Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit
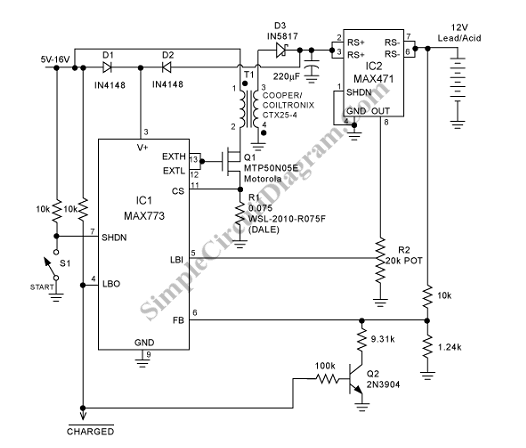
To charge lead-acid batteries, a circuit can be utilized that consists of a current-limited power supply and a flyback converter topology.
The described circuit for charging lead-acid batteries employs a current-limited power supply in conjunction with a flyback converter configuration. This design is effective in ensuring that the batteries receive the appropriate charging current without exceeding their maximum ratings, thus preventing damage and prolonging battery life.
The current-limited power supply is essential for regulating the voltage and current supplied to the battery. It typically includes a transformer, rectifier, and filtering components to convert the AC input into a stable DC output. The flyback converter topology is particularly advantageous in this application due to its ability to provide electrical isolation between the input and output while also allowing for efficient energy transfer.
In the flyback converter, energy is stored in the magnetic field of the transformer during the on-time of the switching device (usually a MOSFET). When the switch is turned off, the stored energy is released to the output through a diode, which rectifies the voltage for charging the battery. This method allows for high efficiency and compact design, making it suitable for applications where space is limited.
The circuit may also incorporate additional features such as over-voltage protection, temperature compensation, and status indicators to enhance functionality and safety. Overall, this charging circuit design is an effective solution for maintaining lead-acid batteries in optimal condition.To charge lead-acid batteries we can use this circuit that consist of a current-limited power supply and a flyback converter topology. Here is the schematic.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit for charging lead-acid batteries employs a current-limited power supply in conjunction with a flyback converter configuration. This design is effective in ensuring that the batteries receive the appropriate charging current without exceeding their maximum ratings, thus preventing damage and prolonging battery life.
The current-limited power supply is essential for regulating the voltage and current supplied to the battery. It typically includes a transformer, rectifier, and filtering components to convert the AC input into a stable DC output. The flyback converter topology is particularly advantageous in this application due to its ability to provide electrical isolation between the input and output while also allowing for efficient energy transfer.
In the flyback converter, energy is stored in the magnetic field of the transformer during the on-time of the switching device (usually a MOSFET). When the switch is turned off, the stored energy is released to the output through a diode, which rectifies the voltage for charging the battery. This method allows for high efficiency and compact design, making it suitable for applications where space is limited.
The circuit may also incorporate additional features such as over-voltage protection, temperature compensation, and status indicators to enhance functionality and safety. Overall, this charging circuit design is an effective solution for maintaining lead-acid batteries in optimal condition.To charge lead-acid batteries we can use this circuit that consist of a current-limited power supply and a flyback converter topology. Here is the schematic.. 🔗 External reference