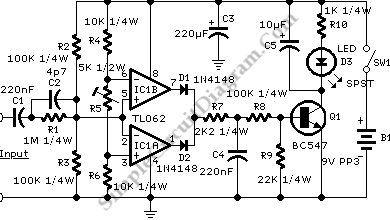
Lithium battery indicator

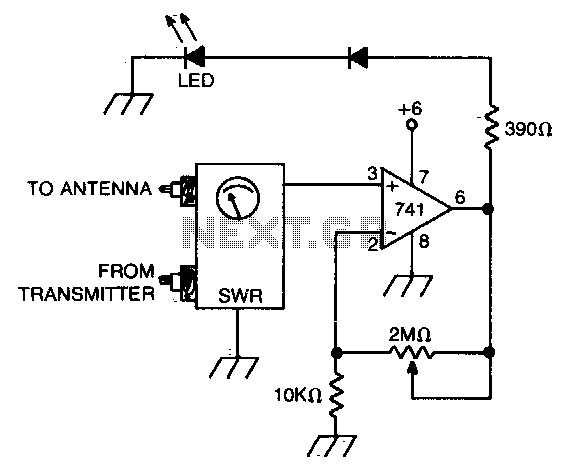
A state-of-charge indication of a sloping-voltage discharge can be utilized as a state-of-charge indicator. A typical voltage comparator circuit that provides a visual indication of the state of charge is presented. Components identified are for a 4-cell input voltage ranging from 9.6 to 5.2 volts.
The circuit for the state-of-charge indicator typically employs a voltage comparator to monitor the voltage levels of a battery pack, specifically a 4-cell arrangement. The voltage range of 9.6 to 5.2 volts corresponds to the nominal fully charged state and the cut-off voltage for the cells. The voltage comparator is configured to compare the voltage from the battery cells against a reference voltage, which is set to indicate specific charge levels.
In this configuration, the battery voltage is fed into the non-inverting input of the comparator, while the reference voltage is connected to the inverting input. As the battery discharges, its voltage decreases, and when it falls below the reference voltage, the output of the comparator changes state, triggering an LED or another visual indicator. This provides a clear visual representation of the state of charge.
The circuit can be designed with hysteresis to prevent rapid toggling of the output due to noise or small fluctuations in the battery voltage. Additionally, resistors and capacitors may be included to fine-tune the response time and stability of the circuit. The choice of components, such as the comparator IC and the visual indicator, should be made based on the intended application and the desired sensitivity and accuracy of the state-of-charge indication.
Overall, this voltage comparator circuit serves as an effective solution for monitoring the state of charge in battery management systems, particularly for applications involving multiple cells in series.State-of-Charge indication of-a sloping-voltage discharge can be used as a state-of-charge indicator. A typical voltage comparator circuit that gives a visual indication of state-of-charge is shown. Components identified are for a 4-cell input voltage of 9.6 to 5.2 volts. 🔗 External reference
The circuit for the state-of-charge indicator typically employs a voltage comparator to monitor the voltage levels of a battery pack, specifically a 4-cell arrangement. The voltage range of 9.6 to 5.2 volts corresponds to the nominal fully charged state and the cut-off voltage for the cells. The voltage comparator is configured to compare the voltage from the battery cells against a reference voltage, which is set to indicate specific charge levels.
In this configuration, the battery voltage is fed into the non-inverting input of the comparator, while the reference voltage is connected to the inverting input. As the battery discharges, its voltage decreases, and when it falls below the reference voltage, the output of the comparator changes state, triggering an LED or another visual indicator. This provides a clear visual representation of the state of charge.
The circuit can be designed with hysteresis to prevent rapid toggling of the output due to noise or small fluctuations in the battery voltage. Additionally, resistors and capacitors may be included to fine-tune the response time and stability of the circuit. The choice of components, such as the comparator IC and the visual indicator, should be made based on the intended application and the desired sensitivity and accuracy of the state-of-charge indication.
Overall, this voltage comparator circuit serves as an effective solution for monitoring the state of charge in battery management systems, particularly for applications involving multiple cells in series.State-of-Charge indication of-a sloping-voltage discharge can be used as a state-of-charge indicator. A typical voltage comparator circuit that gives a visual indication of state-of-charge is shown. Components identified are for a 4-cell input voltage of 9.6 to 5.2 volts. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713