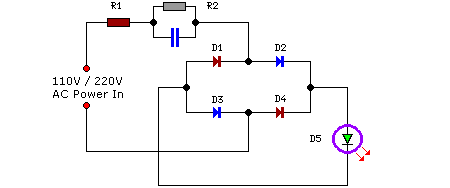
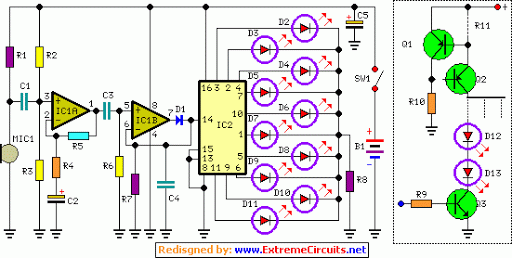
led light flasher
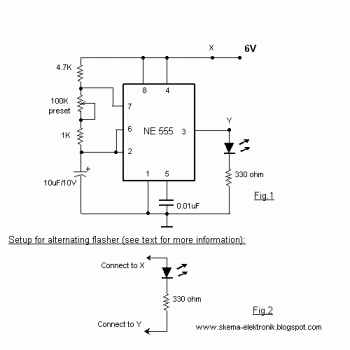
When the preset is set to its maximum, the LED flashes approximately every half second. This flashing rate can be increased by using a larger capacitor value, for instance, changing from 10µF to 22µF will result in a flashing rate of one second. The process of creating a printed circuit board (PCB) can be accomplished in simple steps. Begin by designing the PCB using PCB design software such as Eagle. After completing the design, print it on photo or glossy paper using a laser printer. Adhere the printed design to the copper side of the PCB and apply heat using a hot iron plate to transfer the ink onto the PCB, making it ready for the etching process. If a laser printer is unavailable, the design can be printed on standard paper and then copied onto glossy paper at a local copy service.
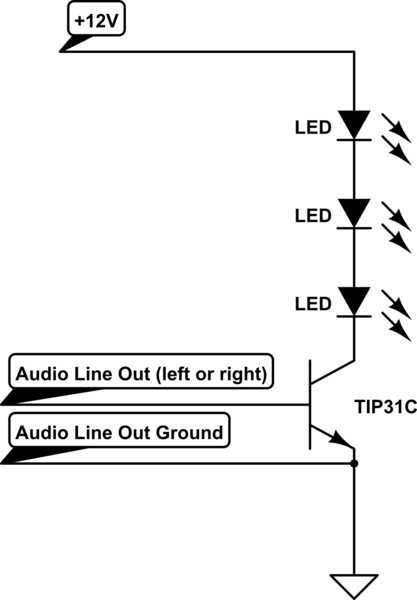
The circuit described revolves around an LED flashing mechanism controlled by a capacitor. The LED's flashing rate is determined by the RC time constant, which is influenced by the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values in the circuit. In this scenario, the initial capacitor value of 10µF allows the LED to flash every half second. By increasing the capacitance to 22µF, the time constant increases, resulting in a longer flashing interval of one second.
To implement this circuit, a basic astable multivibrator can be utilized, which consists of an operational amplifier or a timer IC configured to oscillate. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to ensure proper operation without exceeding its rated current. The resistor value should be calculated based on the supply voltage and the forward voltage drop of the LED.
The PCB design process involves several steps: First, the schematic diagram is created using the chosen PCB design software, ensuring all components are correctly connected. After verifying the design, the layout is generated, which includes the placement of traces, pads, and other necessary features. The design is then printed onto the chosen paper type.
When transferring the design to the PCB, it is crucial to ensure proper alignment and pressure during the heat application to achieve a successful transfer of the ink. After the transfer, the PCB must undergo an etching process to remove the unwanted copper, leaving only the desired traces for the circuit. This can be achieved using a suitable etching solution, such as ferric chloride, and requires careful handling and safety precautions.
Once the etching process is complete, the PCB can be cleaned and drilled for component placement. Components can then be soldered onto the PCB, completing the assembly of the flashing LED circuit. Proper testing should be conducted to ensure the circuit operates as intended, confirming the functionality of the LED flashing mechanism.With the preset at its max. the flashing rate of the LED is about 1/2 a second. It can be increased by increasing the value of the capacitor from 10uF to a higher value. For example if it is increased to 22uF the flashing rate becomes 1 second. Make a PCB in very easy steps. ! Create your PCB design using PCB designer software like Eagle, print out your design on photo paper or glossy paper with laserjet printer. Stick the printed design on the PCB (copper side) and then heat it using hot iron plate. The ink will stick on the PCB and it will be ready for etching process. Note: If you don`t have laserjet printer, then you can print the design on standard paper. Copy the printed design at Copy Service around your location (with glossy paper). 🔗 External reference
The circuit described revolves around an LED flashing mechanism controlled by a capacitor. The LED's flashing rate is determined by the RC time constant, which is influenced by the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values in the circuit. In this scenario, the initial capacitor value of 10µF allows the LED to flash every half second. By increasing the capacitance to 22µF, the time constant increases, resulting in a longer flashing interval of one second.
To implement this circuit, a basic astable multivibrator can be utilized, which consists of an operational amplifier or a timer IC configured to oscillate. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to ensure proper operation without exceeding its rated current. The resistor value should be calculated based on the supply voltage and the forward voltage drop of the LED.
The PCB design process involves several steps: First, the schematic diagram is created using the chosen PCB design software, ensuring all components are correctly connected. After verifying the design, the layout is generated, which includes the placement of traces, pads, and other necessary features. The design is then printed onto the chosen paper type.
When transferring the design to the PCB, it is crucial to ensure proper alignment and pressure during the heat application to achieve a successful transfer of the ink. After the transfer, the PCB must undergo an etching process to remove the unwanted copper, leaving only the desired traces for the circuit. This can be achieved using a suitable etching solution, such as ferric chloride, and requires careful handling and safety precautions.
Once the etching process is complete, the PCB can be cleaned and drilled for component placement. Components can then be soldered onto the PCB, completing the assembly of the flashing LED circuit. Proper testing should be conducted to ensure the circuit operates as intended, confirming the functionality of the LED flashing mechanism.With the preset at its max. the flashing rate of the LED is about 1/2 a second. It can be increased by increasing the value of the capacitor from 10uF to a higher value. For example if it is increased to 22uF the flashing rate becomes 1 second. Make a PCB in very easy steps. ! Create your PCB design using PCB designer software like Eagle, print out your design on photo paper or glossy paper with laserjet printer. Stick the printed design on the PCB (copper side) and then heat it using hot iron plate. The ink will stick on the PCB and it will be ready for etching process. Note: If you don`t have laserjet printer, then you can print the design on standard paper. Copy the printed design at Copy Service around your location (with glossy paper). 🔗 External reference