Light Chaser Circuit
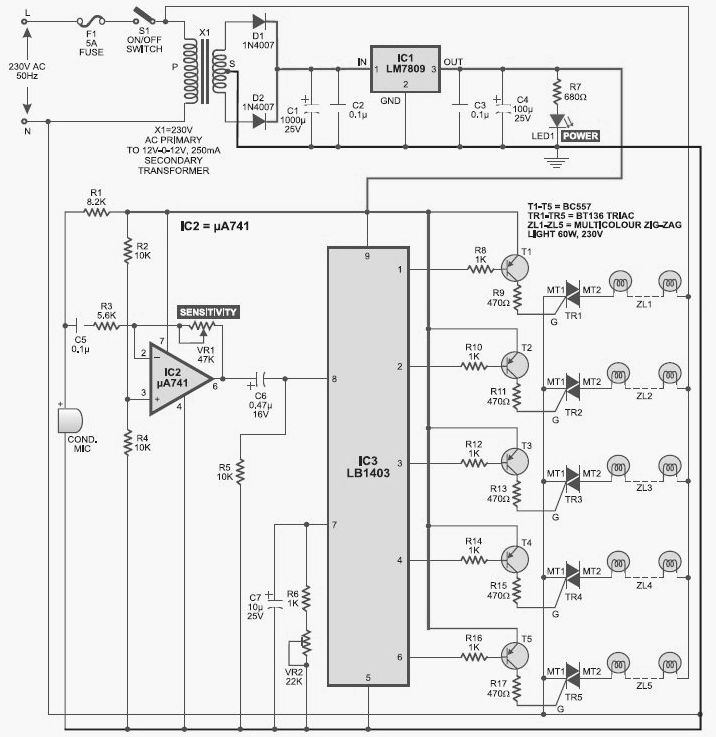
This light chaser circuit, which functions as a music-operated lighting effect generator, consists of five sets of 60W bulbs arranged in a zig-zag configuration.
The light chaser circuit is designed to create dynamic lighting effects that synchronize with music, enhancing the visual experience during performances or events. The configuration of five sets of 60W bulbs allows for bright and vibrant displays. Each set of bulbs can be individually controlled to turn on and off in a sequential manner, creating a chaser effect that moves along the zig-zag arrangement.
The core of the circuit typically includes a microcontroller or a dedicated music detection module that analyzes the audio input. This module processes the sound frequencies and triggers the bulbs based on the rhythm and beats of the music. The output control can be achieved through relays or triacs, which handle the high power requirements of the 60W bulbs while ensuring safe operation.
To enhance the functionality, additional features such as adjustable sensitivity to sound, variable speed control for the chaser effect, and the ability to select different lighting patterns can be incorporated. The power supply must be adequately rated to handle the total wattage of the bulbs, ensuring stable operation without overload. Proper heat dissipation methods should also be considered, especially if the circuit will be used for extended periods.
Overall, this light chaser circuit serves as an engaging tool for creating synchronized lighting displays that react to music, making it suitable for various applications, including parties, concerts, and theatrical performances.This light chaser circuit (music-operated lighting effect generator) comprises five sets of 60W bulbs that are arranged in zig-zag fashion. The bulb sets g.. 🔗 External reference
The light chaser circuit is designed to create dynamic lighting effects that synchronize with music, enhancing the visual experience during performances or events. The configuration of five sets of 60W bulbs allows for bright and vibrant displays. Each set of bulbs can be individually controlled to turn on and off in a sequential manner, creating a chaser effect that moves along the zig-zag arrangement.
The core of the circuit typically includes a microcontroller or a dedicated music detection module that analyzes the audio input. This module processes the sound frequencies and triggers the bulbs based on the rhythm and beats of the music. The output control can be achieved through relays or triacs, which handle the high power requirements of the 60W bulbs while ensuring safe operation.
To enhance the functionality, additional features such as adjustable sensitivity to sound, variable speed control for the chaser effect, and the ability to select different lighting patterns can be incorporated. The power supply must be adequately rated to handle the total wattage of the bulbs, ensuring stable operation without overload. Proper heat dissipation methods should also be considered, especially if the circuit will be used for extended periods.
Overall, this light chaser circuit serves as an engaging tool for creating synchronized lighting displays that react to music, making it suitable for various applications, including parties, concerts, and theatrical performances.This light chaser circuit (music-operated lighting effect generator) comprises five sets of 60W bulbs that are arranged in zig-zag fashion. The bulb sets g.. 🔗 External reference