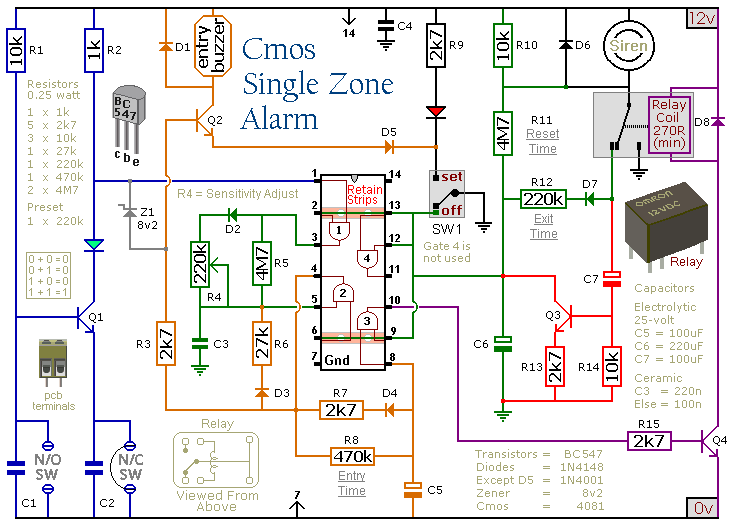
Single transistor phase shifter
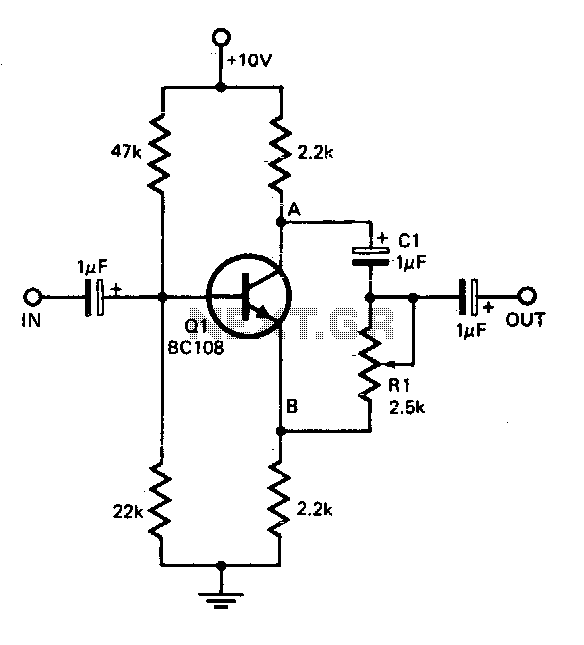
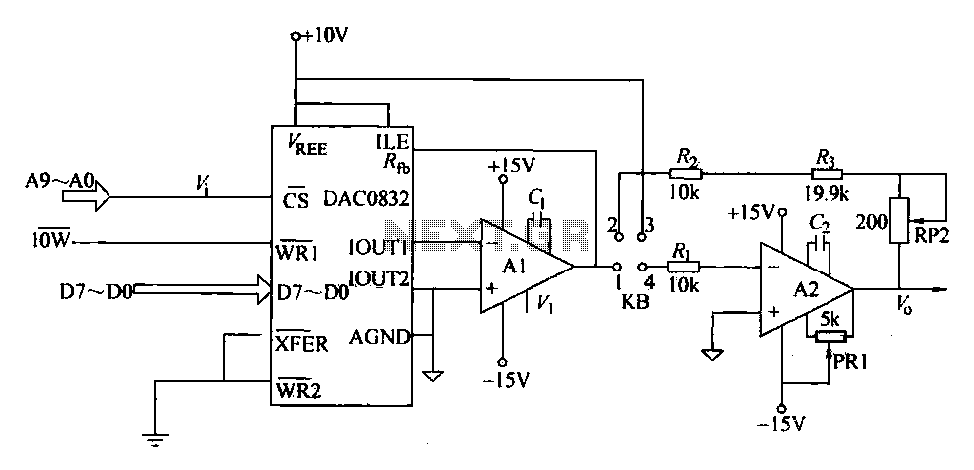
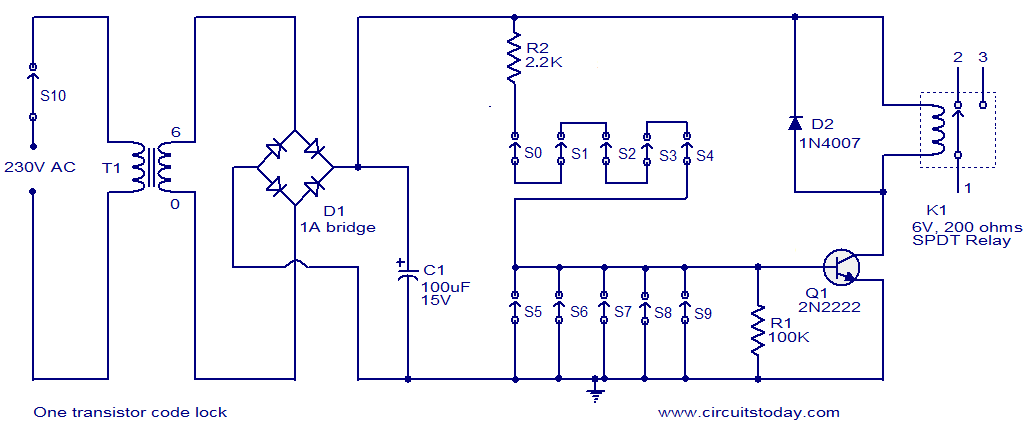
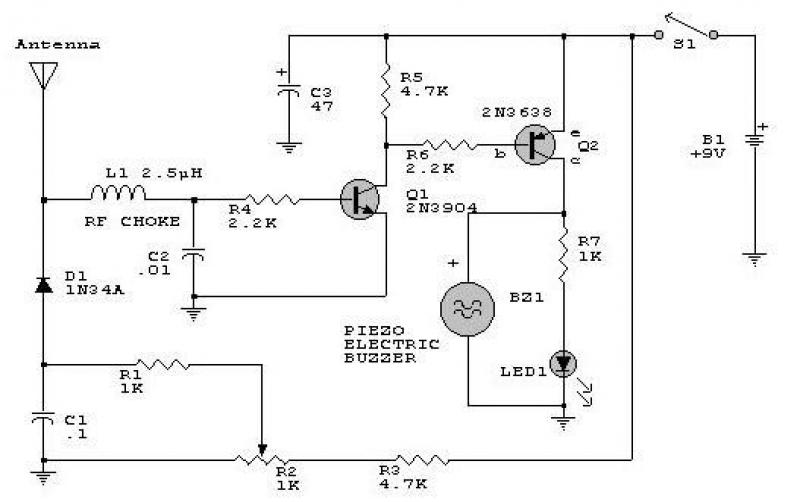
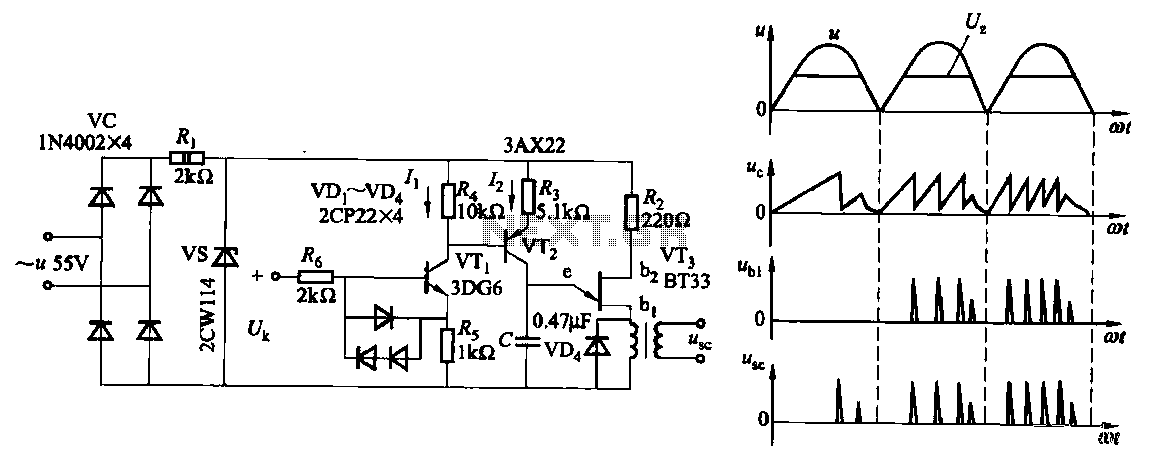
This circuit offers a straightforward method for achieving phase shifts between 0° and 170°. The transistor functions as a phase splitter, with the output at point A being 180° out of phase with the input. Point B remains in phase with the input. By adjusting R1, a combination of various proportions of these outputs can be obtained, resulting in a continuously variable phase shift. The circuit performs effectively within the frequency range of 600 Hz to 4 kHz.
The circuit utilizes a transistor configured as a phase splitter, which is a common arrangement in analog electronics. The transistor's configuration allows it to produce two outputs: one that is inverted (180° phase shift) and another that maintains the same phase as the input signal. This is achieved by connecting the input signal to the base of the transistor, where it is amplified and split into two distinct outputs.
At point A, the output is taken from the collector of the transistor, which provides the inverted signal. Conversely, point B, connected to the emitter, delivers the non-inverted signal. The phase relationship between these two outputs is critical for applications requiring precise phase control, such as in audio processing or signal modulation.
The resistor R1 plays a pivotal role in adjusting the phase shift. By varying the resistance value, the relative proportions of the output signals at points A and B can be manipulated. This adjustment allows for a continuous transition between the two phase states, enabling fine-tuning of the phase shift according to the specific requirements of the application.
The operational frequency range of 600 Hz to 4 kHz indicates that this circuit is well-suited for audio applications, where phase relationships can significantly impact sound quality and spatial effects. The design ensures that the circuit maintains stability and performance within this frequency range, making it ideal for use in audio signal processing, synthesizers, and other electronic devices requiring phase manipulation.
In summary, this circuit is a versatile tool for generating variable phase shifts, leveraging the properties of a transistor to provide both inverted and non-inverted outputs, with the ability to finely adjust the phase relationship through the use of a variable resistor.This circuit provides a simple means of obtaining phase shifts between zero and 170°. The transistor operates as a phase splitter, the output at point A being 180° out of phase with the input. Point B is in phase with the input phase. Adjusting Rl provides the sum of various proportions of these and hence a continuously variable phase shift is provided
The circuit operates well in the 600 Hz to 4 kHz range.
The circuit utilizes a transistor configured as a phase splitter, which is a common arrangement in analog electronics. The transistor's configuration allows it to produce two outputs: one that is inverted (180° phase shift) and another that maintains the same phase as the input signal. This is achieved by connecting the input signal to the base of the transistor, where it is amplified and split into two distinct outputs.
At point A, the output is taken from the collector of the transistor, which provides the inverted signal. Conversely, point B, connected to the emitter, delivers the non-inverted signal. The phase relationship between these two outputs is critical for applications requiring precise phase control, such as in audio processing or signal modulation.
The resistor R1 plays a pivotal role in adjusting the phase shift. By varying the resistance value, the relative proportions of the output signals at points A and B can be manipulated. This adjustment allows for a continuous transition between the two phase states, enabling fine-tuning of the phase shift according to the specific requirements of the application.
The operational frequency range of 600 Hz to 4 kHz indicates that this circuit is well-suited for audio applications, where phase relationships can significantly impact sound quality and spatial effects. The design ensures that the circuit maintains stability and performance within this frequency range, making it ideal for use in audio signal processing, synthesizers, and other electronic devices requiring phase manipulation.
In summary, this circuit is a versatile tool for generating variable phase shifts, leveraging the properties of a transistor to provide both inverted and non-inverted outputs, with the ability to finely adjust the phase relationship through the use of a variable resistor.This circuit provides a simple means of obtaining phase shifts between zero and 170°. The transistor operates as a phase splitter, the output at point A being 180° out of phase with the input. Point B is in phase with the input phase. Adjusting Rl provides the sum of various proportions of these and hence a continuously variable phase shift is provided
The circuit operates well in the 600 Hz to 4 kHz range.