Light Dimmer Using Diac or transistor and triac and description
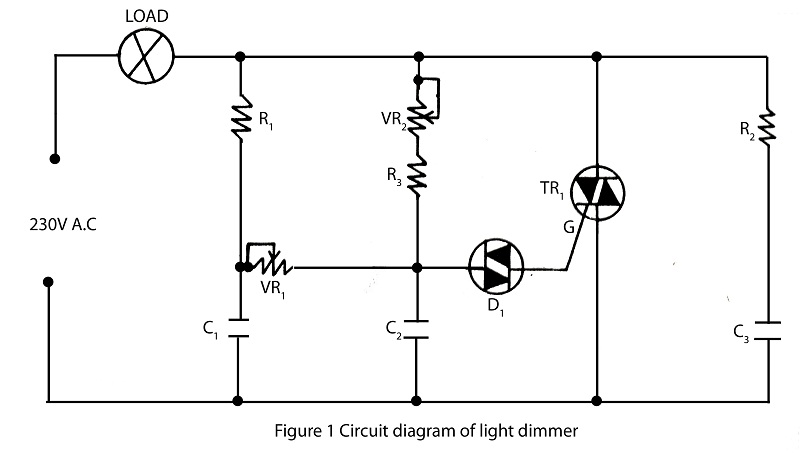
The lighting source, such as a bulb or tube light, illuminates based on its specified wattage. To achieve increased brightness, a higher wattage bulb must be used, while a lower wattage bulb is necessary for reduced brightness. However, it is possible to adjust brightness without changing the light source. This project presents a simple yet effective solution that controls brightness from a constant light source. The fundamental principle of the light dimmer is based on phase control. The variable resistor VR2 serves as the primary controller of the Light Dimmer circuit. The capacitor C2 charges from the main supply, which triggers the DIAC D1. VR1 is utilized for fine-tuning the brightness to a lower level, while resistors R2 and capacitor C3 are employed to mitigate interference issues.
The light dimmer circuit operates by manipulating the phase of the AC voltage supplied to the lighting source. This is achieved through the use of a DIAC, which remains in an off state until a certain voltage threshold is reached. When the voltage across the DIAC exceeds this threshold, it switches on, allowing current to flow through the light source. The variable resistor VR2 adjusts the amount of time the AC waveform is allowed to pass through to the load, effectively controlling the brightness of the light.
In this configuration, capacitor C2 plays a crucial role in determining the timing of the DIAC's triggering. As the capacitor charges, it accumulates voltage until it reaches the breakdown voltage of the DIAC. This process can be influenced by the resistance set by VR2, allowing for a wide range of brightness adjustments. The fine-tuning of brightness is facilitated by VR1, which adjusts the voltage level that the DIAC requires to turn on, enabling precise control over the light output.
Additionally, R2 and C3 are included in the circuit to address potential interference that may arise from the switching action of the DIAC. R2 helps to stabilize the circuit by providing a discharge path for the capacitor, while C3 acts as a filter to smooth out any voltage spikes that could affect the performance of the dimmer.
Overall, this light dimmer circuit exemplifies a practical approach to controlling lighting levels without the need for changing the light source itself, utilizing basic electronic components to achieve the desired functionality.The lighting source (i. e. bulb, tube light) glow according to their specified watt rating. If we need more light then we have to use high watt bulb at the same place if we need low light we have to replace high watt bulb with low rating. But What if there is not necessary to change i. e. different brightness obtained from same source. Here is the s imple but effective project which control brightness according to our use from the unchanged light source. The basic principle of light dimmer is based on phase control. The variable resistor VR2 is main controller of the circuit Light Dimer. From main supply capacitor C2 get charges which trigger DIAC D1. VR1 is used for fine brightness controller which control brightness to lower level. R2 and C3 used to overcome interference problem. 🔗 External reference
The light dimmer circuit operates by manipulating the phase of the AC voltage supplied to the lighting source. This is achieved through the use of a DIAC, which remains in an off state until a certain voltage threshold is reached. When the voltage across the DIAC exceeds this threshold, it switches on, allowing current to flow through the light source. The variable resistor VR2 adjusts the amount of time the AC waveform is allowed to pass through to the load, effectively controlling the brightness of the light.
In this configuration, capacitor C2 plays a crucial role in determining the timing of the DIAC's triggering. As the capacitor charges, it accumulates voltage until it reaches the breakdown voltage of the DIAC. This process can be influenced by the resistance set by VR2, allowing for a wide range of brightness adjustments. The fine-tuning of brightness is facilitated by VR1, which adjusts the voltage level that the DIAC requires to turn on, enabling precise control over the light output.
Additionally, R2 and C3 are included in the circuit to address potential interference that may arise from the switching action of the DIAC. R2 helps to stabilize the circuit by providing a discharge path for the capacitor, while C3 acts as a filter to smooth out any voltage spikes that could affect the performance of the dimmer.
Overall, this light dimmer circuit exemplifies a practical approach to controlling lighting levels without the need for changing the light source itself, utilizing basic electronic components to achieve the desired functionality.The lighting source (i. e. bulb, tube light) glow according to their specified watt rating. If we need more light then we have to use high watt bulb at the same place if we need low light we have to replace high watt bulb with low rating. But What if there is not necessary to change i. e. different brightness obtained from same source. Here is the s imple but effective project which control brightness according to our use from the unchanged light source. The basic principle of light dimmer is based on phase control. The variable resistor VR2 is main controller of the circuit Light Dimer. From main supply capacitor C2 get charges which trigger DIAC D1. VR1 is used for fine brightness controller which control brightness to lower level. R2 and C3 used to overcome interference problem. 🔗 External reference