LED Flasher Circuit Using 555 Timer IC Schematic Diagram
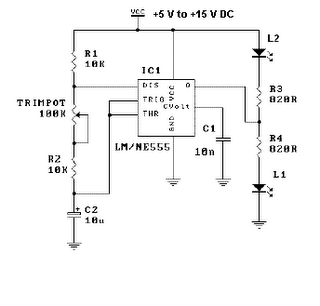
This is a simple LED flasher project that utilizes a common 555 timer integrated circuit (IC) for its operation. It is configured in astable mode, which means its output functions as a square wave oscillator. Two LEDs are connected to its output in such a manner that when one LED is ON, the other LED turns OFF. The circuit comprises only 10 simple components that can be easily sourced from any electronics shop. Capacitor C2 charges exponentially through resistors R1, R2, and the resistance of a trimpot. When C2 charges to approximately 2/3 of VCC, it stops charging and discharges to about 1/3 of VCC through R2 and the trimpot resistance via pin 7. This represents the standard operation of a 555 timer. When a VCC of 5 V to 15 V DC is applied to the circuit, the LED will begin to flash. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the potentiometer or trimpot.
The parts list for this simple LED project includes the following components:
1. 555 Timer IC
2. Resistors (R1, R2)
3. Trimpot (Potentiometer)
4. Capacitor (C2)
5. Two LEDs
6. Power supply (5 V to 15 V DC)
In this LED flasher circuit, the 555 timer operates in astable mode, generating a continuous square wave output. The configuration allows for a self-oscillating circuit, where the timing components (R1, R2, and C2) determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal. The LEDs are connected in a complementary fashion, ensuring that only one LED is illuminated at any given time, creating a flashing effect.
The charging and discharging process of capacitor C2 is crucial for the operation of the circuit. As C2 charges through the resistors, it reaches a threshold voltage of 2/3 VCC, at which point the 555 timer toggles its output state. The discharge occurs through R2 and the trimpot, allowing C2 to drop to 1/3 VCC before the cycle repeats. By adjusting the trimpot, the resistance in the charging path can be varied, effectively changing the timing intervals and thus the flashing frequency of the LEDs.
This simple yet effective LED flasher circuit can serve various applications, including visual indicators, teaching aids for electronics students, or decorative lighting effects. The straightforward design and minimal component count make it an excellent project for beginners in electronics.This is a simple LED flasher project that uses a common 555 timer IC for its operation. It is configured as an astable mode which means that its output is a square wave oscillator. Two LEDs are connected to its output in such a way that when one LED is ON, the other LED will turn OFF. It uses only 10 simple parts that are easily available at any e lectronic shops. Capacitor C2 charges exponentially through resistors R1, R2 and the resistance of the trimpot. When C2 has charged to about 2/3 VCC it stops charging and it discharges to about 1/3 VCC through R2 and the trimpot resistance via pin 7. This is the standard operation of a 555 timer. When a Vcc of 5 V to 15 V DC is applied to the circuit, the LED will start to flash. The frequency of the flashing can be changed by varying the resistance of the potentiometer or trimpot.
Parts List The parts list of the simple LED project is as shown below. You are reading the Circuits of LED Flasher Circuit Using 555 Timer IC And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference
The parts list for this simple LED project includes the following components:
1. 555 Timer IC
2. Resistors (R1, R2)
3. Trimpot (Potentiometer)
4. Capacitor (C2)
5. Two LEDs
6. Power supply (5 V to 15 V DC)
In this LED flasher circuit, the 555 timer operates in astable mode, generating a continuous square wave output. The configuration allows for a self-oscillating circuit, where the timing components (R1, R2, and C2) determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal. The LEDs are connected in a complementary fashion, ensuring that only one LED is illuminated at any given time, creating a flashing effect.
The charging and discharging process of capacitor C2 is crucial for the operation of the circuit. As C2 charges through the resistors, it reaches a threshold voltage of 2/3 VCC, at which point the 555 timer toggles its output state. The discharge occurs through R2 and the trimpot, allowing C2 to drop to 1/3 VCC before the cycle repeats. By adjusting the trimpot, the resistance in the charging path can be varied, effectively changing the timing intervals and thus the flashing frequency of the LEDs.
This simple yet effective LED flasher circuit can serve various applications, including visual indicators, teaching aids for electronics students, or decorative lighting effects. The straightforward design and minimal component count make it an excellent project for beginners in electronics.This is a simple LED flasher project that uses a common 555 timer IC for its operation. It is configured as an astable mode which means that its output is a square wave oscillator. Two LEDs are connected to its output in such a way that when one LED is ON, the other LED will turn OFF. It uses only 10 simple parts that are easily available at any e lectronic shops. Capacitor C2 charges exponentially through resistors R1, R2 and the resistance of the trimpot. When C2 has charged to about 2/3 VCC it stops charging and it discharges to about 1/3 VCC through R2 and the trimpot resistance via pin 7. This is the standard operation of a 555 timer. When a Vcc of 5 V to 15 V DC is applied to the circuit, the LED will start to flash. The frequency of the flashing can be changed by varying the resistance of the potentiometer or trimpot.
Parts List The parts list of the simple LED project is as shown below. You are reading the Circuits of LED Flasher Circuit Using 555 Timer IC And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference