Line Preamplifier Circuit with Tube Acquisition
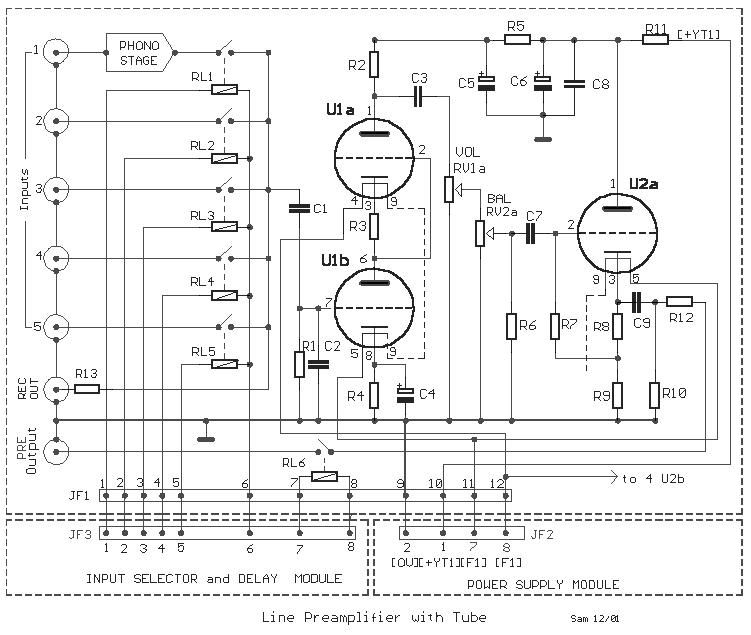
The circuit was designed to create a line preamplifier using double triode tubes. It consists of three parts, including the main preamplifier.
The line preamplifier circuit utilizing double triode tubes is structured to enhance audio signals by amplifying low-level signals before they are processed by further audio equipment. The design typically includes three primary sections: the input stage, the amplification stage, and the output stage.
The input stage is responsible for receiving the audio signal, which is often weak and needs to be amplified. It may include coupling capacitors to block any DC offset and allow only the AC audio signal to pass through. The use of double triode tubes in this stage provides high input impedance, ensuring minimal loading on the source device, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
The amplification stage is where the primary signal boosting occurs. The double triode tubes function as voltage amplifiers, utilizing their characteristics to provide significant gain while maintaining linearity. Biasing resistors are employed to set the operating point of the tubes, ensuring they function within their optimal range. Feedback mechanisms may also be integrated to stabilize gain and reduce distortion, enhancing overall audio quality.
Finally, the output stage is designed to deliver the amplified signal to the next stage in the audio chain, such as a power amplifier or audio processor. Output transformers may be used to match the impedance of the preamplifier with that of the subsequent stage, ensuring efficient signal transfer and minimizing signal loss.
Overall, the circuit is engineered to provide high-fidelity audio amplification, leveraging the unique properties of double triode tubes to achieve a warm and rich sound characteristic, often preferred in high-end audio applications. Proper attention to component selection, layout, and power supply design is essential to optimize performance and reliability in the final implementation.The circuit was designed to create a line preamplifier by acquiring the use of double triode tubes. The circuit comprises of three parts, the main preampl.. 🔗 External reference
The line preamplifier circuit utilizing double triode tubes is structured to enhance audio signals by amplifying low-level signals before they are processed by further audio equipment. The design typically includes three primary sections: the input stage, the amplification stage, and the output stage.
The input stage is responsible for receiving the audio signal, which is often weak and needs to be amplified. It may include coupling capacitors to block any DC offset and allow only the AC audio signal to pass through. The use of double triode tubes in this stage provides high input impedance, ensuring minimal loading on the source device, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
The amplification stage is where the primary signal boosting occurs. The double triode tubes function as voltage amplifiers, utilizing their characteristics to provide significant gain while maintaining linearity. Biasing resistors are employed to set the operating point of the tubes, ensuring they function within their optimal range. Feedback mechanisms may also be integrated to stabilize gain and reduce distortion, enhancing overall audio quality.
Finally, the output stage is designed to deliver the amplified signal to the next stage in the audio chain, such as a power amplifier or audio processor. Output transformers may be used to match the impedance of the preamplifier with that of the subsequent stage, ensuring efficient signal transfer and minimizing signal loss.
Overall, the circuit is engineered to provide high-fidelity audio amplification, leveraging the unique properties of double triode tubes to achieve a warm and rich sound characteristic, often preferred in high-end audio applications. Proper attention to component selection, layout, and power supply design is essential to optimize performance and reliability in the final implementation.The circuit was designed to create a line preamplifier by acquiring the use of double triode tubes. The circuit comprises of three parts, the main preampl.. 🔗 External reference