Light Activated Switch
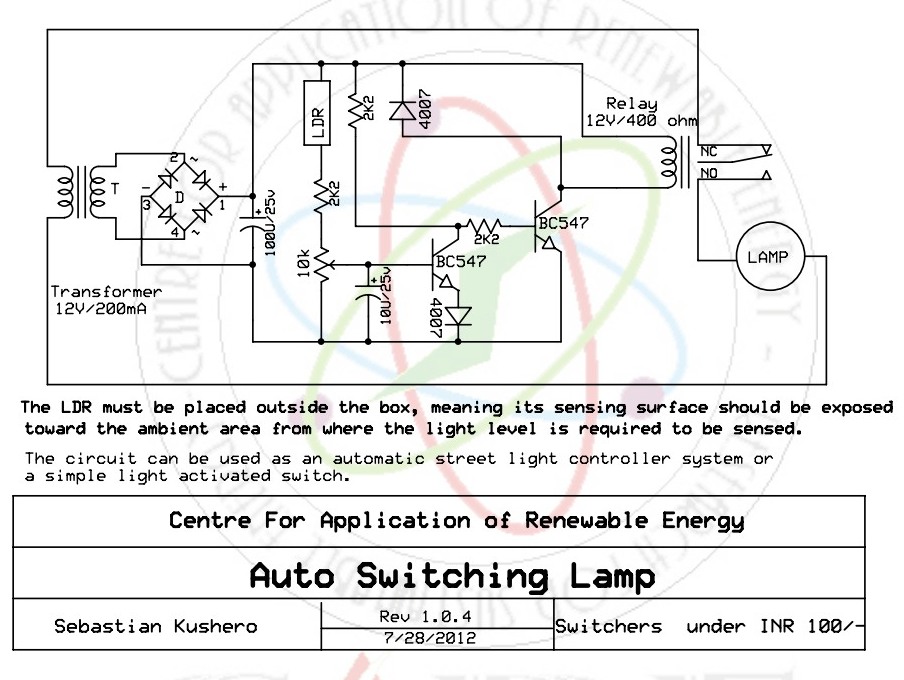
The light-activated switch circuit can be used for switching off a particular lamp or group of lamps in response to varying ambient light levels.
The light-activated switch circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) as the primary sensing element to detect ambient light levels. When the ambient light intensity falls below a predetermined threshold, the resistance of the LDR increases, triggering the circuit to switch off the connected lamp or lamps. This functionality is particularly useful in applications where automatic control of lighting is desired, such as in outdoor lighting systems or energy-saving applications.
The circuit typically includes a power supply, an LDR, a comparator or operational amplifier, and a relay or transistor to control the lamp. The LDR is connected to a voltage divider configuration, which allows the output voltage to vary based on the light intensity. The comparator compares this output voltage to a reference voltage set by a potentiometer. When the LDR's voltage falls below the reference voltage, the comparator activates the control element, either a relay or a transistor, to disconnect the power from the lamp.
Additional components may include a capacitor for noise filtering, diodes for reverse voltage protection, and resistors to limit current through the LDR and control the sensitivity of the circuit. The design can be further enhanced with adjustable thresholds for light sensitivity and time delays to prevent flickering due to transient light changes.
This circuit provides an efficient solution for automatically managing lighting based on environmental conditions, contributing to energy conservation and convenience in various applications.The light activated switch circuit can be used for switching OFF a particular lamp or group of lamps in response to the varying ambient light levels. The u.. 🔗 External reference
The light-activated switch circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) as the primary sensing element to detect ambient light levels. When the ambient light intensity falls below a predetermined threshold, the resistance of the LDR increases, triggering the circuit to switch off the connected lamp or lamps. This functionality is particularly useful in applications where automatic control of lighting is desired, such as in outdoor lighting systems or energy-saving applications.
The circuit typically includes a power supply, an LDR, a comparator or operational amplifier, and a relay or transistor to control the lamp. The LDR is connected to a voltage divider configuration, which allows the output voltage to vary based on the light intensity. The comparator compares this output voltage to a reference voltage set by a potentiometer. When the LDR's voltage falls below the reference voltage, the comparator activates the control element, either a relay or a transistor, to disconnect the power from the lamp.
Additional components may include a capacitor for noise filtering, diodes for reverse voltage protection, and resistors to limit current through the LDR and control the sensitivity of the circuit. The design can be further enhanced with adjustable thresholds for light sensitivity and time delays to prevent flickering due to transient light changes.
This circuit provides an efficient solution for automatically managing lighting based on environmental conditions, contributing to energy conservation and convenience in various applications.The light activated switch circuit can be used for switching OFF a particular lamp or group of lamps in response to the varying ambient light levels. The u.. 🔗 External reference