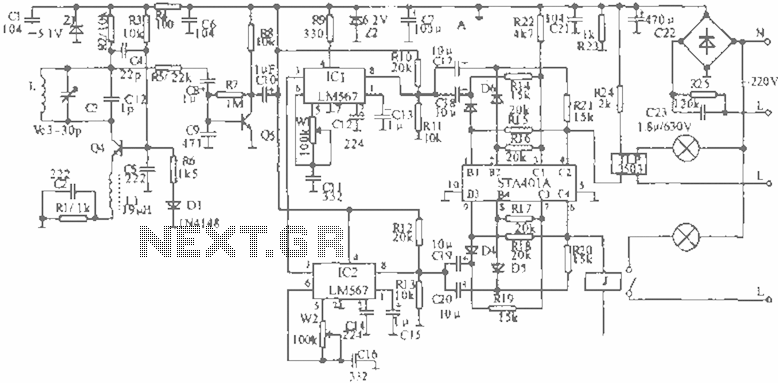
Isolated send receive ring circuit diagram XTR105 RCV420
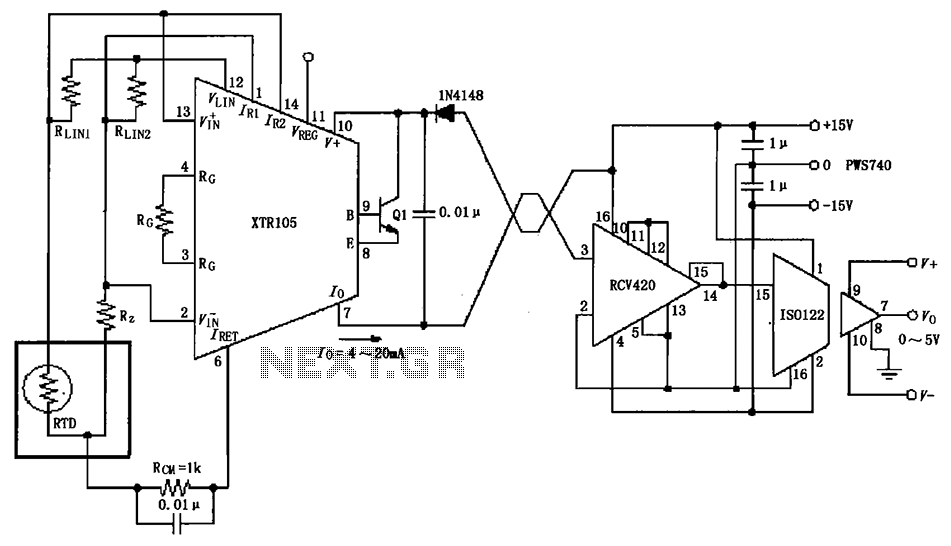
The RTD temperature sensor, as illustrated in the subsequent figure, collects temperature data from the field. This data is converted into a voltage signal by the XTR105, which is then transformed into a 4 to 20 mA current output. The signal is transmitted using twisted pair wiring and received by the RCV420. Following this, an isolation amplifier, ISO122, is employed to provide an output voltage ranging from 0 to 5V. The circuit exhibits excellent anti-jamming performance, making it suitable for long-distance transmission in environments with significant interference. The figure depicts a three-wire RTD connection; if a two-wire RTD connection is utilized, RLIN2 should be removed.
The circuit design begins with the RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensor, which operates by varying its resistance in response to temperature changes. The XTR105 is a precision current loop transmitter that converts the resistance change into a proportional voltage signal. This voltage is then converted into a 4 to 20 mA current output, a standard in industrial applications for ensuring reliable signal transmission over long distances.
Twisted pair wiring is utilized for the transmission of the 4 to 20 mA signal to minimize electromagnetic interference, which is critical in environments with high levels of electrical noise. The RCV420 receiver is designed to accurately convert the current signal back into a usable voltage signal. This receiver is particularly effective in maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
The ISO122 isolation amplifier plays a crucial role in protecting the measurement system from ground loops and high common-mode voltages, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and within the desired range of 0 to 5V. This isolation is vital for maintaining measurement accuracy and system reliability, especially in industrial settings.
Furthermore, the circuit’s design allows for flexibility in RTD connection configurations. The three-wire RTD connection method compensates for lead resistance, enhancing measurement accuracy. However, if a two-wire RTD configuration is preferred, the removal of RLIN2 is necessary to adapt the circuit accordingly. Overall, this circuit design is optimized for robustness, accuracy, and adaptability in various temperature measurement applications. As shown in FIG later, RTD temperature collected in the field, which was converted into a voltage by the XTR105 voltage is converted into 4 ~ 20mA current output, and then the twisted pair transmission, received by RCV420, after isolation amplifier ISO122 isolation amplifier, output 0 ~ 5V voltage. Excellent anti-jamming performance of the circuit can be used for long-distance transmission interference or big occasions.
The figure for the three-wire RTD connection, if used for two-wire RTD connection, remove RLIN2.
The circuit design begins with the RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensor, which operates by varying its resistance in response to temperature changes. The XTR105 is a precision current loop transmitter that converts the resistance change into a proportional voltage signal. This voltage is then converted into a 4 to 20 mA current output, a standard in industrial applications for ensuring reliable signal transmission over long distances.
Twisted pair wiring is utilized for the transmission of the 4 to 20 mA signal to minimize electromagnetic interference, which is critical in environments with high levels of electrical noise. The RCV420 receiver is designed to accurately convert the current signal back into a usable voltage signal. This receiver is particularly effective in maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
The ISO122 isolation amplifier plays a crucial role in protecting the measurement system from ground loops and high common-mode voltages, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and within the desired range of 0 to 5V. This isolation is vital for maintaining measurement accuracy and system reliability, especially in industrial settings.
Furthermore, the circuit’s design allows for flexibility in RTD connection configurations. The three-wire RTD connection method compensates for lead resistance, enhancing measurement accuracy. However, if a two-wire RTD configuration is preferred, the removal of RLIN2 is necessary to adapt the circuit accordingly. Overall, this circuit design is optimized for robustness, accuracy, and adaptability in various temperature measurement applications. As shown in FIG later, RTD temperature collected in the field, which was converted into a voltage by the XTR105 voltage is converted into 4 ~ 20mA current output, and then the twisted pair transmission, received by RCV420, after isolation amplifier ISO122 isolation amplifier, output 0 ~ 5V voltage. Excellent anti-jamming performance of the circuit can be used for long-distance transmission interference or big occasions.
The figure for the three-wire RTD connection, if used for two-wire RTD connection, remove RLIN2.