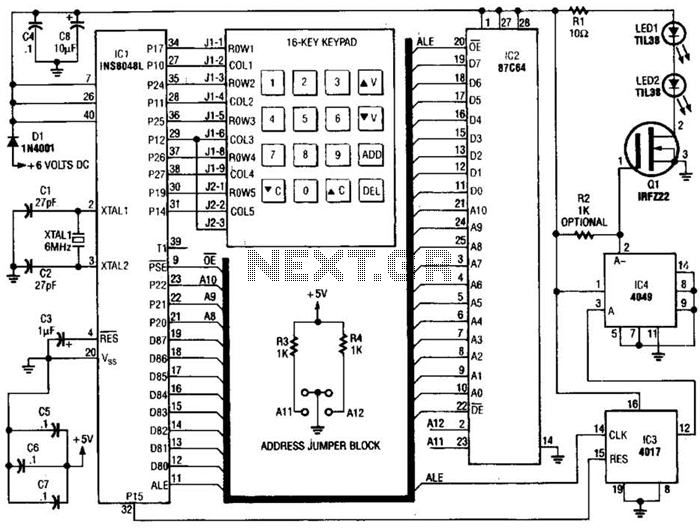
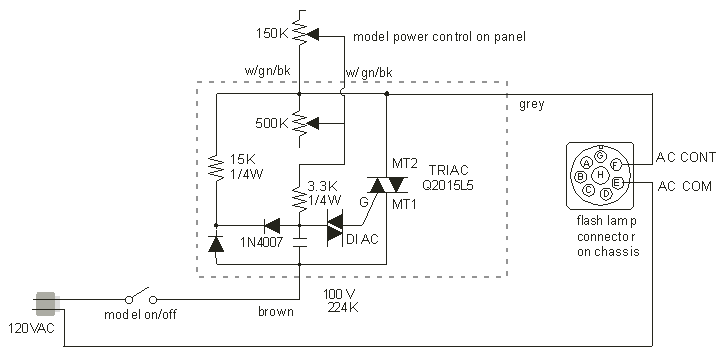
Ir-Controlled Remote A/B Switch Circuit
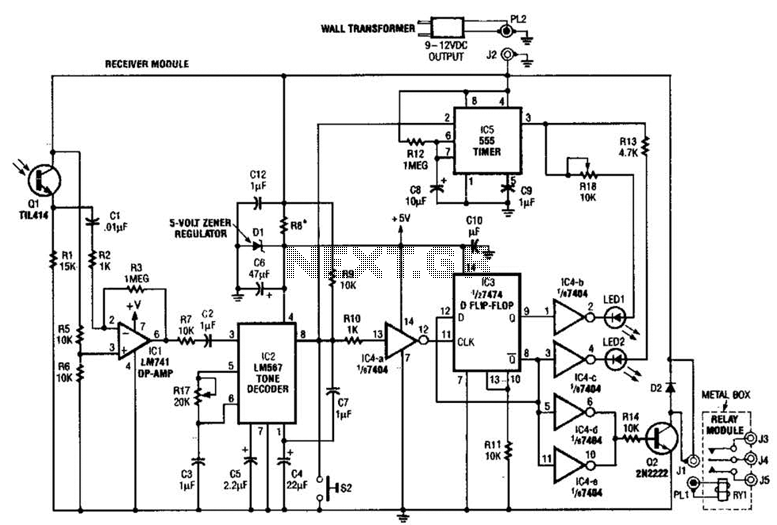
Useful for A/B control, the IR receiver shown controls a relay from an infrared beam that has a pulsed tone-modulated signal. Q1 is the photo receptor feeding op amp IC1, tone decoder IC2, and flip-flop IC3. IC5 turns off the indicator LEDs after about 15 seconds.
The described circuit utilizes an infrared (IR) receiver for A/B control applications, leveraging a pulsed tone-modulated signal to operate a relay. The core of the system includes a photo receptor, designated as Q1, which detects the incoming IR signal. This signal is then processed by an operational amplifier (op amp) IC1, which amplifies the weak signal received from Q1 to a usable level.
Following amplification, the signal is sent to a tone decoder IC2. This component is responsible for demodulating the tone-modulated signal, extracting the relevant control information necessary for the operation of the relay. The output from IC2 is then fed into a flip-flop IC3, which provides a stable output that can be used to control the relay's switching action. The flip-flop ensures that the relay remains in the desired state until a new command is received, enabling reliable A/B switching.
Additionally, the circuit includes an indicator LED system that provides visual feedback on the relay's status. This is managed by IC5, which is designed to turn off the indicator LEDs approximately 15 seconds after the last command is issued. This feature helps in conserving power and reducing unnecessary visual distractions when the system is idle.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient for applications requiring remote control via infrared signals, offering a straightforward yet effective solution for A/B control scenarios. Useful for A/B control, the IR receiver shown controls a relay from an infrared beam that has a pulsed tone-modulated signal. Ql is the photo receptor feeding op amp IC1, tone decoder IC2, and flip-flop IC3. IC5 turns off the indicator LEDs after about 15 seconds. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes an infrared (IR) receiver for A/B control applications, leveraging a pulsed tone-modulated signal to operate a relay. The core of the system includes a photo receptor, designated as Q1, which detects the incoming IR signal. This signal is then processed by an operational amplifier (op amp) IC1, which amplifies the weak signal received from Q1 to a usable level.
Following amplification, the signal is sent to a tone decoder IC2. This component is responsible for demodulating the tone-modulated signal, extracting the relevant control information necessary for the operation of the relay. The output from IC2 is then fed into a flip-flop IC3, which provides a stable output that can be used to control the relay's switching action. The flip-flop ensures that the relay remains in the desired state until a new command is received, enabling reliable A/B switching.
Additionally, the circuit includes an indicator LED system that provides visual feedback on the relay's status. This is managed by IC5, which is designed to turn off the indicator LEDs approximately 15 seconds after the last command is issued. This feature helps in conserving power and reducing unnecessary visual distractions when the system is idle.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient for applications requiring remote control via infrared signals, offering a straightforward yet effective solution for A/B control scenarios. Useful for A/B control, the IR receiver shown controls a relay from an infrared beam that has a pulsed tone-modulated signal. Ql is the photo receptor feeding op amp IC1, tone decoder IC2, and flip-flop IC3. IC5 turns off the indicator LEDs after about 15 seconds. 🔗 External reference