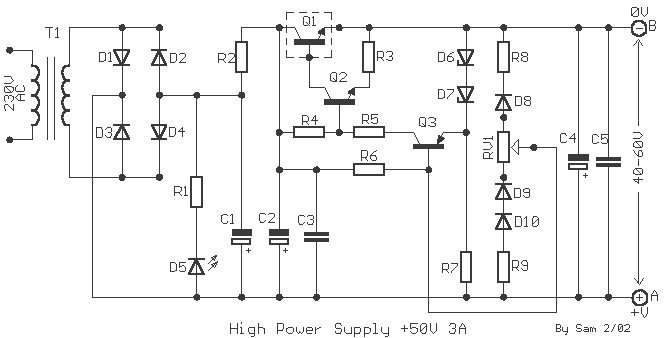
Joule Thief Power Overload circuit
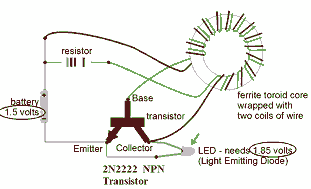
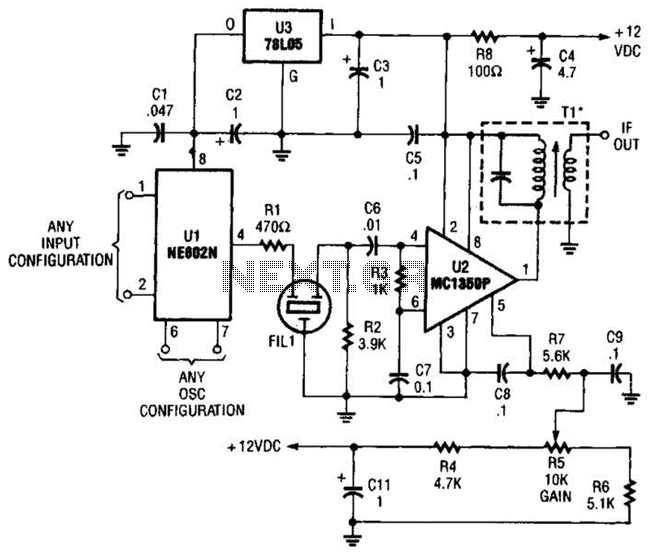
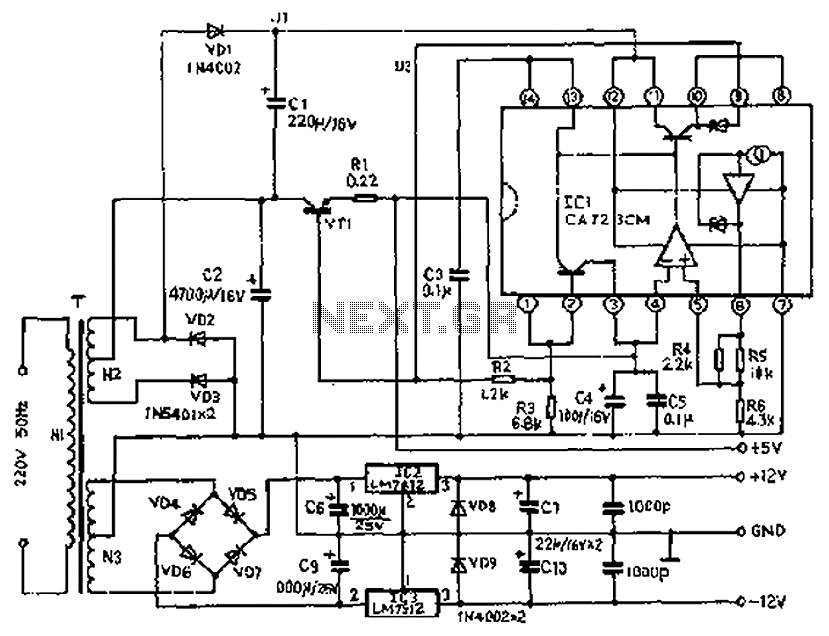
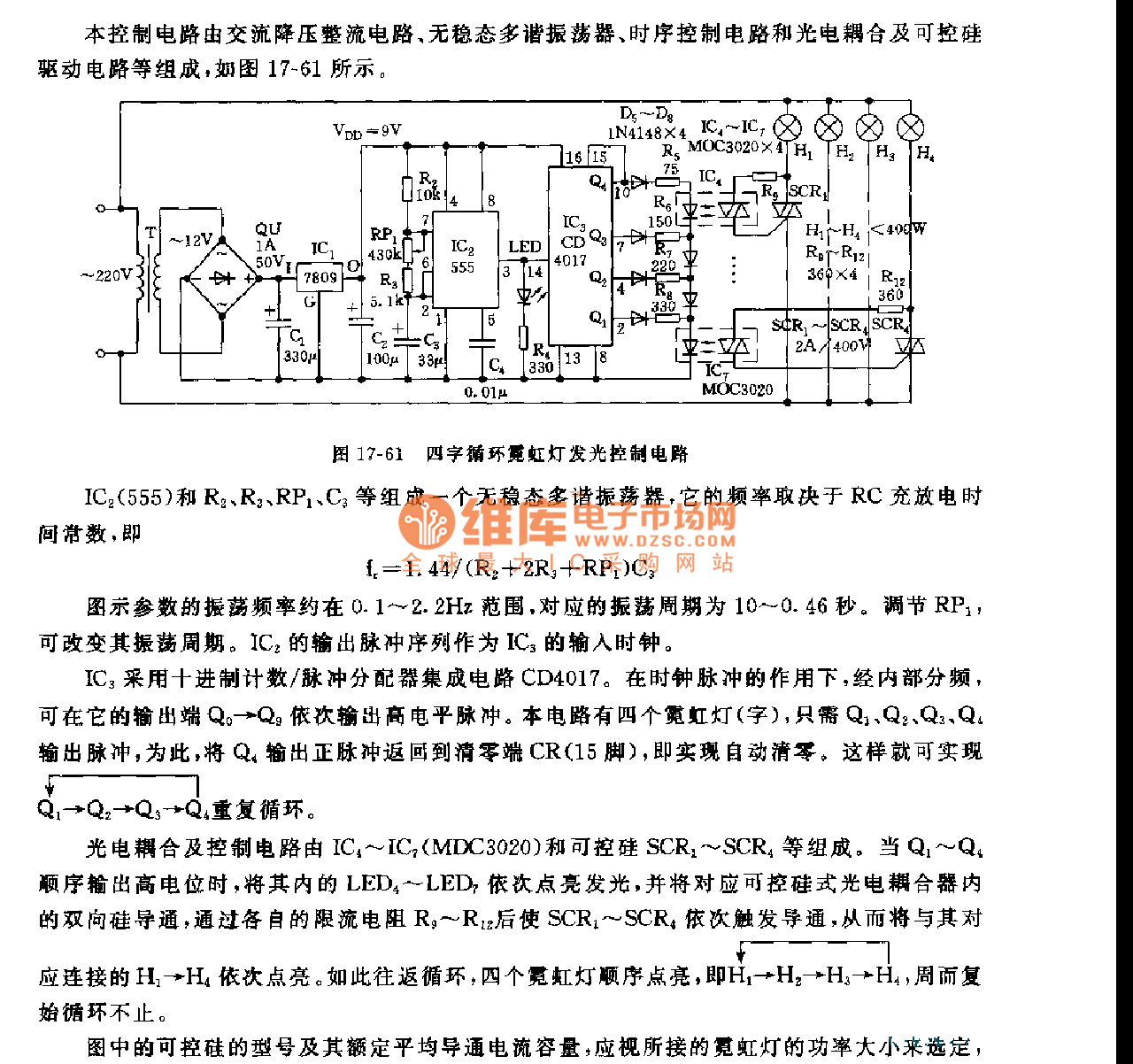
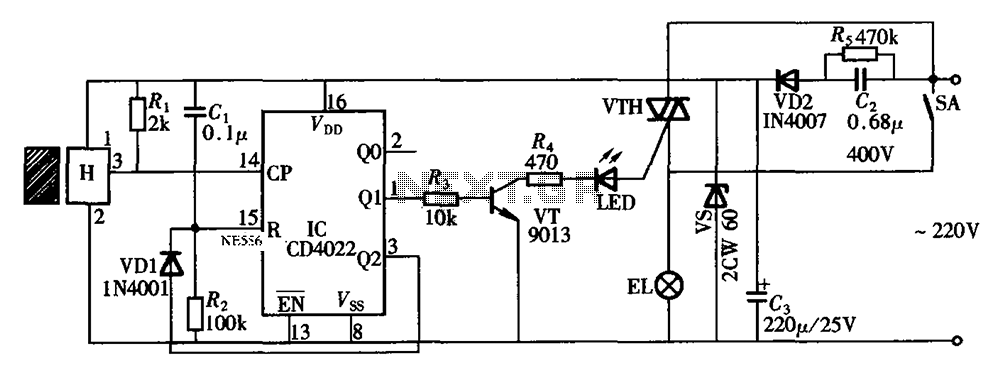
This circuit is known as the Joule Thief. For those unfamiliar with it, an image of the circuit is provided.
The Joule Thief is a minimalist circuit designed to extract usable voltage from a low-voltage power source, such as a single AA or AAA battery, which may be nearing depletion. The circuit is particularly effective in harvesting energy from batteries that would otherwise be discarded due to insufficient voltage for standard applications.
The core components of a Joule Thief circuit typically include a transistor, a resistor, a toroidal inductor, and a diode. The transistor acts as a switch that alternates the current through the inductor, creating a magnetic field. When the magnetic field collapses, it induces a higher voltage in the inductor, which is then rectified by the diode and can be used to power a load, such as an LED.
The basic operation begins when the circuit is powered on. A small current flows through the resistor into the base of the transistor, turning it on and allowing a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This current energizes the inductor, building a magnetic field around it. Once the magnetic field reaches a certain level, the transistor turns off, causing the magnetic field to collapse rapidly. This collapse induces a high voltage across the inductor, which is then directed through the diode to the load.
The Joule Thief circuit is highly efficient, capable of operating with input voltages as low as 0.5 volts, making it an ideal solution for applications requiring low-power energy harvesting. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice among hobbyists and engineers looking to maximize the utility of depleted batteries.Well, this particular circuit is called the Joule Thief, and for those of you that arent familiar with the circuit, here is an image of it. 🔗 External reference
The Joule Thief is a minimalist circuit designed to extract usable voltage from a low-voltage power source, such as a single AA or AAA battery, which may be nearing depletion. The circuit is particularly effective in harvesting energy from batteries that would otherwise be discarded due to insufficient voltage for standard applications.
The core components of a Joule Thief circuit typically include a transistor, a resistor, a toroidal inductor, and a diode. The transistor acts as a switch that alternates the current through the inductor, creating a magnetic field. When the magnetic field collapses, it induces a higher voltage in the inductor, which is then rectified by the diode and can be used to power a load, such as an LED.
The basic operation begins when the circuit is powered on. A small current flows through the resistor into the base of the transistor, turning it on and allowing a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This current energizes the inductor, building a magnetic field around it. Once the magnetic field reaches a certain level, the transistor turns off, causing the magnetic field to collapse rapidly. This collapse induces a high voltage across the inductor, which is then directed through the diode to the load.
The Joule Thief circuit is highly efficient, capable of operating with input voltages as low as 0.5 volts, making it an ideal solution for applications requiring low-power energy harvesting. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice among hobbyists and engineers looking to maximize the utility of depleted batteries.Well, this particular circuit is called the Joule Thief, and for those of you that arent familiar with the circuit, here is an image of it. 🔗 External reference