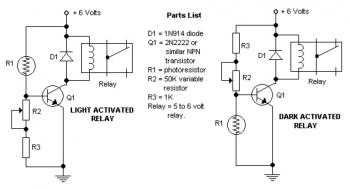
Rc 3 way Light Switch
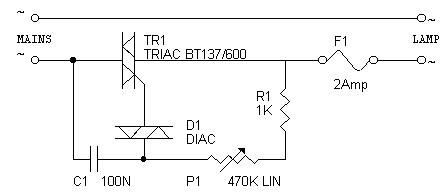
The receiver section was not illustrated as it is considered standard. The TRIAC switch section depicted below can be controlled using standard 4000 series CMOS logic.
The TRIAC switch section operates by utilizing a TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) component, which is a semiconductor device that can control power flow in AC circuits. The 4000 series CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) logic family provides the necessary control signals to trigger the TRIAC.
In a typical configuration, the TRIAC is connected in series with the load (e.g., a lamp or motor), and it is triggered into conduction when a gate pulse is applied. The gate pulse can be generated by the CMOS logic gates, which may include NOT, AND, OR, or NAND gates, depending on the desired control logic for the application.
The input to the CMOS logic can be derived from various sensors or switches, allowing for flexible control schemes. For example, a simple button press can trigger a logic high, which then activates the corresponding gate in the CMOS logic to send a pulse to the TRIAC gate.
The use of 4000 series CMOS logic is advantageous due to its low power consumption and compatibility with a wide range of input voltages, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or low-power applications. Additionally, the TRIAC allows for efficient control of AC loads, enabling features such as dimming lights or controlling the speed of motors.
It is essential to include protective components, such as snubber circuits, to prevent voltage spikes from damaging the TRIAC or the CMOS logic. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be implemented to ensure reliable operation of the TRIAC under load conditions.
Overall, the integration of a TRIAC with 4000 series CMOS logic provides a robust solution for controlling AC loads in various electronic applications.Did not bother to draw out the receiver section because it is quite ordinary. The TRIAC switch section shown below can be controlled by ordinary 4000 series CMOS logic. 🔗 External reference
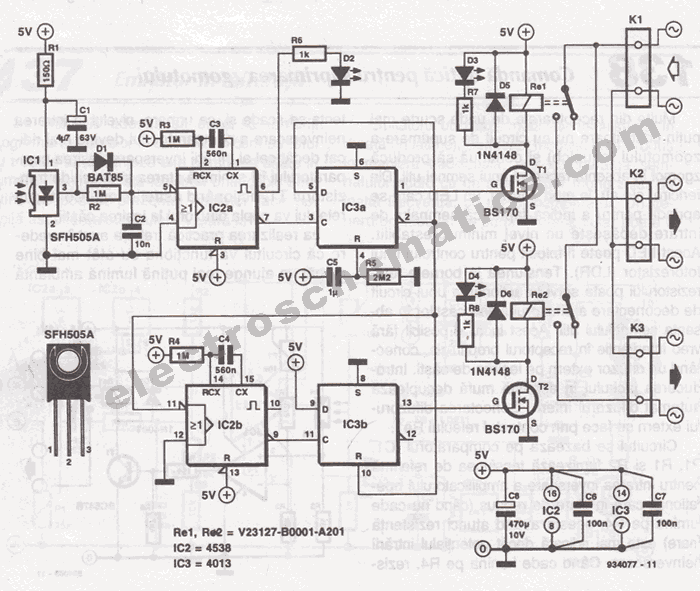
The TRIAC switch section operates by utilizing a TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) component, which is a semiconductor device that can control power flow in AC circuits. The 4000 series CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) logic family provides the necessary control signals to trigger the TRIAC.
In a typical configuration, the TRIAC is connected in series with the load (e.g., a lamp or motor), and it is triggered into conduction when a gate pulse is applied. The gate pulse can be generated by the CMOS logic gates, which may include NOT, AND, OR, or NAND gates, depending on the desired control logic for the application.
The input to the CMOS logic can be derived from various sensors or switches, allowing for flexible control schemes. For example, a simple button press can trigger a logic high, which then activates the corresponding gate in the CMOS logic to send a pulse to the TRIAC gate.
The use of 4000 series CMOS logic is advantageous due to its low power consumption and compatibility with a wide range of input voltages, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or low-power applications. Additionally, the TRIAC allows for efficient control of AC loads, enabling features such as dimming lights or controlling the speed of motors.
It is essential to include protective components, such as snubber circuits, to prevent voltage spikes from damaging the TRIAC or the CMOS logic. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be implemented to ensure reliable operation of the TRIAC under load conditions.
Overall, the integration of a TRIAC with 4000 series CMOS logic provides a robust solution for controlling AC loads in various electronic applications.Did not bother to draw out the receiver section because it is quite ordinary. The TRIAC switch section shown below can be controlled by ordinary 4000 series CMOS logic. 🔗 External reference