Fast charge Controller with MAX712 / MAX713
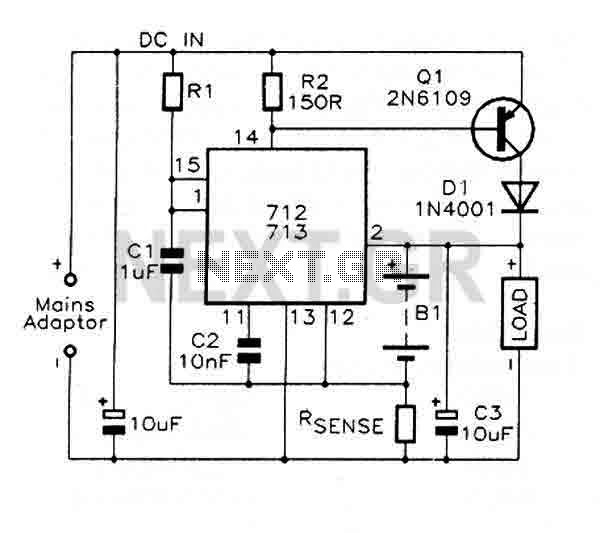
The MAX712 and MAX713 are nickel cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery fast charge controllers that facilitate the rapid charging of batteries from a DC source, which must be at least 1V higher than the maximum battery voltage. These controllers can charge from 1 to 16 series cells at rates of up to 4C. Charge completion is determined by a voltage-slope detecting analog-to-digital converter, a timer, and a temperature window comparator. The MAX712 or MAX713 is powered by the DC source through an on-clip +5V shunt regulator and consumes a maximum of 5µA from the battery when not in the charging state. A low-side current-sense resistor enables the regulation of battery charge current while still providing power to the battery's load. The MAX712 terminates fast charge by detecting zero voltage slope, while the MAX713 employs a negative voltage-slope detection method. Both devices are packaged identically in 16-pin DIL and share the same pin numbering and fundamental functions.
The MAX712 and MAX713 serve as advanced control systems for efficient charging of Ni-Cd batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The architecture of these controllers includes several critical components that enhance their functionality. The voltage-slope detection mechanism is vital, as it accurately identifies when the battery reaches full charge, thus preventing overcharging, which can lead to battery damage.
The analog-to-digital converter plays a crucial role in monitoring the voltage slope, providing real-time feedback to the controller. This feedback is essential for the timely termination of the charging process, which is particularly important in applications where battery health is paramount.
The inclusion of a timer further aids in defining charging cycles, allowing for adjustments based on specific battery chemistry and manufacturer recommendations. This feature is essential for ensuring that the charging process is not only efficient but also aligned with the battery's specifications.
Temperature management is another critical aspect, as the temperature window comparator ensures that the charging process is suspended if the battery temperature exceeds safe limits. This safety feature protects the battery from thermal runaway conditions, which can occur during rapid charging.
The low-side current-sense resistor is integral to the system, as it allows for the monitoring and regulation of the charging current. This ensures that the battery receives an appropriate charge rate, which is crucial for maintaining battery performance over its lifecycle.
Overall, the MAX712 and MAX713 provide a robust solution for fast charging Ni-Cd batteries, with built-in safeguards and monitoring capabilities that enhance their reliability and efficiency in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems. Their identical packaging and pin configuration allow for easy interchangeability, making them versatile components in battery management systems.The MAX712 and MAX713 are nickel cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery fast charge controllers which will fast charge batteries from a DC source at least 1V higher than the maximum battery voltage. 1 to 16 series cells can be charged at rates up to 4C. A voltage-slope detecting analogue-to-digital converter, timer, and temperature window comparator determine charge completion.
The MAX712 or 713 are powered by the DC source via an on-clip +5V shunt regulator, and draw a maximum of 5uA from the battery when not charging. A low-side current-sense resistor allows the battery charge current to be regulated while still supplying the power to the battery's load.
The MAX712 terminates fast charge by detecting zero voltage slope, while the MAX713 uses a negative voltage-slope detection scheme. Both devices are identically packaged as 16-pin DIL and share the same pin numbering and basic functions.
An external power 🔗 External reference
The MAX712 and MAX713 serve as advanced control systems for efficient charging of Ni-Cd batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The architecture of these controllers includes several critical components that enhance their functionality. The voltage-slope detection mechanism is vital, as it accurately identifies when the battery reaches full charge, thus preventing overcharging, which can lead to battery damage.
The analog-to-digital converter plays a crucial role in monitoring the voltage slope, providing real-time feedback to the controller. This feedback is essential for the timely termination of the charging process, which is particularly important in applications where battery health is paramount.
The inclusion of a timer further aids in defining charging cycles, allowing for adjustments based on specific battery chemistry and manufacturer recommendations. This feature is essential for ensuring that the charging process is not only efficient but also aligned with the battery's specifications.
Temperature management is another critical aspect, as the temperature window comparator ensures that the charging process is suspended if the battery temperature exceeds safe limits. This safety feature protects the battery from thermal runaway conditions, which can occur during rapid charging.
The low-side current-sense resistor is integral to the system, as it allows for the monitoring and regulation of the charging current. This ensures that the battery receives an appropriate charge rate, which is crucial for maintaining battery performance over its lifecycle.
Overall, the MAX712 and MAX713 provide a robust solution for fast charging Ni-Cd batteries, with built-in safeguards and monitoring capabilities that enhance their reliability and efficiency in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems. Their identical packaging and pin configuration allow for easy interchangeability, making them versatile components in battery management systems.The MAX712 and MAX713 are nickel cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery fast charge controllers which will fast charge batteries from a DC source at least 1V higher than the maximum battery voltage. 1 to 16 series cells can be charged at rates up to 4C. A voltage-slope detecting analogue-to-digital converter, timer, and temperature window comparator determine charge completion.
The MAX712 or 713 are powered by the DC source via an on-clip +5V shunt regulator, and draw a maximum of 5uA from the battery when not charging. A low-side current-sense resistor allows the battery charge current to be regulated while still supplying the power to the battery's load.
The MAX712 terminates fast charge by detecting zero voltage slope, while the MAX713 uses a negative voltage-slope detection scheme. Both devices are identically packaged as 16-pin DIL and share the same pin numbering and basic functions.
An external power 🔗 External reference