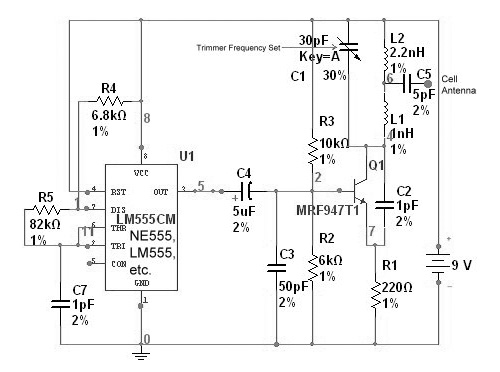
Local Oscillator For Double Balanced Mixers Circuit

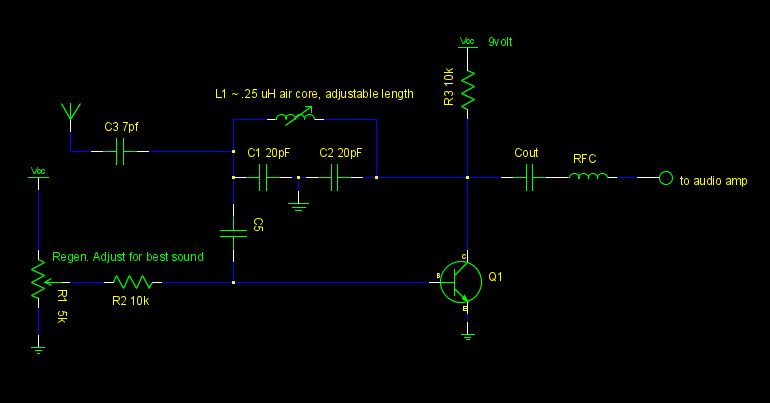
This circuit includes an amplifier designed to deliver +10 dBm to an SBL series (Mini-Circuits) or a similar type of doubly-balanced mixer assembly. The circuit parameters are specified for 80 to 90 MHz crystals, although the values of the oscillator circuit constants can be adjusted for higher or lower frequencies.
The described circuit serves as a critical component in RF applications, particularly in the context of frequency conversion using a doubly-balanced mixer. The amplifier's output power level of +10 dBm is suitable for driving the mixer, ensuring optimal performance and signal integrity during the mixing process.
The selection of 80 to 90 MHz crystals indicates that the circuit is intended for use in the VHF range, where it can be employed in various communication systems. The ability to scale the oscillator circuit constants allows for flexibility in design, enabling the circuit to accommodate different frequency requirements by adjusting component values such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
In the schematic, the amplifier may be implemented using a high-frequency transistor or an operational amplifier configured for RF applications. Proper biasing must be considered to maintain linearity and prevent distortion at the output stage. The input stage should also include impedance matching to optimize power transfer from the source to the amplifier.
The doubly-balanced mixer assembly is designed to provide excellent isolation between input and output ports while minimizing unwanted intermodulation products. This is particularly important in applications where multiple signals may be present, as it helps maintain signal quality and reduces the potential for cross-talk.
Overall, the circuit design should include considerations for layout and component placement to minimize parasitic capacitances and inductances that could affect performance at RF frequencies. Additionally, proper power supply decoupling techniques should be employed to ensure stable operation under varying load conditions. This circuit has an amplifier to supply +10 dBm to an SBL series (Mini-circuits) or similar type doubly-balanced mixer assembly. This circuit has values shown for =80- to 90-MHz crystals, although values of oscillator circuit constants can be scaled for higher or lower frequencies. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves as a critical component in RF applications, particularly in the context of frequency conversion using a doubly-balanced mixer. The amplifier's output power level of +10 dBm is suitable for driving the mixer, ensuring optimal performance and signal integrity during the mixing process.
The selection of 80 to 90 MHz crystals indicates that the circuit is intended for use in the VHF range, where it can be employed in various communication systems. The ability to scale the oscillator circuit constants allows for flexibility in design, enabling the circuit to accommodate different frequency requirements by adjusting component values such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
In the schematic, the amplifier may be implemented using a high-frequency transistor or an operational amplifier configured for RF applications. Proper biasing must be considered to maintain linearity and prevent distortion at the output stage. The input stage should also include impedance matching to optimize power transfer from the source to the amplifier.
The doubly-balanced mixer assembly is designed to provide excellent isolation between input and output ports while minimizing unwanted intermodulation products. This is particularly important in applications where multiple signals may be present, as it helps maintain signal quality and reduces the potential for cross-talk.
Overall, the circuit design should include considerations for layout and component placement to minimize parasitic capacitances and inductances that could affect performance at RF frequencies. Additionally, proper power supply decoupling techniques should be employed to ensure stable operation under varying load conditions. This circuit has an amplifier to supply +10 dBm to an SBL series (Mini-circuits) or similar type doubly-balanced mixer assembly. This circuit has values shown for =80- to 90-MHz crystals, although values of oscillator circuit constants can be scaled for higher or lower frequencies. 🔗 External reference