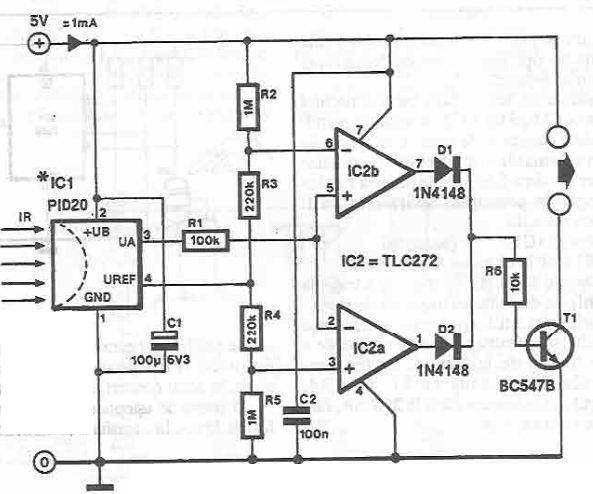
IR DETECTOR CIRCUIT
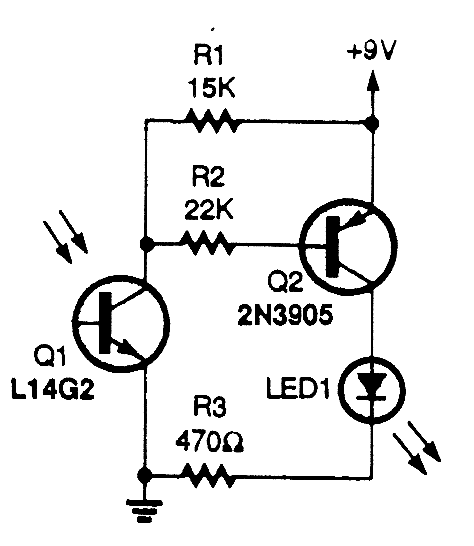
The circuit employs an infrared (IR) phototransistor, designated as Q1, to sense the IR output signal from a remote control. The output from Q1 is then amplified by a PNP transistor, labeled Q2, which activates LED1. This illumination indicates that an infrared signal has been detected by the phototransistor, confirming the functionality of the remote control.
The described circuit operates as a basic IR signal detection system. The IR phototransistor Q1 is sensitive to infrared light emitted by remote control devices. When the remote control is activated, it emits a modulated IR signal, which the phototransistor detects. The phototransistor is typically connected in a common emitter configuration, allowing it to convert the received IR light into a small current.
The output current from Q1 is insufficient to drive an LED directly, hence the inclusion of the PNP transistor Q2. When Q1 detects the IR signal, it generates a collector current that flows into the base of Q2. This base current turns Q2 on, allowing a larger current to flow from its collector to emitter, thus powering LED1. The LED lights up as a visual indicator that an IR signal has been successfully received.
Proper biasing of both transistors is essential for the circuit's functionality. Resistors may be used in series with the phototransistor and the base of the PNP transistor to ensure they operate within their specified ranges. Additionally, a current-limiting resistor should be placed in series with LED1 to prevent excessive current from damaging it.
This circuit can be used in various applications, including remote control verification systems, IR signal testing devices, and simple home automation projects, where it is necessary to confirm the operation of remote control devices. The simplicity of the design makes it suitable for educational purposes as well, demonstrating the principles of phototransistor operation and transistor amplification.The circuit uses an IR phototransistor, Q1, to detect a remote control`s IR output signal. A PNP transistor, Q2, then amplifies Q1`s output and lights LED1. That indicates that an infrared signal has been detected by the phototransistor, or in other words, that your remote control works. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a basic IR signal detection system. The IR phototransistor Q1 is sensitive to infrared light emitted by remote control devices. When the remote control is activated, it emits a modulated IR signal, which the phototransistor detects. The phototransistor is typically connected in a common emitter configuration, allowing it to convert the received IR light into a small current.
The output current from Q1 is insufficient to drive an LED directly, hence the inclusion of the PNP transistor Q2. When Q1 detects the IR signal, it generates a collector current that flows into the base of Q2. This base current turns Q2 on, allowing a larger current to flow from its collector to emitter, thus powering LED1. The LED lights up as a visual indicator that an IR signal has been successfully received.
Proper biasing of both transistors is essential for the circuit's functionality. Resistors may be used in series with the phototransistor and the base of the PNP transistor to ensure they operate within their specified ranges. Additionally, a current-limiting resistor should be placed in series with LED1 to prevent excessive current from damaging it.
This circuit can be used in various applications, including remote control verification systems, IR signal testing devices, and simple home automation projects, where it is necessary to confirm the operation of remote control devices. The simplicity of the design makes it suitable for educational purposes as well, demonstrating the principles of phototransistor operation and transistor amplification.The circuit uses an IR phototransistor, Q1, to detect a remote control`s IR output signal. A PNP transistor, Q2, then amplifies Q1`s output and lights LED1. That indicates that an infrared signal has been detected by the phototransistor, or in other words, that your remote control works. 🔗 External reference