ISO107 ripple reduction circuit
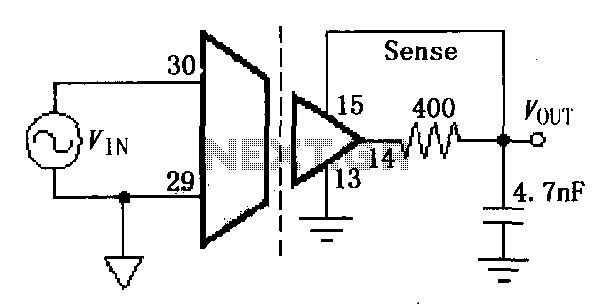
The ISO107 ripple reduction circuit includes an RC high-pass filter at the output to filter the output voltage ripple without impacting the DC characteristics. This configuration allows for a reduction of the 800kHz ripple voltage to less than 3mVp-p.
The ISO107 is a precision isolation amplifier designed to provide high common-mode rejection and low noise performance. In applications where power supply ripple can affect the performance of sensitive analog circuits, implementing a ripple reduction mechanism is crucial. The circuit utilizes an RC high-pass filter, which consists of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) in series, to effectively attenuate high-frequency noise while allowing the desired DC signal to pass through.
The RC filter operates by allowing AC signals to pass while blocking DC signals. The cutoff frequency of the filter is determined by the values of R and C, calculated using the formula:
\[ f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC} \]
where \( f_c \) is the cutoff frequency. For the ISO107 application, careful selection of resistor and capacitor values ensures that the cutoff frequency is set above the ripple frequency (800kHz in this case) while maintaining the integrity of the DC signal.
By configuring the circuit this way, the output voltage ripple can be significantly reduced to less than 3mVp-p, which is critical for applications requiring high precision and stability. This design not only enhances the performance of the ISO107 but also extends its usability in environments where ripple noise can compromise the accuracy of the measurements or signals being processed.
In summary, the combination of the ISO107 with an RC high-pass filter presents an effective solution for reducing ripple voltage, ensuring cleaner, more reliable output for sensitive electronic applications.As shown for the ISO107 ripple reduction circuit. The circuit at the output plus an RC high-pass filter for filtering the output voltage ripple, without affecting the DC characteristics conditions 800kHz ripple voltage can be reduced to <3mVp-p.
The ISO107 is a precision isolation amplifier designed to provide high common-mode rejection and low noise performance. In applications where power supply ripple can affect the performance of sensitive analog circuits, implementing a ripple reduction mechanism is crucial. The circuit utilizes an RC high-pass filter, which consists of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) in series, to effectively attenuate high-frequency noise while allowing the desired DC signal to pass through.
The RC filter operates by allowing AC signals to pass while blocking DC signals. The cutoff frequency of the filter is determined by the values of R and C, calculated using the formula:
\[ f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC} \]
where \( f_c \) is the cutoff frequency. For the ISO107 application, careful selection of resistor and capacitor values ensures that the cutoff frequency is set above the ripple frequency (800kHz in this case) while maintaining the integrity of the DC signal.
By configuring the circuit this way, the output voltage ripple can be significantly reduced to less than 3mVp-p, which is critical for applications requiring high precision and stability. This design not only enhances the performance of the ISO107 but also extends its usability in environments where ripple noise can compromise the accuracy of the measurements or signals being processed.
In summary, the combination of the ISO107 with an RC high-pass filter presents an effective solution for reducing ripple voltage, ensuring cleaner, more reliable output for sensitive electronic applications.As shown for the ISO107 ripple reduction circuit. The circuit at the output plus an RC high-pass filter for filtering the output voltage ripple, without affecting the DC characteristics conditions 800kHz ripple voltage can be reduced to <3mVp-p.