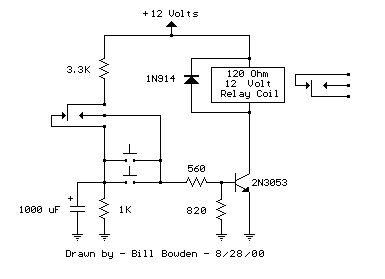
Laser torch schematic
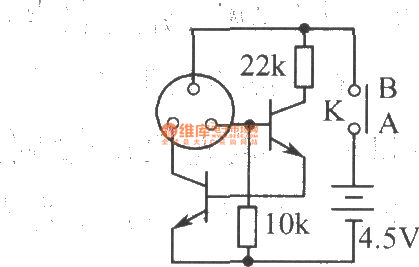
The laser torch is an economical device with impressive cost-performance characteristics. Its primary feature is the exceptional performance of the condenser, allowing for an optical range of 1200 to 1500 meters. The beam remains focused and small even at distances of several hundred meters, making it suitable for applications in education, guided tours, and entertainment. Testing has demonstrated its capability for long-distance protective guarding and remote data transmission. The schematic for the laser torch is illustrated in the accompanying figure, featuring surface-mount device (SMD) components that contribute to its compact design. The laser power is significant, and direct exposure to the human eye should be avoided.
The laser torch circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to produce a focused beam of light. At the heart of the system is the laser diode, which generates the laser light when an electrical current passes through it. The diode is usually driven by a constant current source to ensure stable operation and prevent damage due to overheating or excessive current.
A condenser lens is an essential component, strategically positioned in front of the laser diode. This lens is designed to collimate the light emitted from the diode, allowing it to travel long distances while maintaining a small spot size. The optical design of the lens is critical for achieving the desired beam characteristics, and it should be chosen based on the specific application requirements.
Power management is another crucial aspect of the laser torch circuit. A power supply circuit is implemented to convert input voltage to the appropriate level needed for the laser diode. This may involve the use of voltage regulators or DC-DC converters to ensure that the laser operates within its specified voltage and current ratings.
To enhance portability and usability, the laser torch may include a microcontroller or a simple switch mechanism for controlling the laser operation. This allows users to easily turn the device on and off, as well as potentially control the laser's intensity or pulse width for various applications.
Safety features are also vital in the design of a laser torch. A safety interlock may be included to prevent accidental activation, and warning indicators can be implemented to alert users when the laser is in operation. Additionally, proper housing and protective components should be designed to minimize the risk of direct eye exposure to the laser beam.
Overall, the laser torch circuit combines advanced optical components, efficient power management, and user-friendly controls to deliver a compact and powerful tool suitable for a wide range of applications.Laser torch is cheap and has high cost performance. The main feature is the excellent performance of the condenser, and the optical rangeis up to 1200m ~ 1500m, and the spot is still small from a few hundred meters in visual observation, so it is widely used in teaching, guided tours and entertainment. According to tests, it can be used for long-distance of the protective guard and the remote data transmission.
Laser torch schematic is shown in Fig, the components are SMD components, so the device is small, and the power of laser is great, it can not direct shoot the human eye. 🔗 External reference
The laser torch circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to produce a focused beam of light. At the heart of the system is the laser diode, which generates the laser light when an electrical current passes through it. The diode is usually driven by a constant current source to ensure stable operation and prevent damage due to overheating or excessive current.
A condenser lens is an essential component, strategically positioned in front of the laser diode. This lens is designed to collimate the light emitted from the diode, allowing it to travel long distances while maintaining a small spot size. The optical design of the lens is critical for achieving the desired beam characteristics, and it should be chosen based on the specific application requirements.
Power management is another crucial aspect of the laser torch circuit. A power supply circuit is implemented to convert input voltage to the appropriate level needed for the laser diode. This may involve the use of voltage regulators or DC-DC converters to ensure that the laser operates within its specified voltage and current ratings.
To enhance portability and usability, the laser torch may include a microcontroller or a simple switch mechanism for controlling the laser operation. This allows users to easily turn the device on and off, as well as potentially control the laser's intensity or pulse width for various applications.
Safety features are also vital in the design of a laser torch. A safety interlock may be included to prevent accidental activation, and warning indicators can be implemented to alert users when the laser is in operation. Additionally, proper housing and protective components should be designed to minimize the risk of direct eye exposure to the laser beam.
Overall, the laser torch circuit combines advanced optical components, efficient power management, and user-friendly controls to deliver a compact and powerful tool suitable for a wide range of applications.Laser torch is cheap and has high cost performance. The main feature is the excellent performance of the condenser, and the optical rangeis up to 1200m ~ 1500m, and the spot is still small from a few hundred meters in visual observation, so it is widely used in teaching, guided tours and entertainment. According to tests, it can be used for long-distance of the protective guard and the remote data transmission.
Laser torch schematic is shown in Fig, the components are SMD components, so the device is small, and the power of laser is great, it can not direct shoot the human eye. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713