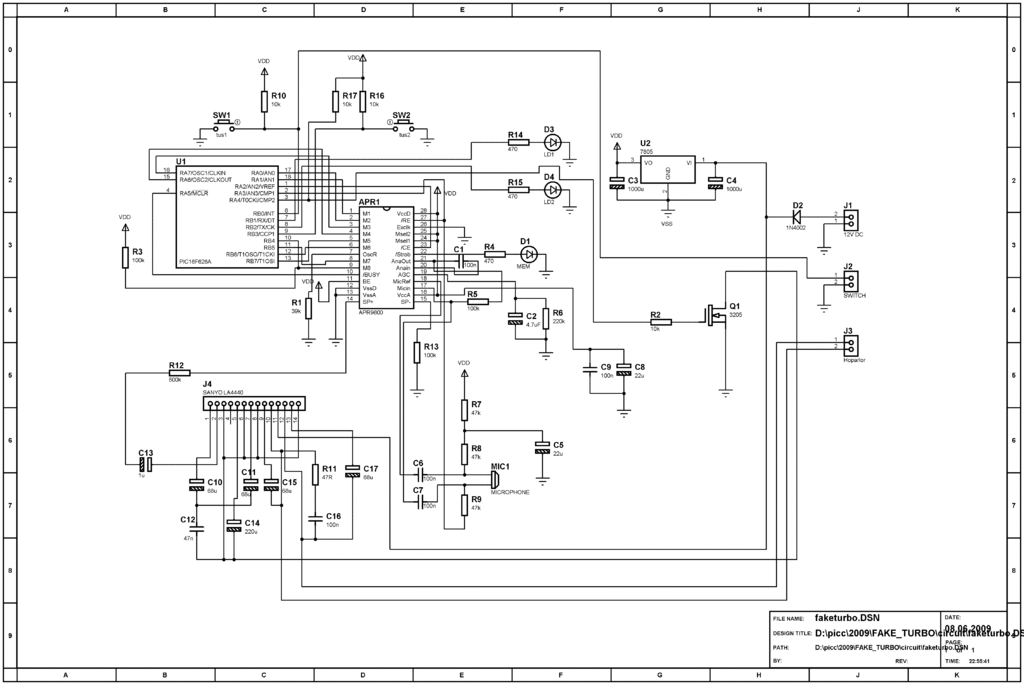
jet engine sound generator
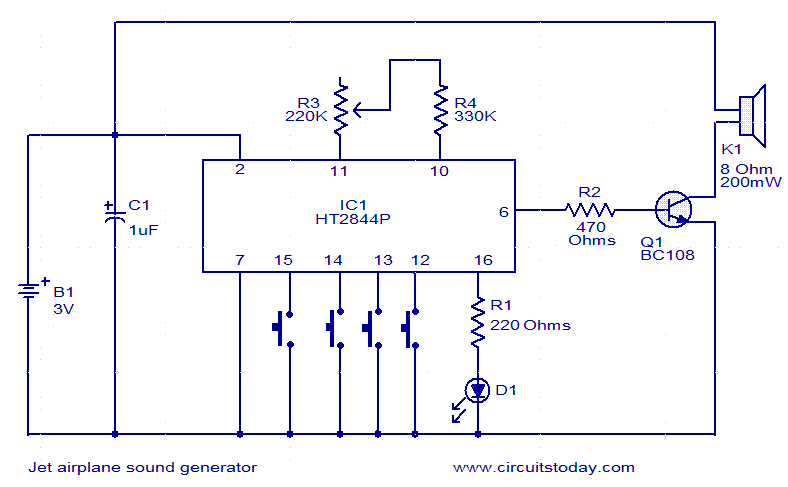
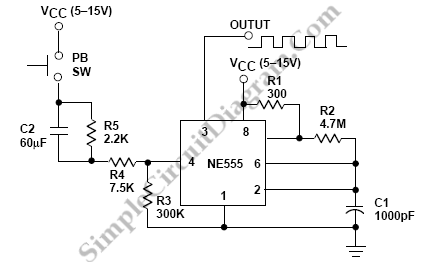
This jet engine sound generator circuit utilizes the sound generator IC HT2844P from Holtek Semiconductors. The IC is capable of producing four distinct sounds: the low-speed sound of a jet engine, the high-speed sound of a jet engine, a missile sound, and a machine gun sound. Each sound can be triggered by connecting pins 12, 13, 14, and 15 to ground using the corresponding push button switches. Resistor R3 allows for manual adjustment of the sound speed, while LED D1 provides a visual indication of the sound being generated.
The jet engine sound generator circuit is designed to create realistic audio effects for various applications, such as model aircraft or sound simulation projects. The HT2844P IC serves as the core component, featuring integrated sound generation capabilities that simplify the circuit design. The four different sound outputs can be selected through a straightforward user interface, implemented with push button switches connected to specific pins on the IC.
The push button switches act as momentary contacts that, when pressed, connect the designated pins to ground. This action activates the corresponding sound effect, allowing for an interactive experience. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components, such as capacitors for noise filtering and improved sound quality.
Resistor R3 plays a crucial role in controlling the output frequency of the sound generator, enabling users to manually increase or decrease the speed of the sound effects. This feature can be particularly useful for achieving a more dynamic audio experience, simulating the varying speeds of jet engines or other sound effects.
LED D1 is included in the circuit as a visual feedback mechanism. It illuminates when a sound is being generated, providing an effective means of indicating operational status. This feature not only enhances user interaction but also aids in troubleshooting by confirming that the circuit is functioning correctly.
Overall, this jet engine sound generator circuit represents a versatile and engaging solution for sound simulation, leveraging the capabilities of the HT2844P IC to deliver a range of audio effects with user-friendly controls.This jet engine sound generator circuit is based on the sound generator IC HT2844P from Holtek Semiconductors. This particular IC can make four sounds namely low speed sound of jet engine, high speed sound of jet engine, missile sound and machine gun sound.
Each of these sounds can be activated by connecting the pins 12, 13, 14and 15 to ground by using the respective push button switches. Resistor R3 can be used for manually increasing or decreasing the speed. LED D1 gives a visible indication of the sound. 🔗 External reference
The jet engine sound generator circuit is designed to create realistic audio effects for various applications, such as model aircraft or sound simulation projects. The HT2844P IC serves as the core component, featuring integrated sound generation capabilities that simplify the circuit design. The four different sound outputs can be selected through a straightforward user interface, implemented with push button switches connected to specific pins on the IC.
The push button switches act as momentary contacts that, when pressed, connect the designated pins to ground. This action activates the corresponding sound effect, allowing for an interactive experience. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components, such as capacitors for noise filtering and improved sound quality.
Resistor R3 plays a crucial role in controlling the output frequency of the sound generator, enabling users to manually increase or decrease the speed of the sound effects. This feature can be particularly useful for achieving a more dynamic audio experience, simulating the varying speeds of jet engines or other sound effects.
LED D1 is included in the circuit as a visual feedback mechanism. It illuminates when a sound is being generated, providing an effective means of indicating operational status. This feature not only enhances user interaction but also aids in troubleshooting by confirming that the circuit is functioning correctly.
Overall, this jet engine sound generator circuit represents a versatile and engaging solution for sound simulation, leveraging the capabilities of the HT2844P IC to deliver a range of audio effects with user-friendly controls.This jet engine sound generator circuit is based on the sound generator IC HT2844P from Holtek Semiconductors. This particular IC can make four sounds namely low speed sound of jet engine, high speed sound of jet engine, missile sound and machine gun sound.
Each of these sounds can be activated by connecting the pins 12, 13, 14and 15 to ground by using the respective push button switches. Resistor R3 can be used for manually increasing or decreasing the speed. LED D1 gives a visible indication of the sound. 🔗 External reference