mc2833 fm transmitter circuit design electronic project
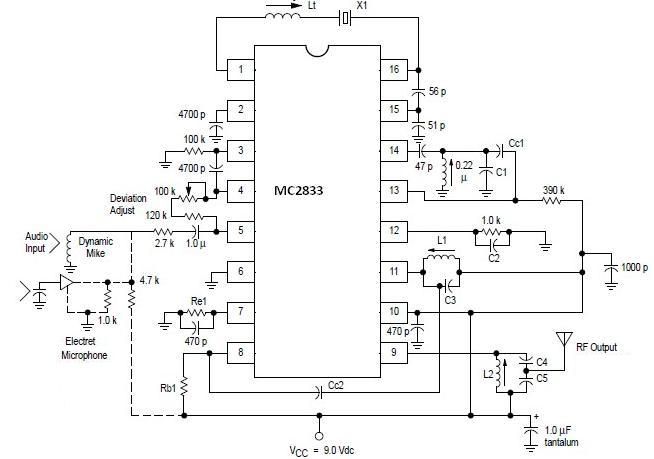
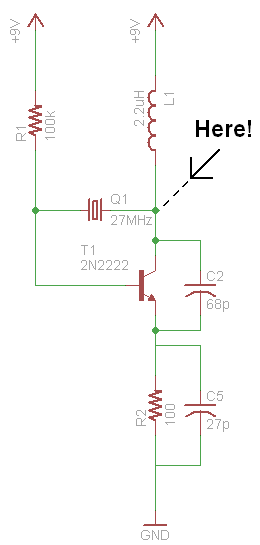
A simple FM transmitter circuit can be designed using the MC2833 integrated circuit, which is intended for cordless telephones and FM communication equipment. It features a microphone amplifier, a voltage-controlled oscillator, and two auxiliary transistors. The final output frequency is produced through frequency multiplication within the MC2833 IC. The RF output buffer (Pin 14) and the Q2 transistor function as a frequency tripler and doubler, respectively, for the 76 MHz and 144 MHz transmitters. The power output is 9 + 10 dBm for the 50 MHz and 76 MHz transmitters, and 9 + 5 dBm for the 144 MHz transmitter when VCC is set to 8.0 V. Power output decreases with lower VCC.
The FM transmitter circuit utilizing the MC2833 integrated circuit is a compact and efficient design suitable for various applications in wireless communication. The MC2833 is a versatile IC that integrates multiple functionalities, making it ideal for creating a straightforward FM transmitter.
The circuit begins with a microphone amplifier that captures audio signals and amplifies them for processing. This amplified audio signal is then fed into a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) within the MC2833, which modulates the signal onto a carrier frequency. The VCO is essential for ensuring that the frequency can be adjusted according to the desired transmission specifications.
The output from the VCO is then routed to the RF output buffer located at Pin 14 of the MC2833. This buffer stage is crucial as it provides the necessary power to drive the subsequent frequency multiplication stages. The circuit employs two auxiliary transistors, where Q2 acts as a frequency doubler and another transistor functions as a frequency tripler. This configuration allows the circuit to generate the desired frequencies of 76 MHz and 144 MHz efficiently.
Power output levels are an important consideration in the design. For optimal performance, the circuit can deliver a power output of 9 + 10 dBm at both the 50 MHz and 76 MHz frequencies. For the 144 MHz transmission, the output is slightly lower at 9 + 5 dBm. These output levels are achieved when the power supply voltage (VCC) is maintained at 8.0 V. It is important to note that as VCC decreases, the power output will also drop, which can affect the transmission range and overall performance of the circuit.
This FM transmitter circuit design is particularly advantageous for applications requiring low-cost and low-power solutions in wireless communication, such as hobbyist projects and educational demonstrations. The integration of multiple functions into a single IC simplifies the design process and reduces the component count, making it an effective solution for achieving reliable FM transmission.A very simple FM transmitter circuit can be designed using MC2833 integrated circuit, designed for cordless telephone and FM communication equipment. It includes a microphone amplifier, voltage controlled oscillator and two auxiliary transistors. The final output frequency is generated by frequency multiplication within the MC2833 IC. The RF outpu t buffer (Pin 14) and Q2 transistor are used as a frequency tripler and doubler, respectively, in the 76 and 144 MHz transmitters. Power output is 9 + 10 dBm for 50 MHz and 76 MHz transmitters, and 9 + 5. 0 dBm for the 144 MHz transmitter at VCC = 8. 0 V. Power output drops with lower VCC. 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit utilizing the MC2833 integrated circuit is a compact and efficient design suitable for various applications in wireless communication. The MC2833 is a versatile IC that integrates multiple functionalities, making it ideal for creating a straightforward FM transmitter.
The circuit begins with a microphone amplifier that captures audio signals and amplifies them for processing. This amplified audio signal is then fed into a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) within the MC2833, which modulates the signal onto a carrier frequency. The VCO is essential for ensuring that the frequency can be adjusted according to the desired transmission specifications.
The output from the VCO is then routed to the RF output buffer located at Pin 14 of the MC2833. This buffer stage is crucial as it provides the necessary power to drive the subsequent frequency multiplication stages. The circuit employs two auxiliary transistors, where Q2 acts as a frequency doubler and another transistor functions as a frequency tripler. This configuration allows the circuit to generate the desired frequencies of 76 MHz and 144 MHz efficiently.
Power output levels are an important consideration in the design. For optimal performance, the circuit can deliver a power output of 9 + 10 dBm at both the 50 MHz and 76 MHz frequencies. For the 144 MHz transmission, the output is slightly lower at 9 + 5 dBm. These output levels are achieved when the power supply voltage (VCC) is maintained at 8.0 V. It is important to note that as VCC decreases, the power output will also drop, which can affect the transmission range and overall performance of the circuit.
This FM transmitter circuit design is particularly advantageous for applications requiring low-cost and low-power solutions in wireless communication, such as hobbyist projects and educational demonstrations. The integration of multiple functions into a single IC simplifies the design process and reduces the component count, making it an effective solution for achieving reliable FM transmission.A very simple FM transmitter circuit can be designed using MC2833 integrated circuit, designed for cordless telephone and FM communication equipment. It includes a microphone amplifier, voltage controlled oscillator and two auxiliary transistors. The final output frequency is generated by frequency multiplication within the MC2833 IC. The RF outpu t buffer (Pin 14) and Q2 transistor are used as a frequency tripler and doubler, respectively, in the 76 and 144 MHz transmitters. Power output is 9 + 10 dBm for 50 MHz and 76 MHz transmitters, and 9 + 5. 0 dBm for the 144 MHz transmitter at VCC = 8. 0 V. Power output drops with lower VCC. 🔗 External reference